1. CASE tools are software used to support various activities in the software development process by automating some activities and providing information about the software.
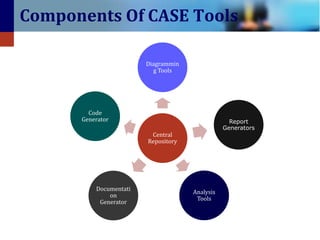
2. CASE tools have several key components including diagramming tools, central repositories, report generators, documentation generators, and code generators.
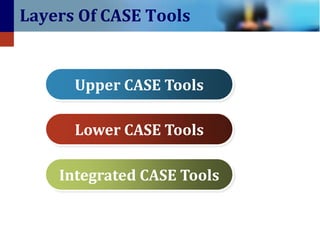
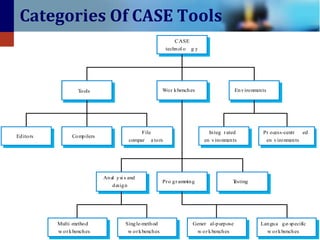
3. CASE tools can be categorized as upper CASE tools which focus on analysis, lower CASE tools which focus on programming and integration, or integrated CASE tools which support the entire process.