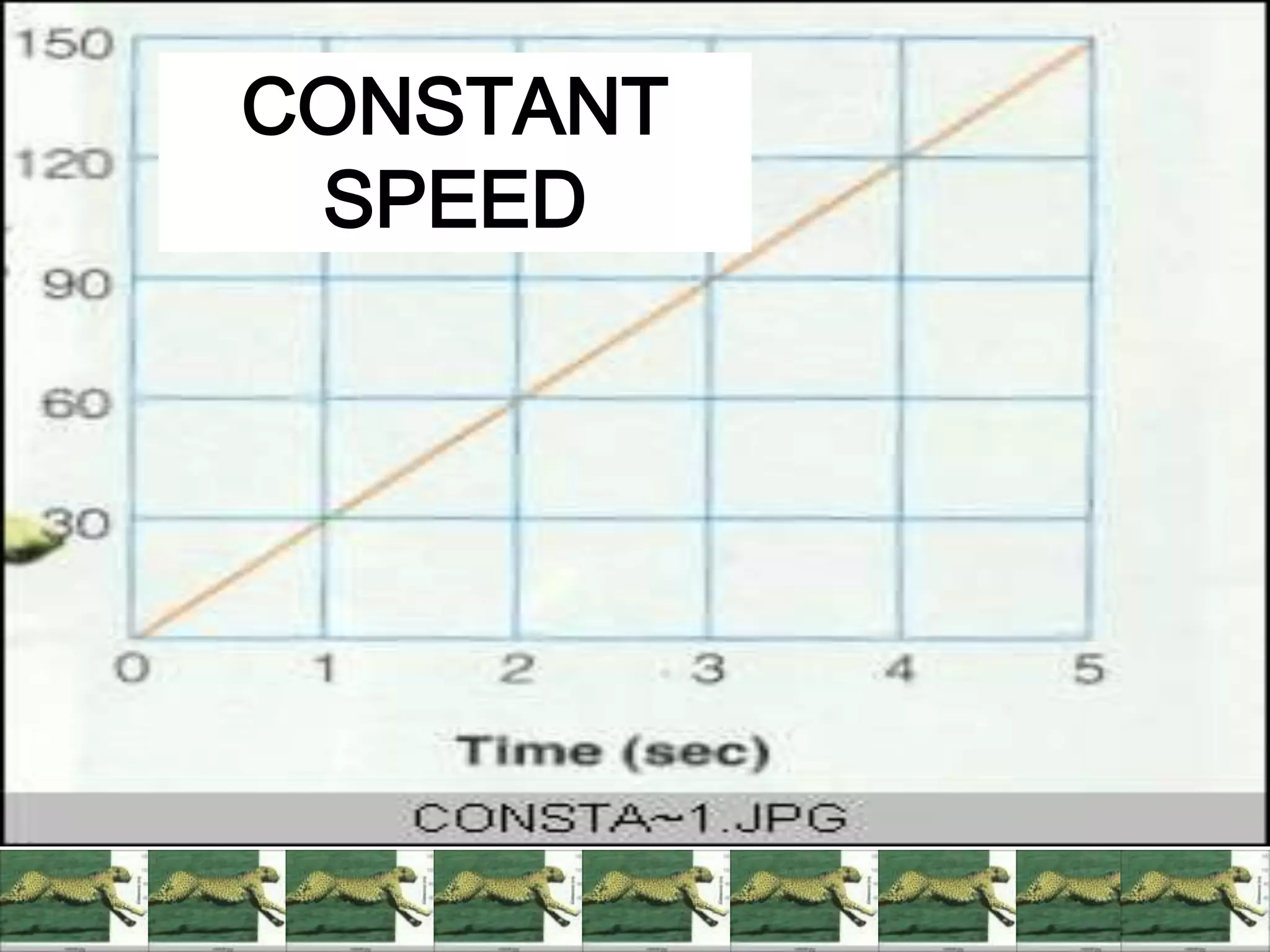
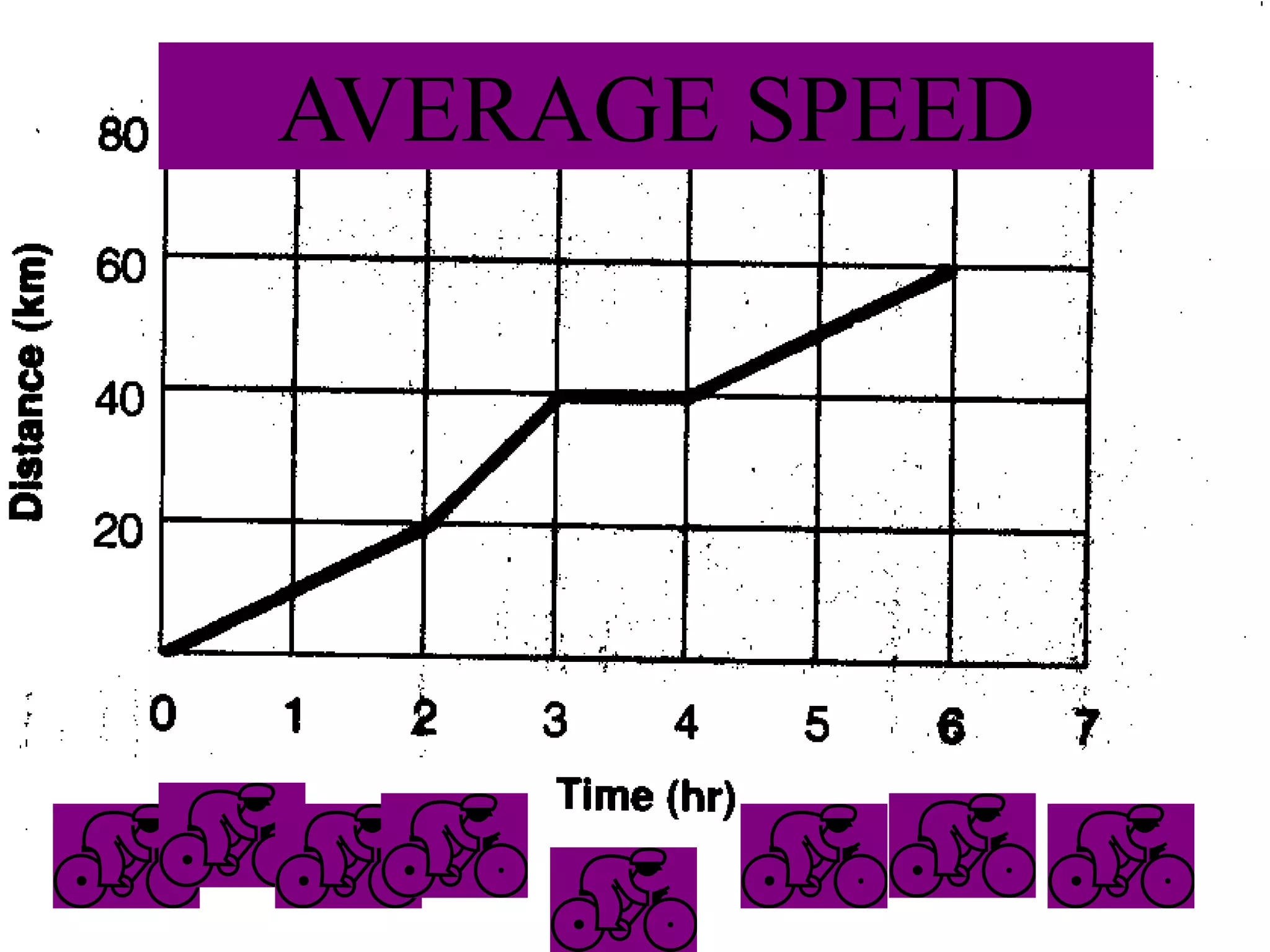
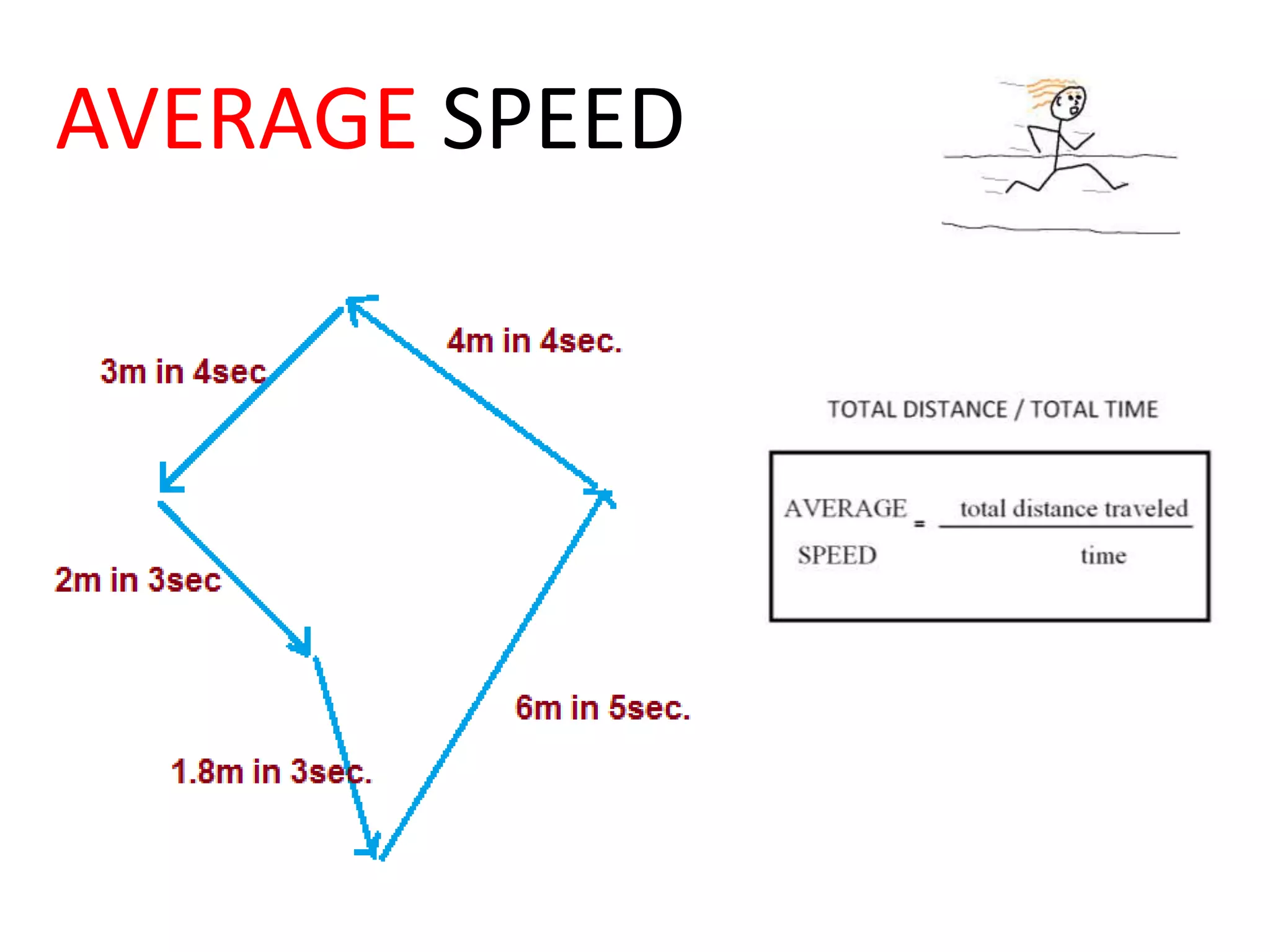
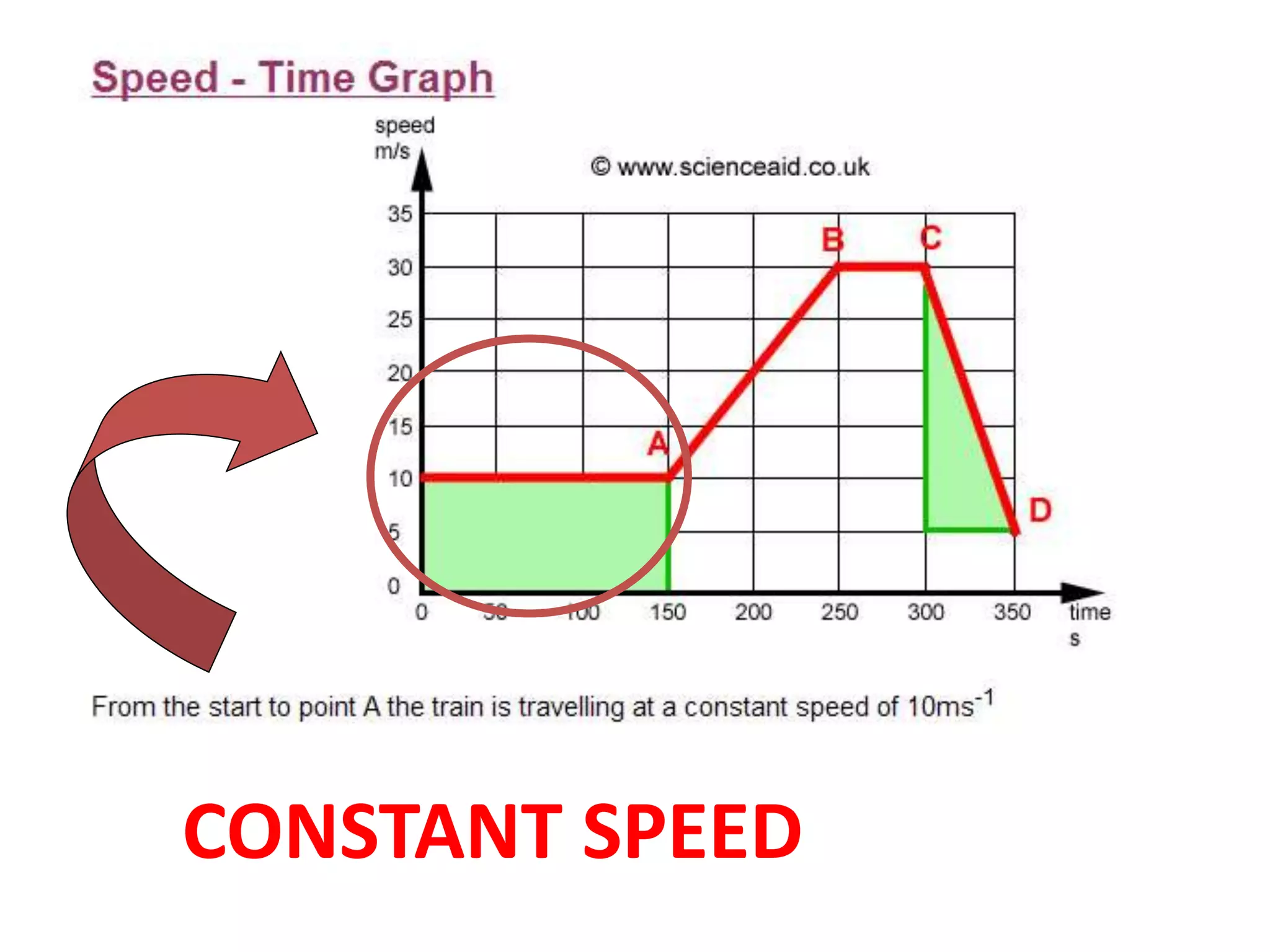
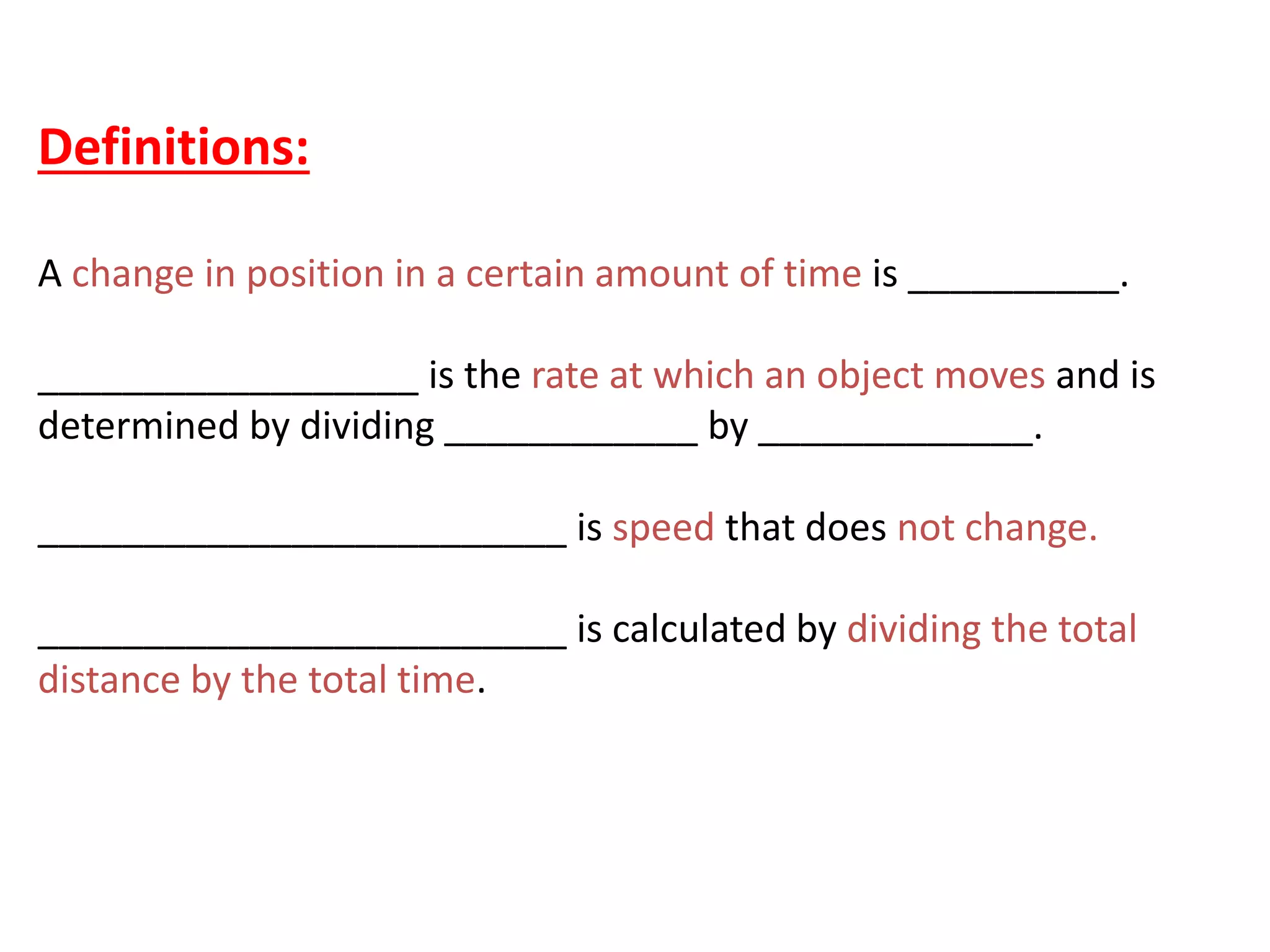
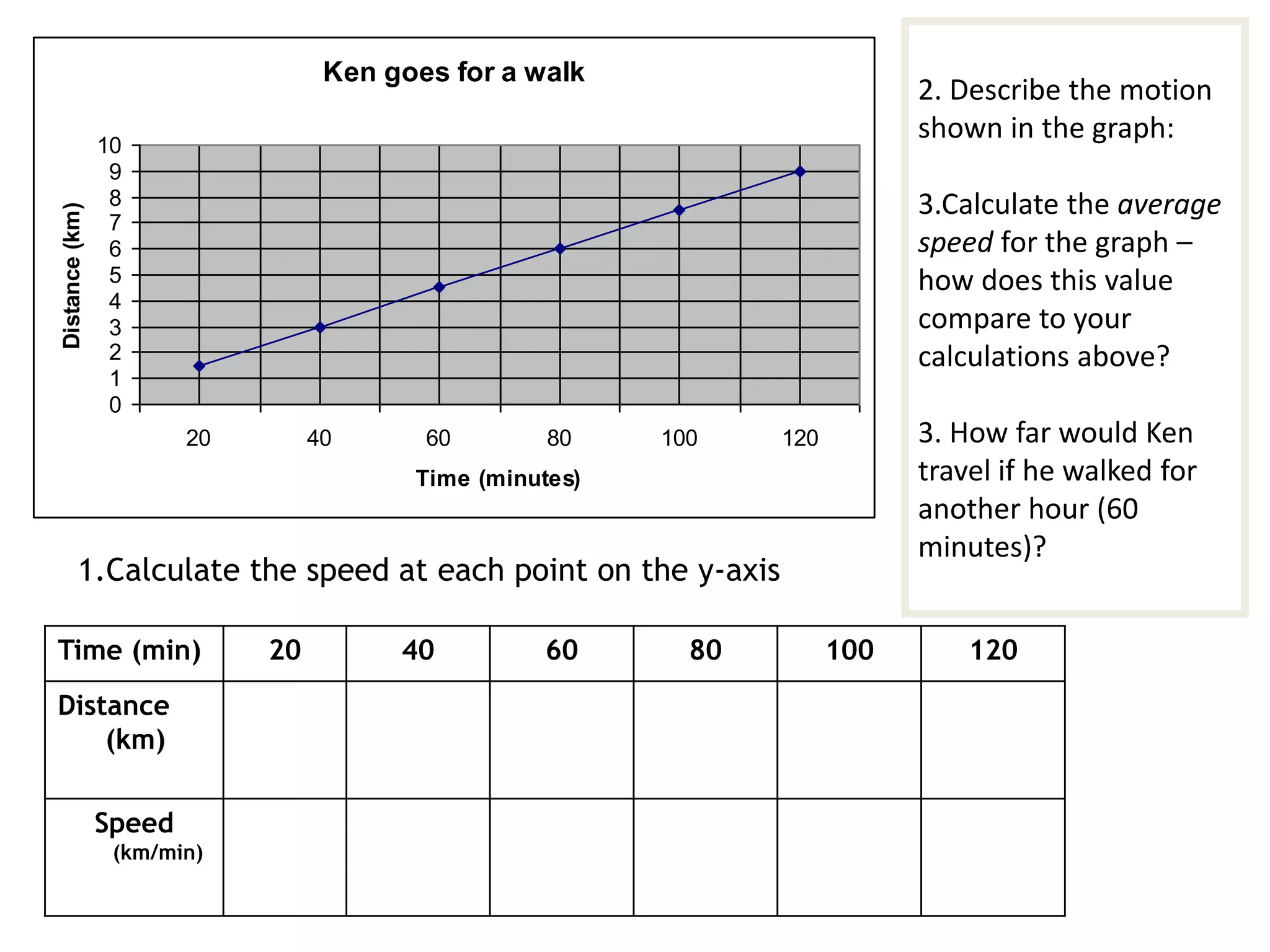
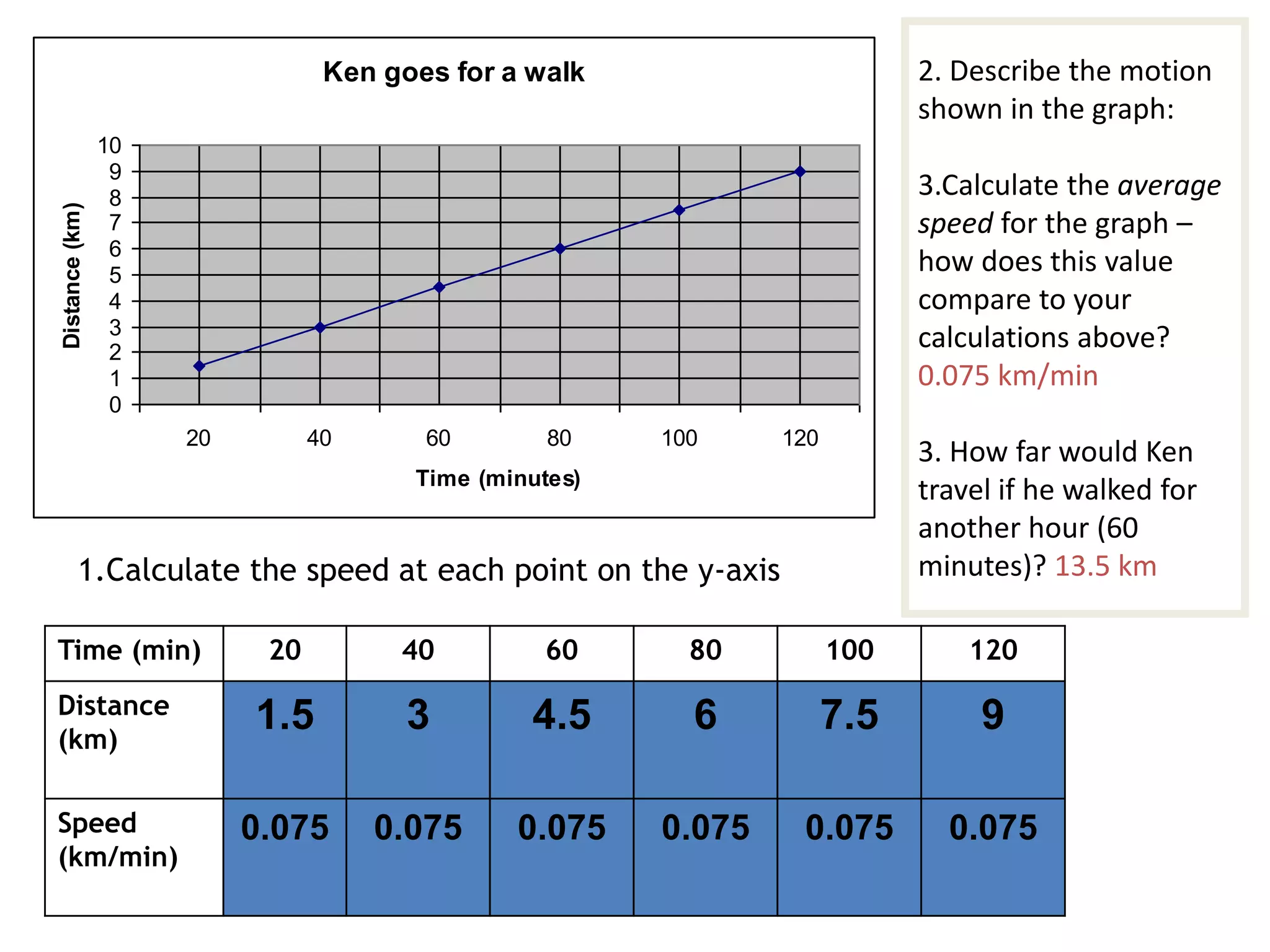
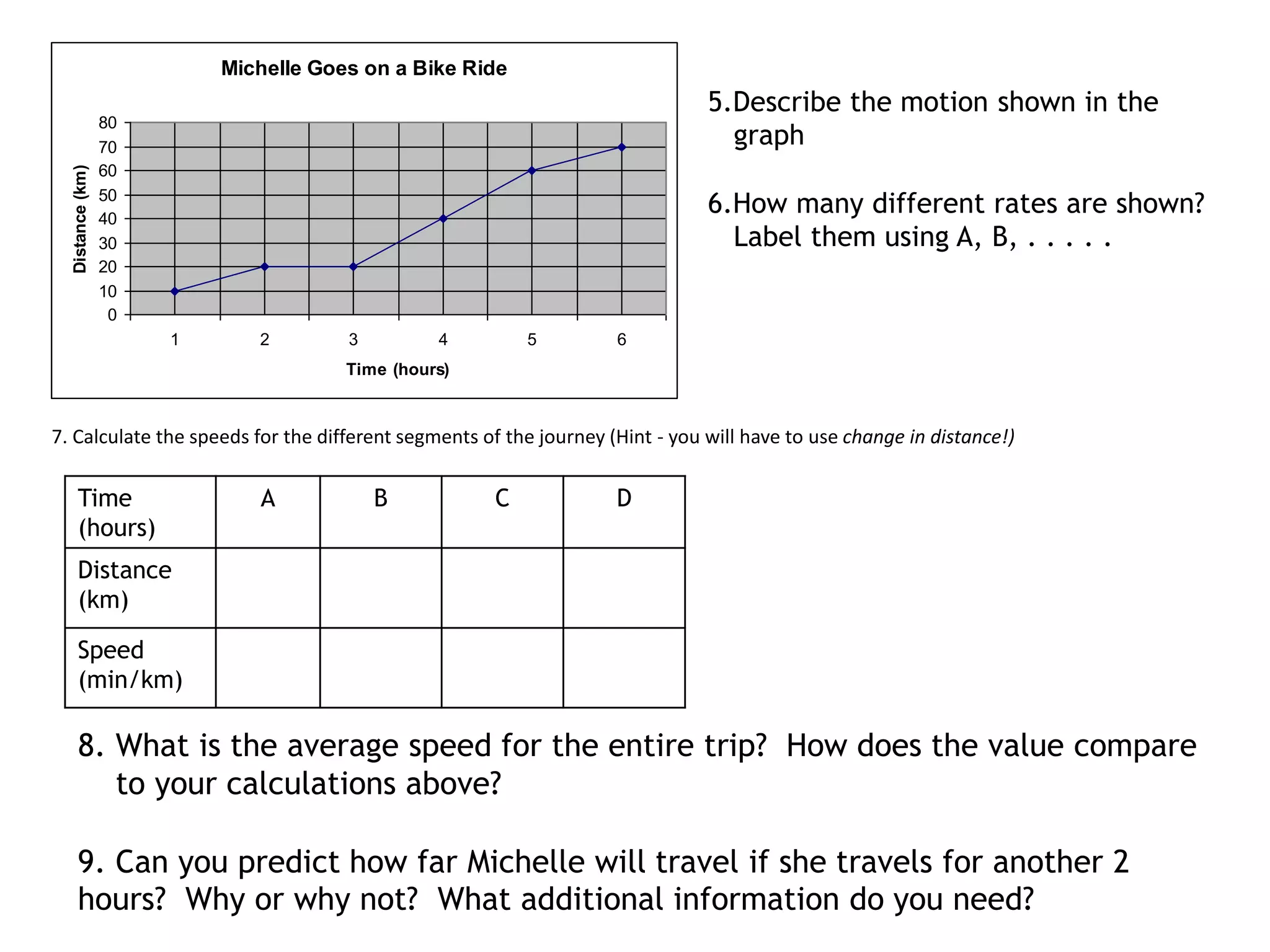
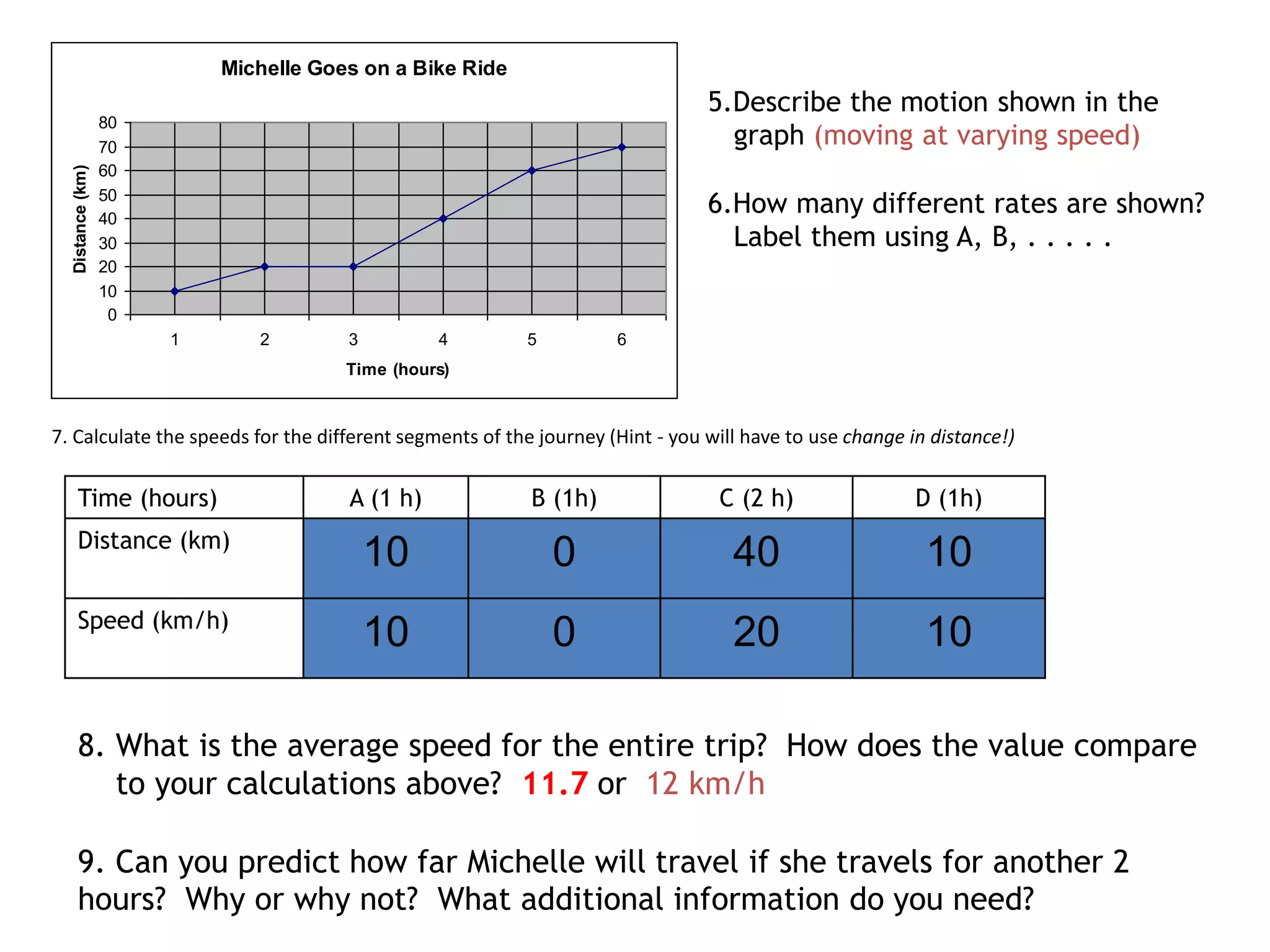
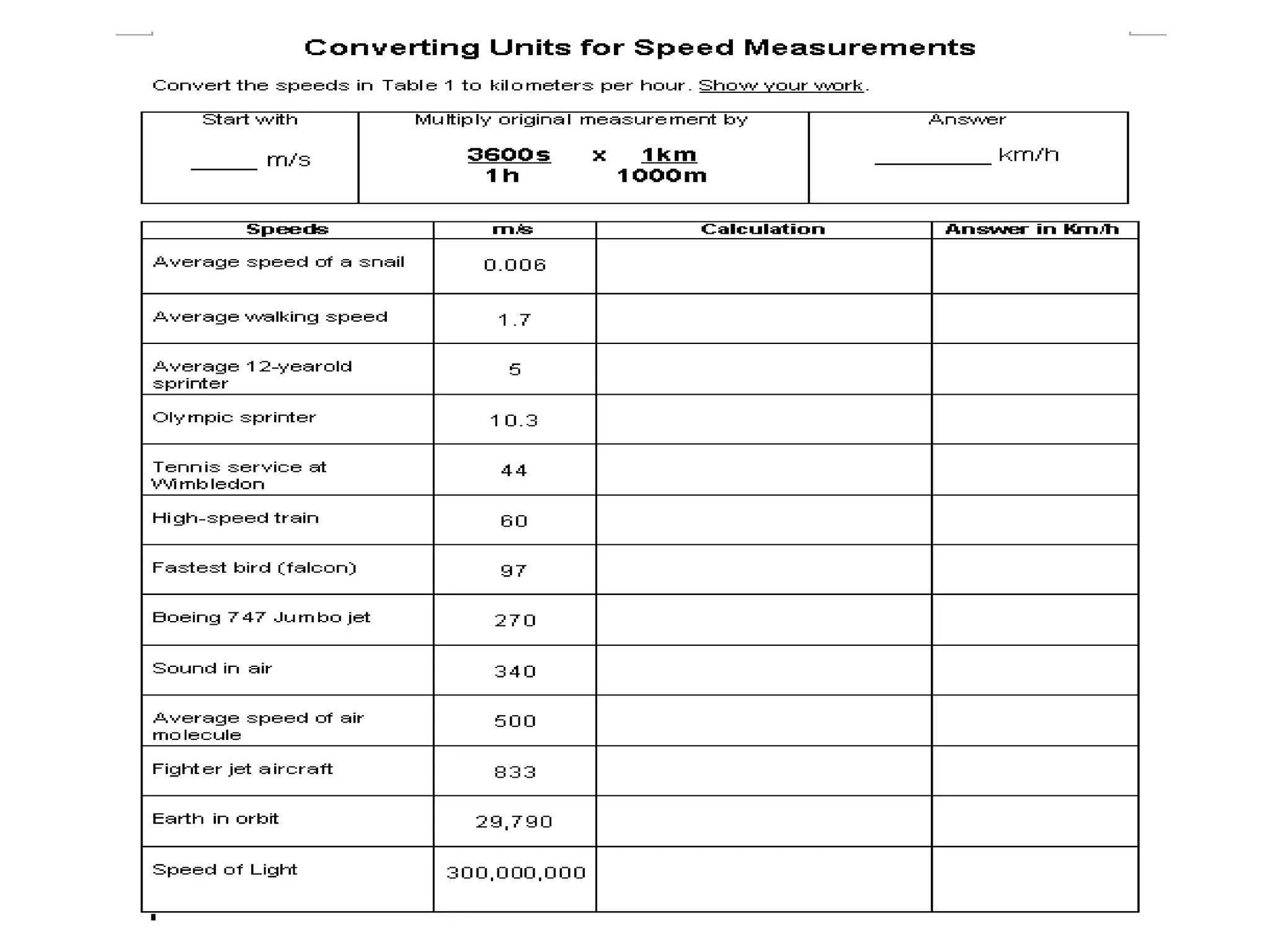
This document defines key terms related to speed, distance, and time. It includes examples comparing the constant versus average speed of objects. Constant speed is speed that does not change over time, while average speed is calculated by dividing total distance by total time. The document also contains sample speed and distance vs. time graphs and worksheets for calculating speed from the graphs.