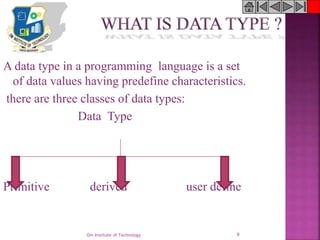
The document discusses key concepts of the C programming language including its history, structure, data types, variables, operators, input/output functions, and preprocessor directives. Specifically, it covers C's modular structure using functions, header files that enable code reuse, and the main function which acts as the program entry point. It also describes primitive, derived and user-defined data types in C as well as common constants, variables, and operators supported.