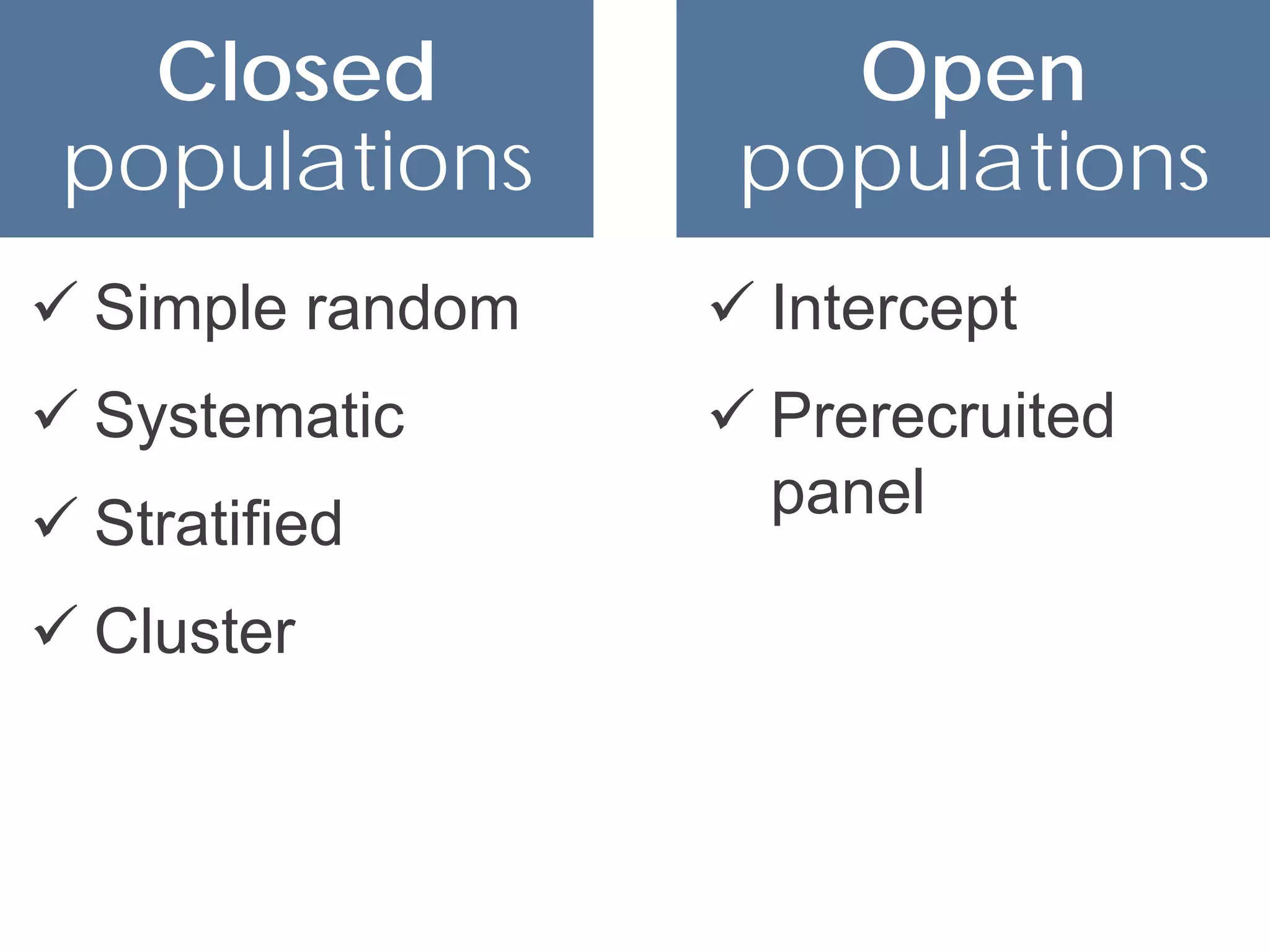
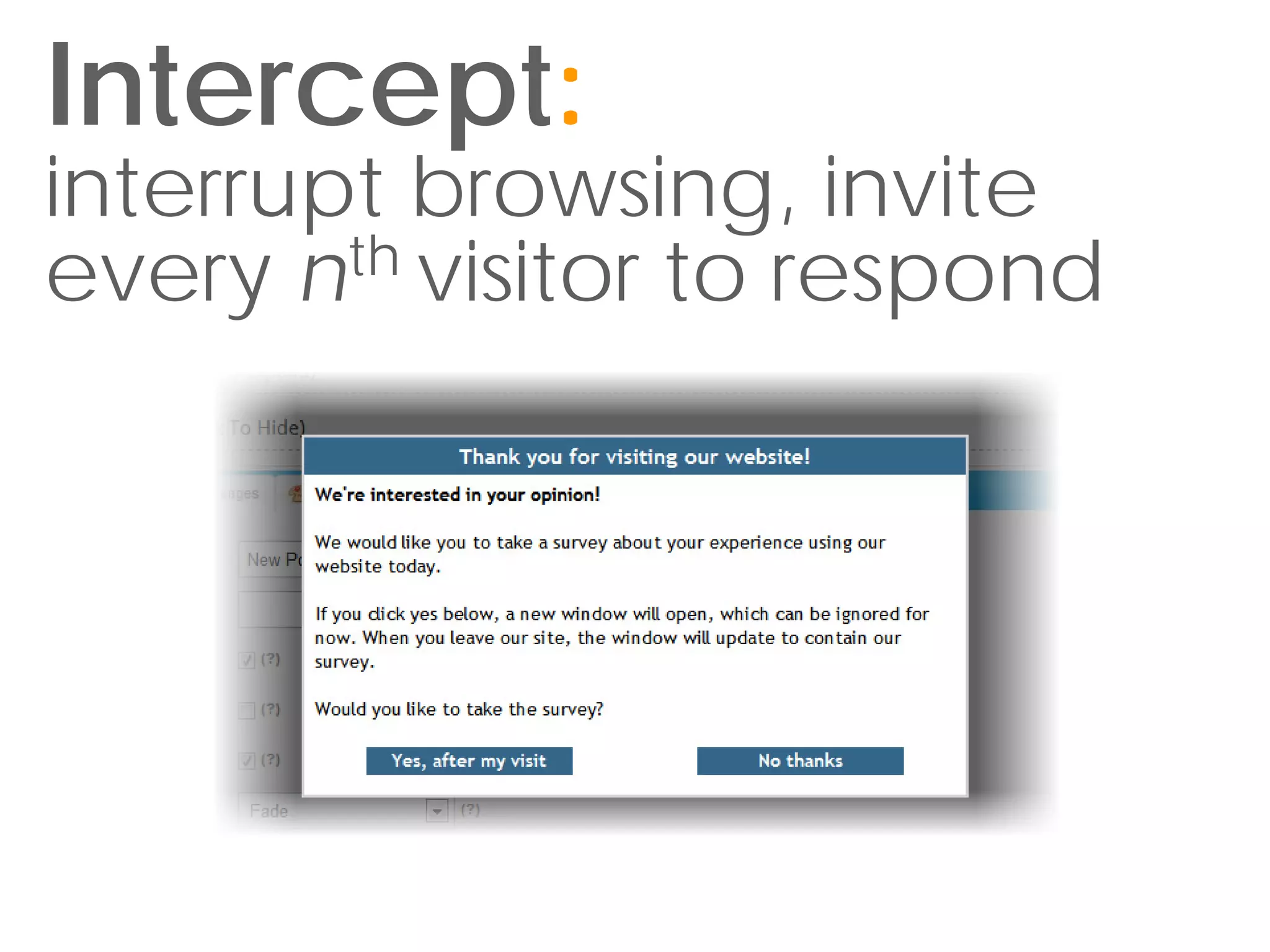
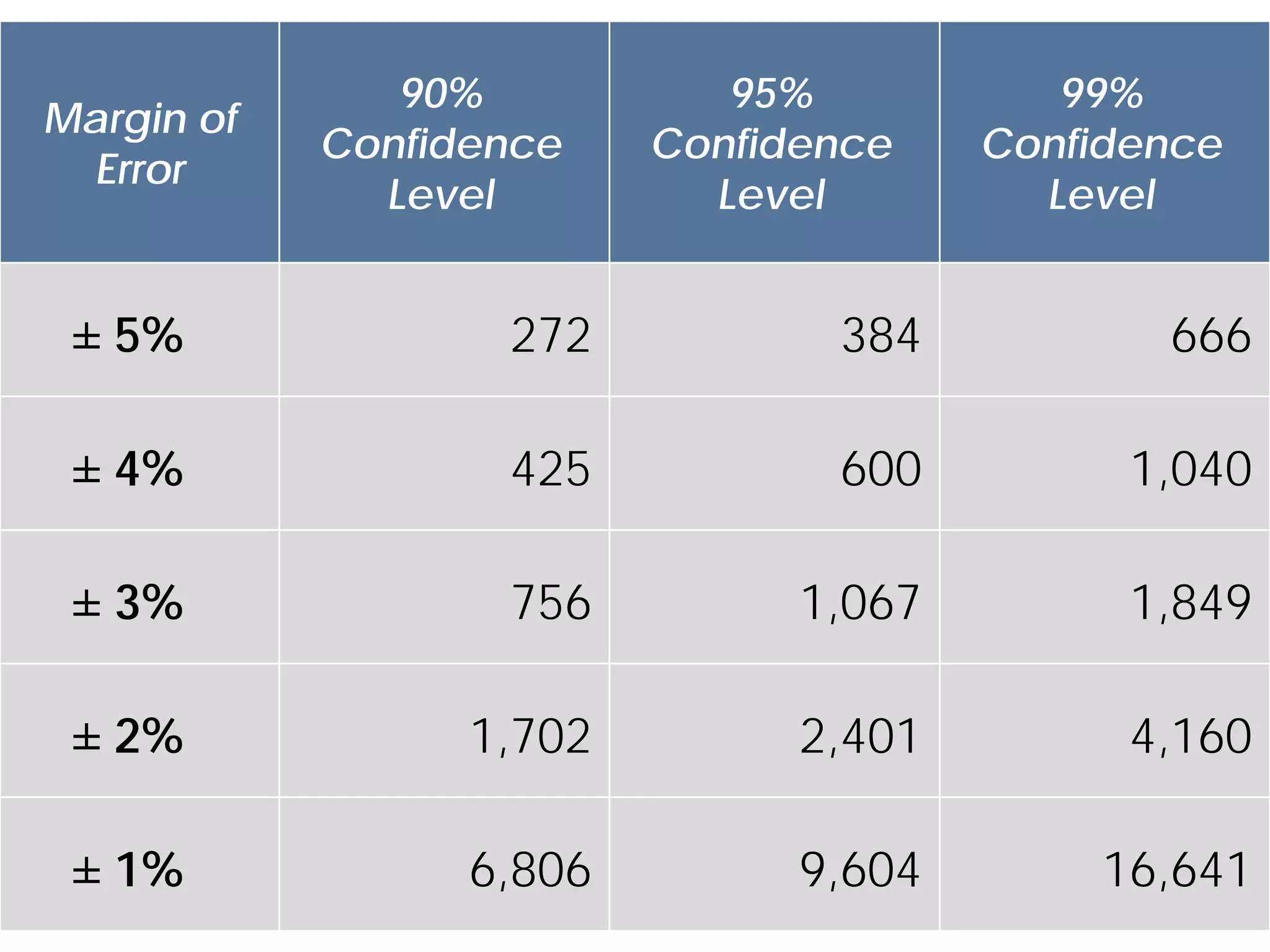
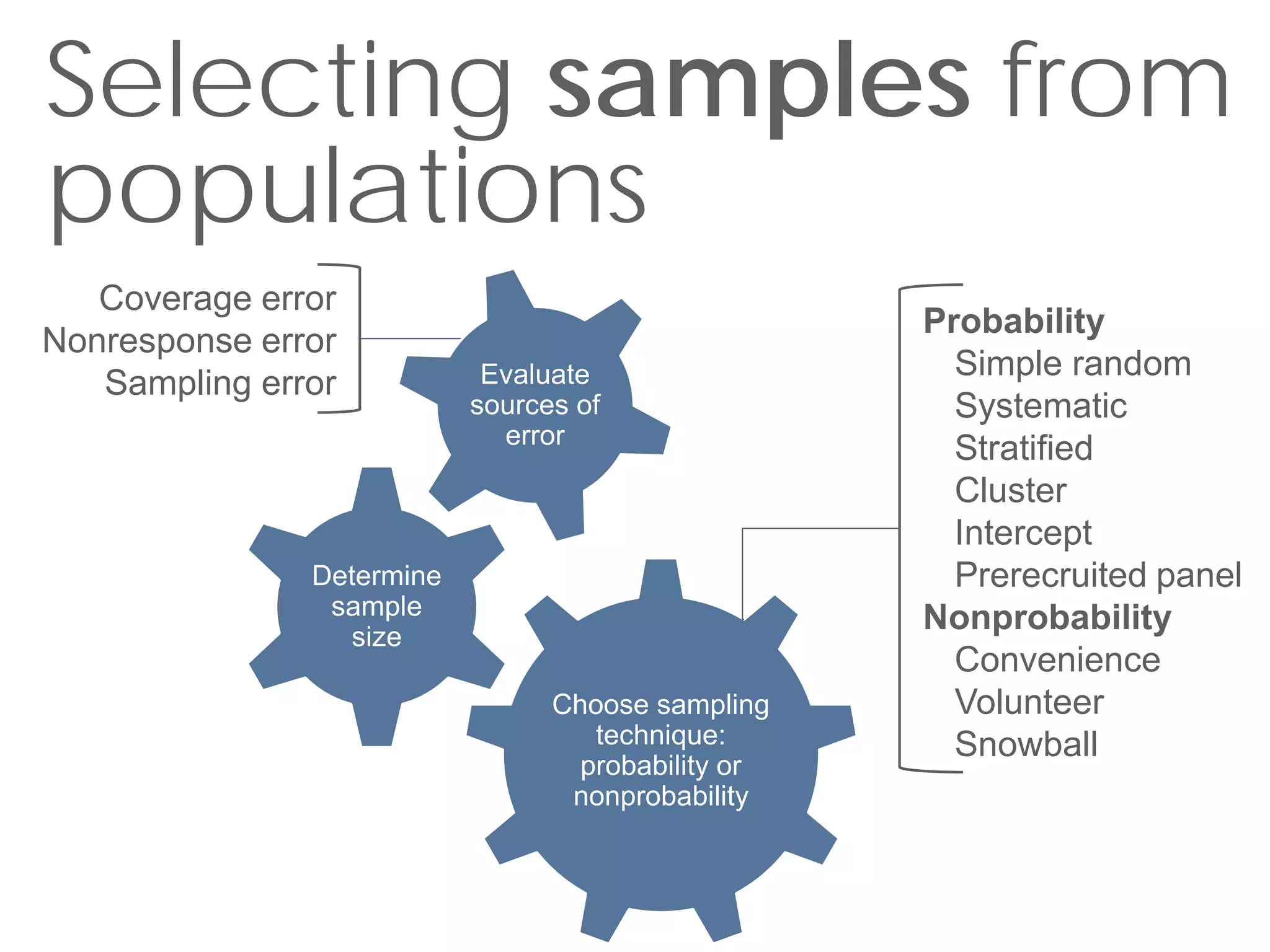
This document discusses sampling techniques for online surveys. It distinguishes between populations and samples, and identifies probability sampling techniques like simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling. It also identifies nonprobability sampling techniques like convenience sampling and snowball sampling. The document emphasizes evaluating sample size and sources of error in survey samples, like coverage error, nonresponse error, and sampling error. It provides guidelines for determining an appropriate sample size based on the desired confidence level and margin of error.