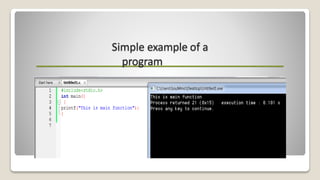
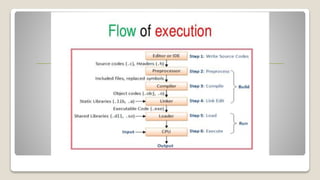
The document outlines the basic structure of the C programming language, emphasizing its importance in programming and problem-solving. It explains key concepts such as header files, the main function, comments, variables, and constants, along with example code snippets. Additionally, it highlights opportunities in coding, such as creating websites or starting a business in software or app development.