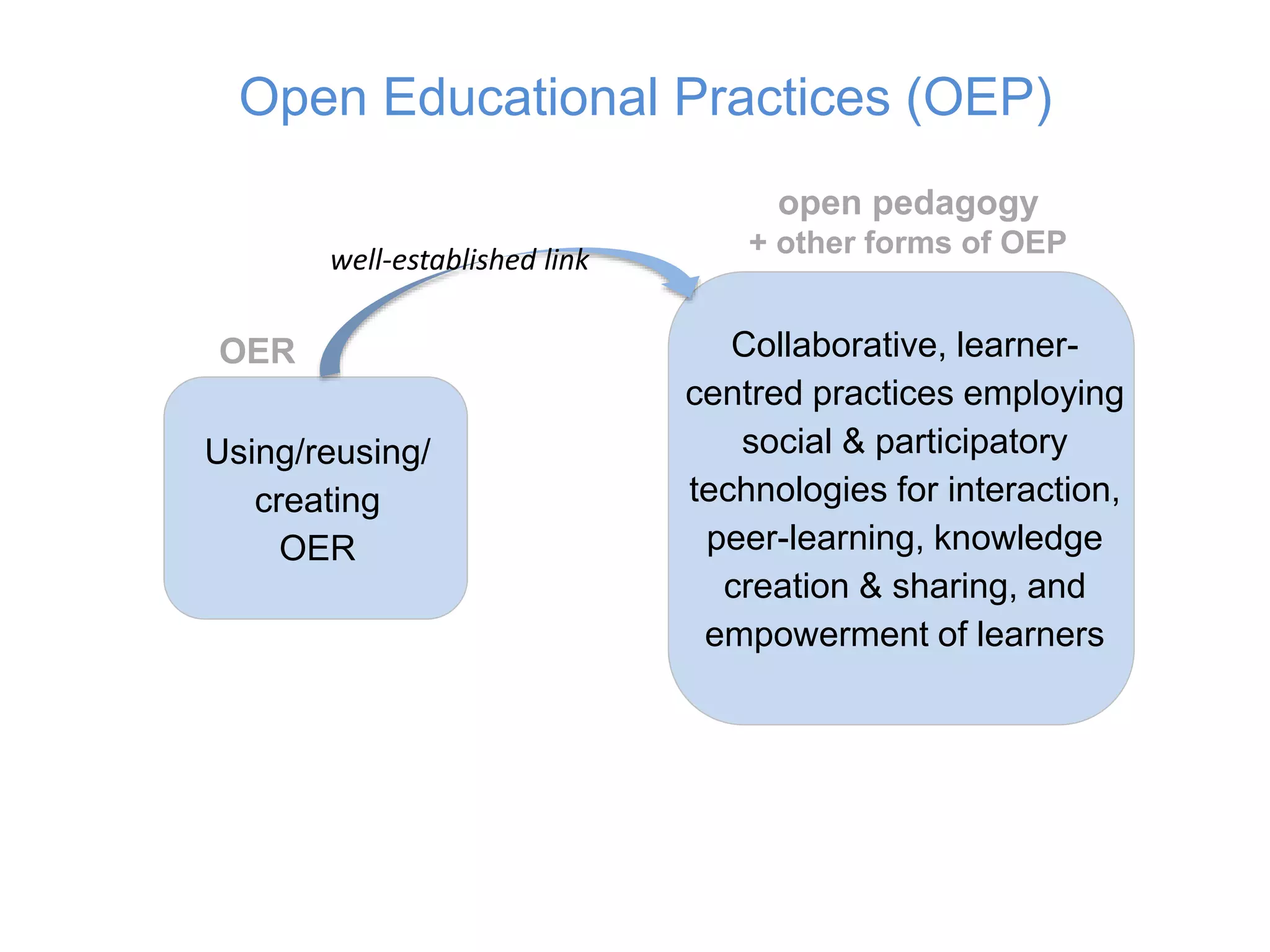
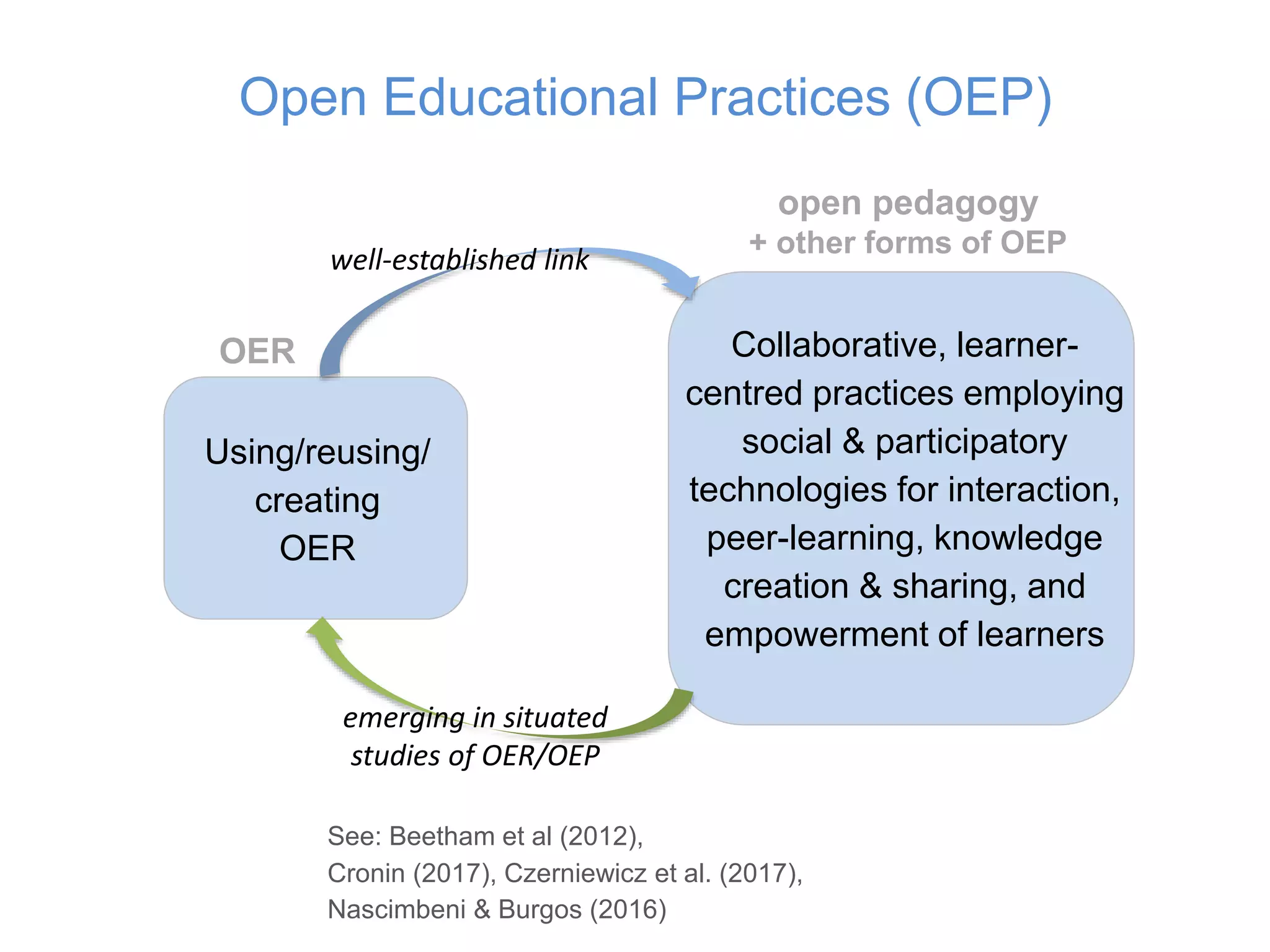
1) Definitions of open educational practices (OEP) have expanded over time from a focus on open educational resources (OER) use, reuse, and creation to include collaborative, learner-centered practices employing social and participatory technologies.
2) Later definitions broadened the concept of OEP to include open/public pedagogies, open learning, open scholarship, and open sharing of teaching ideas in addition to OER.
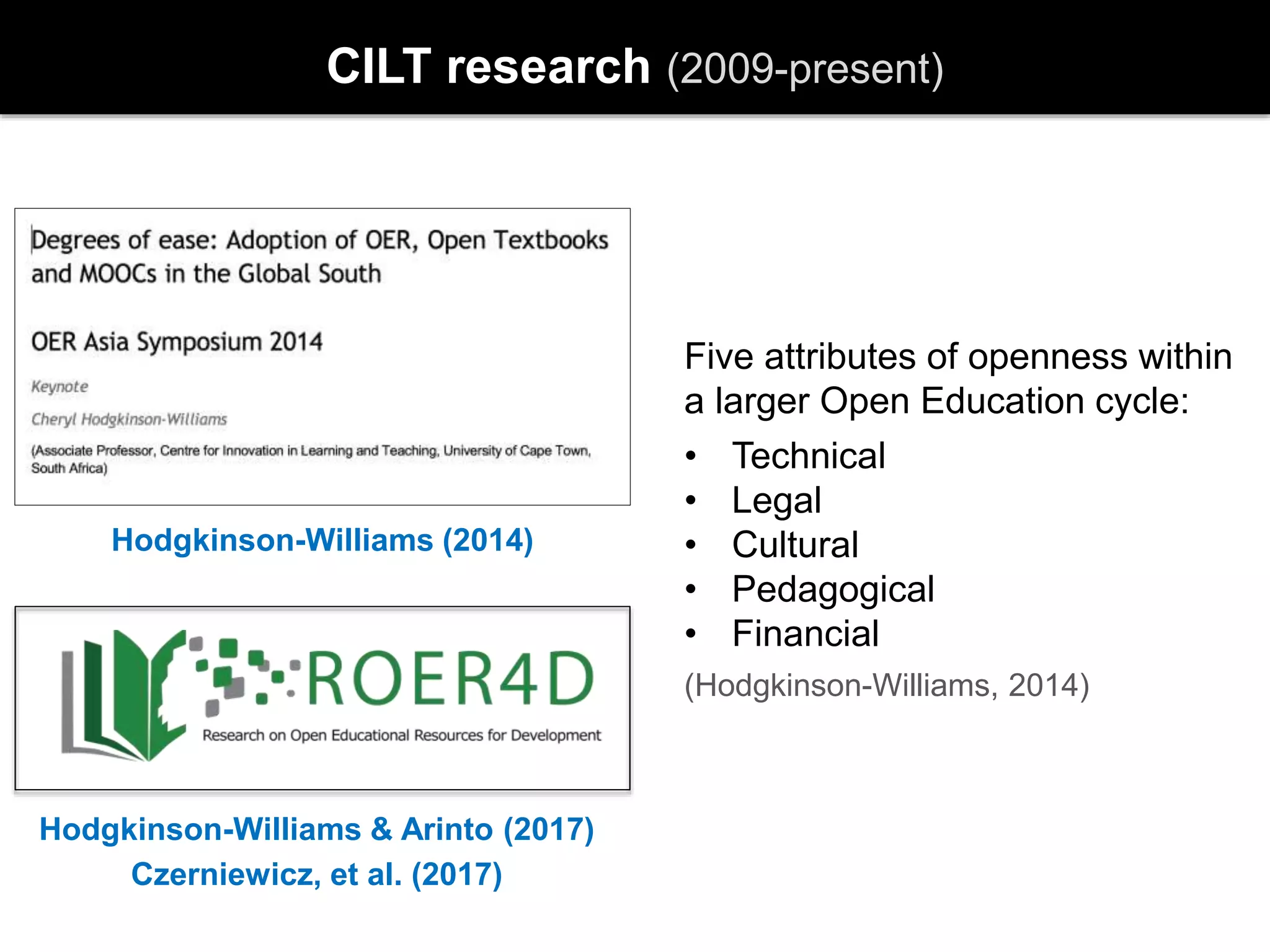
3) Recent literature has recognized that OER and OEP can be decoupled and that context is integral to understanding OEP, which encompasses technical, legal, cultural, pedagogical and financial dimensions of openness.