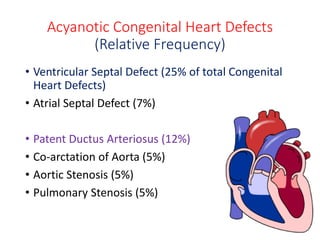
This document discusses congenital heart disease, including its classification, epidemiology, etiology, and clinical features. Congenital heart defects are classified as cyanotic or acyanotic. Cyanotic defects include tetralogy of Fallot and transposition of the great arteries, which allow deoxygenated blood to mix with oxygenated blood. Acyanotic defects allow oxygenated blood to shunt left-to-right, such as ventricular septal defects, atrial septal defects, and patent ductus arteriosus. Obstructive lesions include aortic and pulmonary stenosis. Congenital heart disease has an incidence of 8 per 1000 live births. Clinical features may include cyanosis, heart murmurs, heart failure symptoms