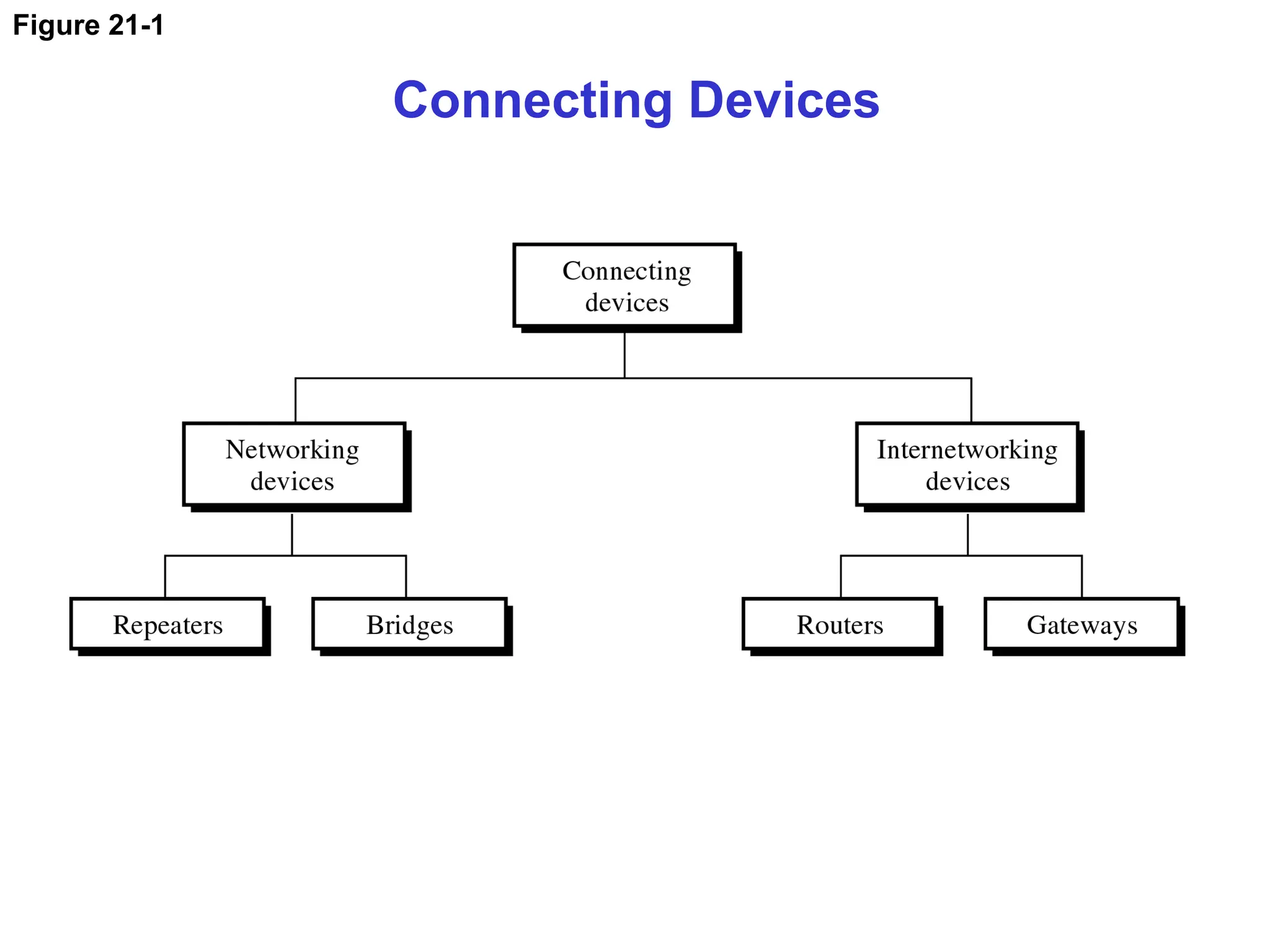
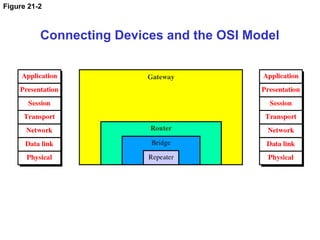
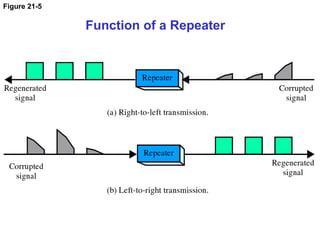
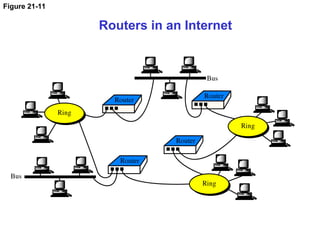
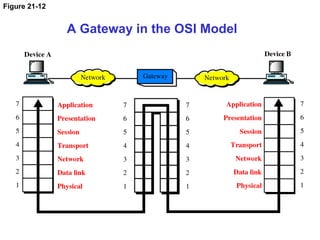
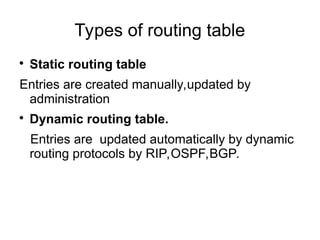
The document details the functions and characteristics of gateways and routers in network connectivity. Gateways serve as intermediaries connecting users to the internet, while routers forward data packets between networks. It also discusses routing processes, including static and dynamic routing tables, and the algorithms used to determine optimal routes.