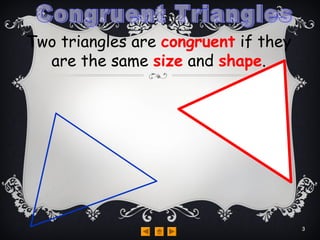
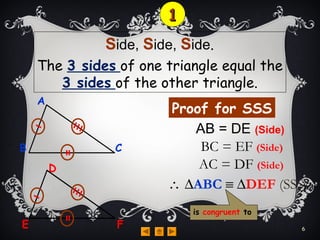
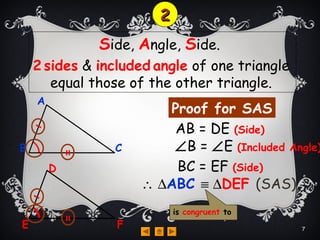
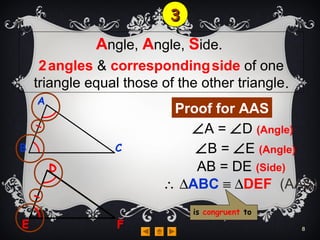
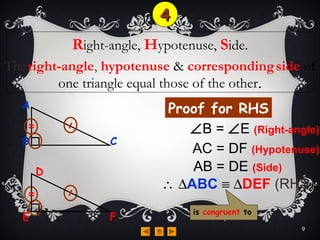
Triangles are congruent if they have the same size and shape. There are four rules to determine if triangles are congruent: side-side-side, side-angle-side, angle-angle-side, and right-angle-hypotenuse-side. The rules state that if two triangles have either three matching sides, two matching sides and the angle between them, two matching angles and a matching side, or a right angle, matching hypotenuse, and matching side, then the triangles are congruent.