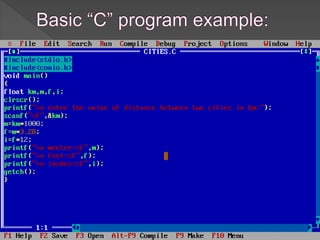
This document provides an overview of the C programming language, including its history, features, data types, control characters, input/output functions, and examples. It discusses how C was created at Bell Labs as a portable, general-purpose language suitable for system programming. The document also covers C keywords, character sets, compiling and executing C programs, functions, libraries, and standardization.








![ A character denotes any alphabet, digit or
special symbol used to represent
information.
Following are the valid alphabets, numbers
and special symbols allowed in C:
Alphabets - A, B, ….., Y, Z a, b, ……, y, z
Digits - 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
Special symbols - ~ ‘ ! @ # % ^ & * ( ) _ - +
= | { } [ ] : ; " ' < > , . ? /](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoc-200404135927/85/Introduction-to-C-Programming-11-320.jpg)