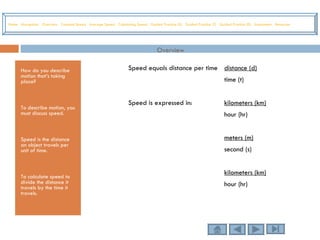
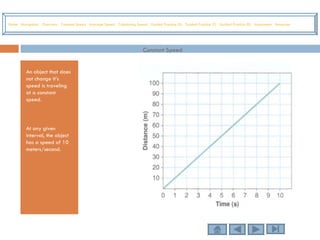
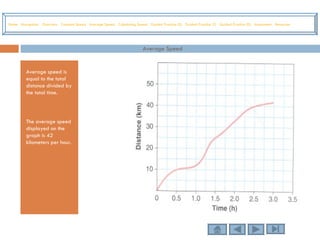
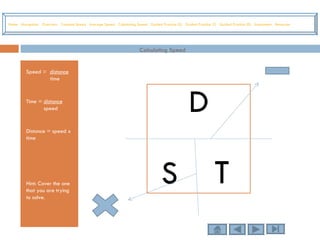
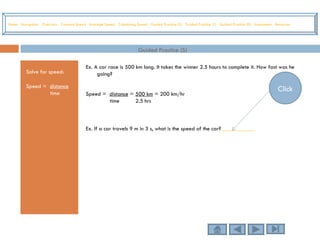
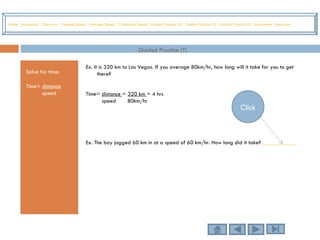
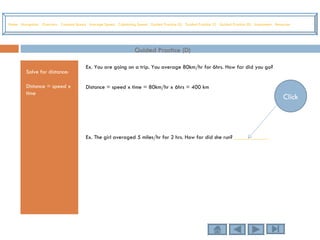
This tutorial teaches students how to measure motion in terms of speed, time, and distance. It defines speed as the distance traveled per unit of time. The document provides examples of constant speed, average speed, and how to calculate speed, time, and distance using the formulas. It includes guided practice problems for students to solve for speed, time, and distance.