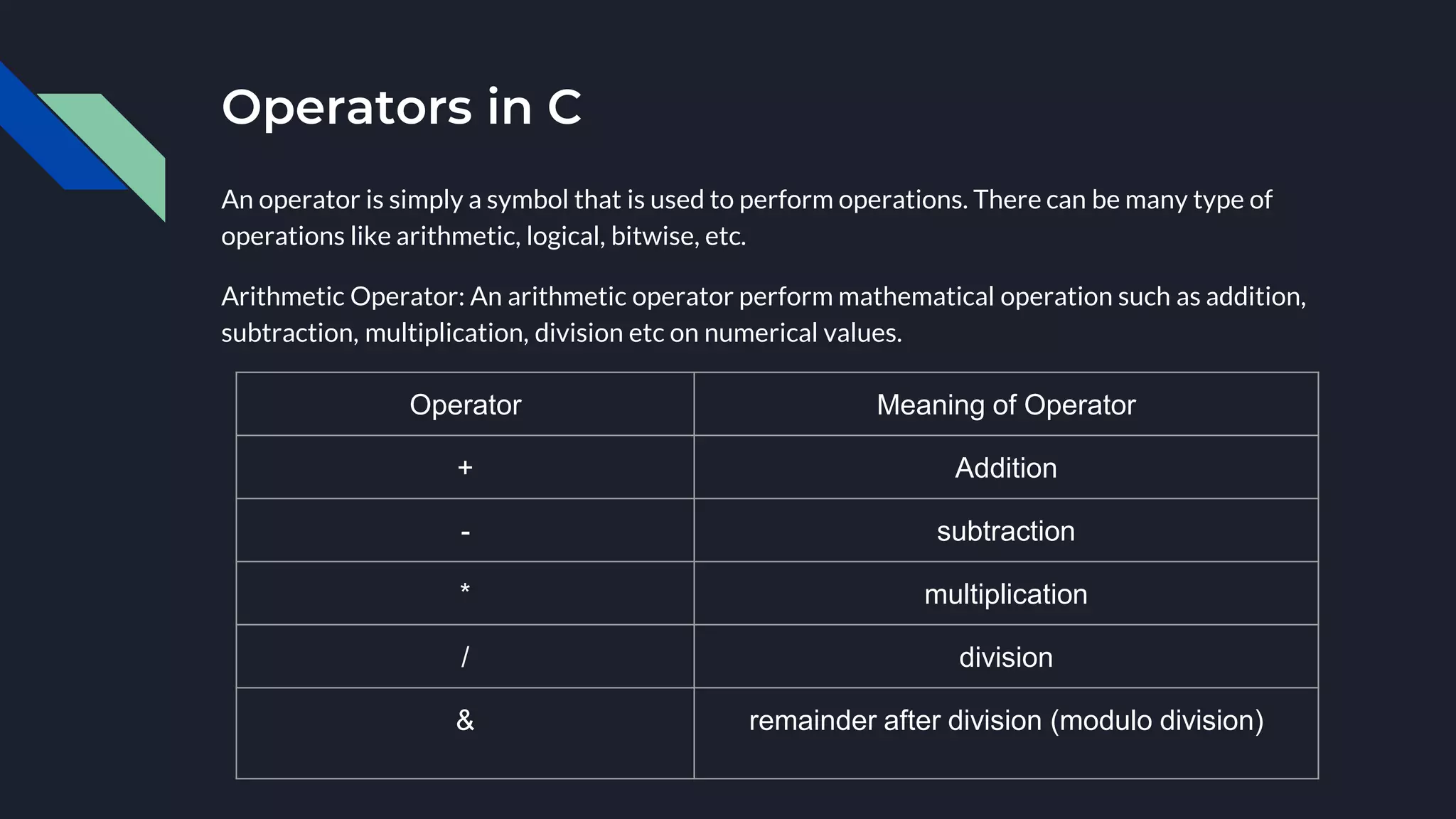
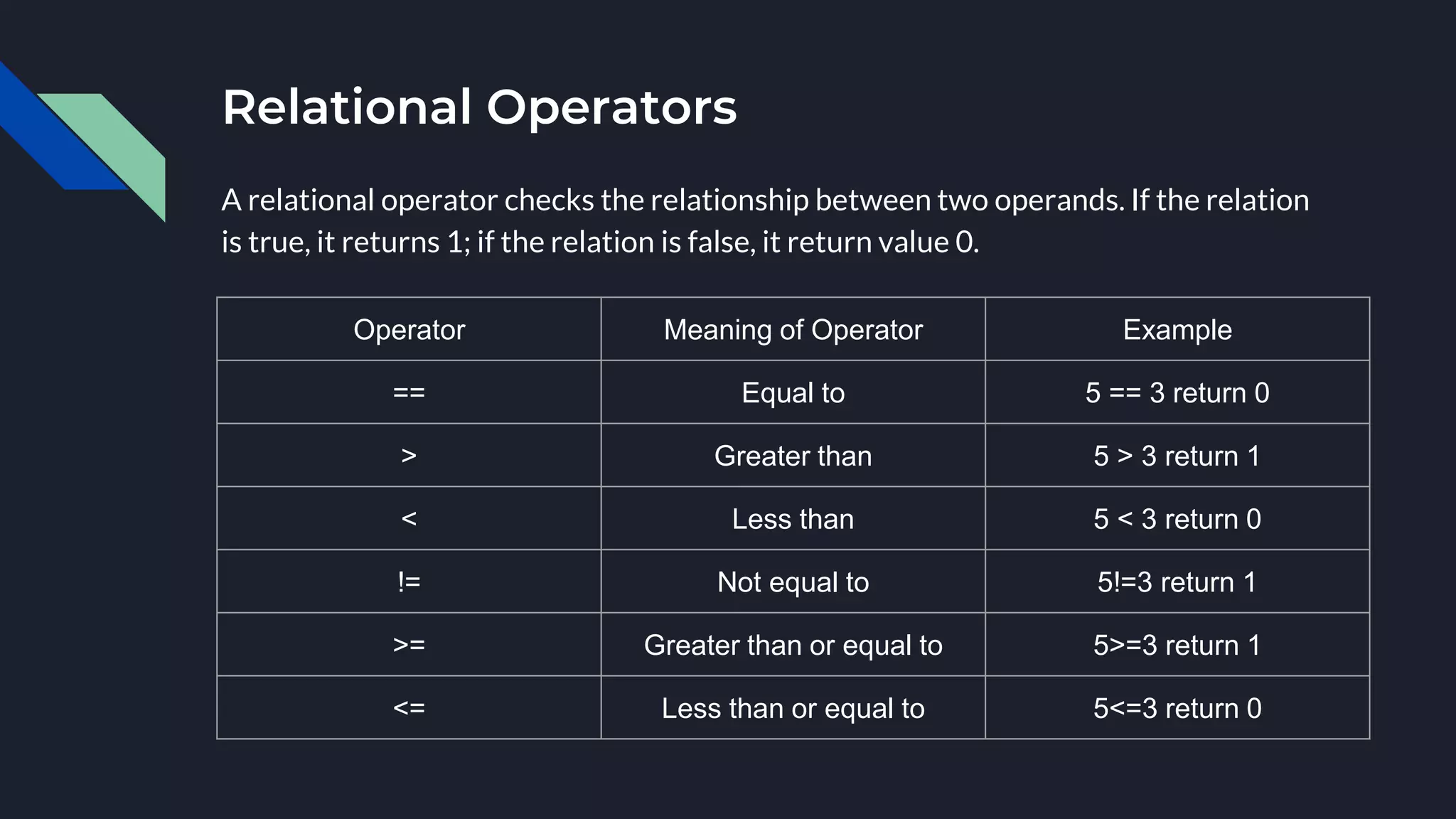
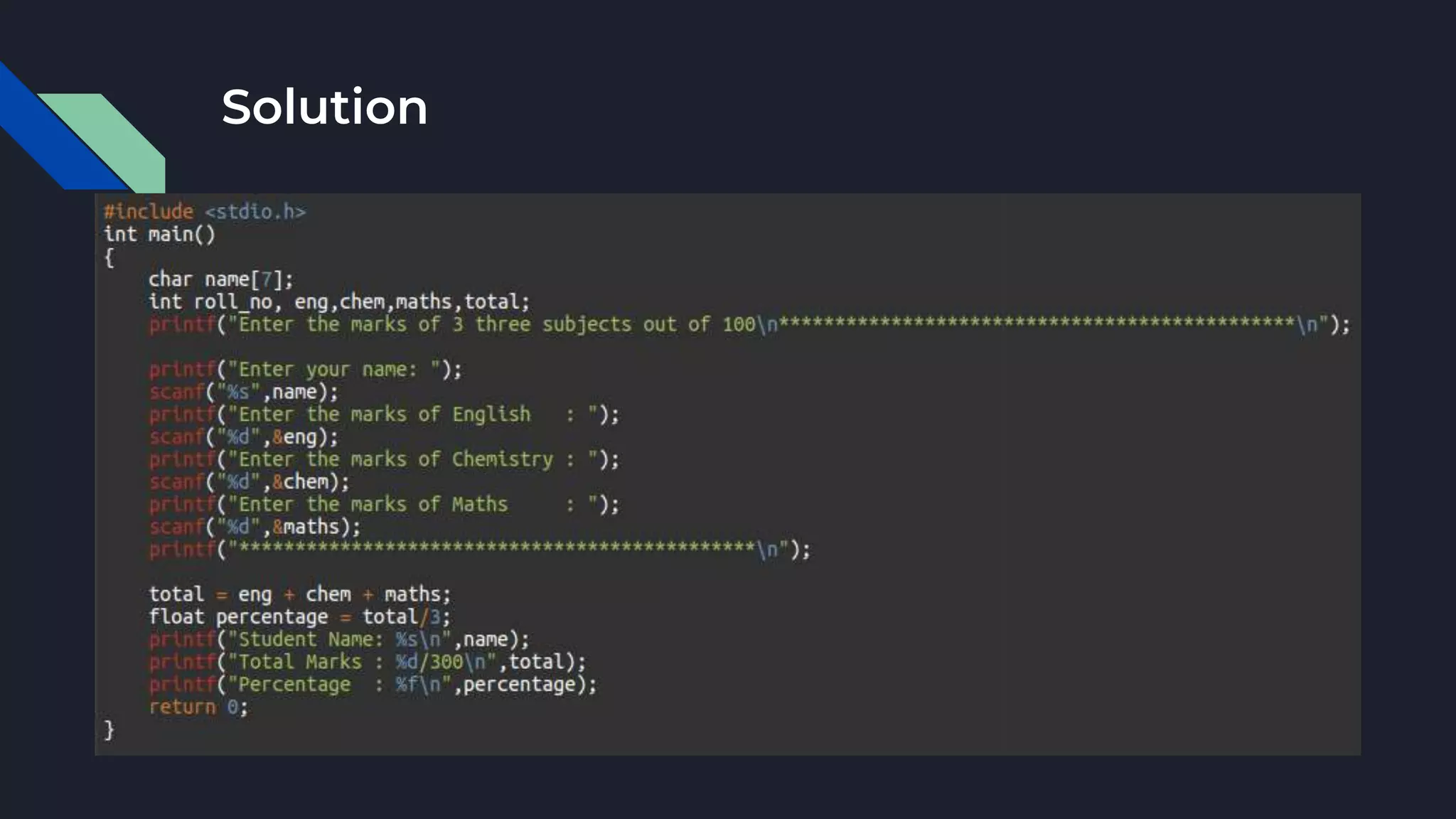
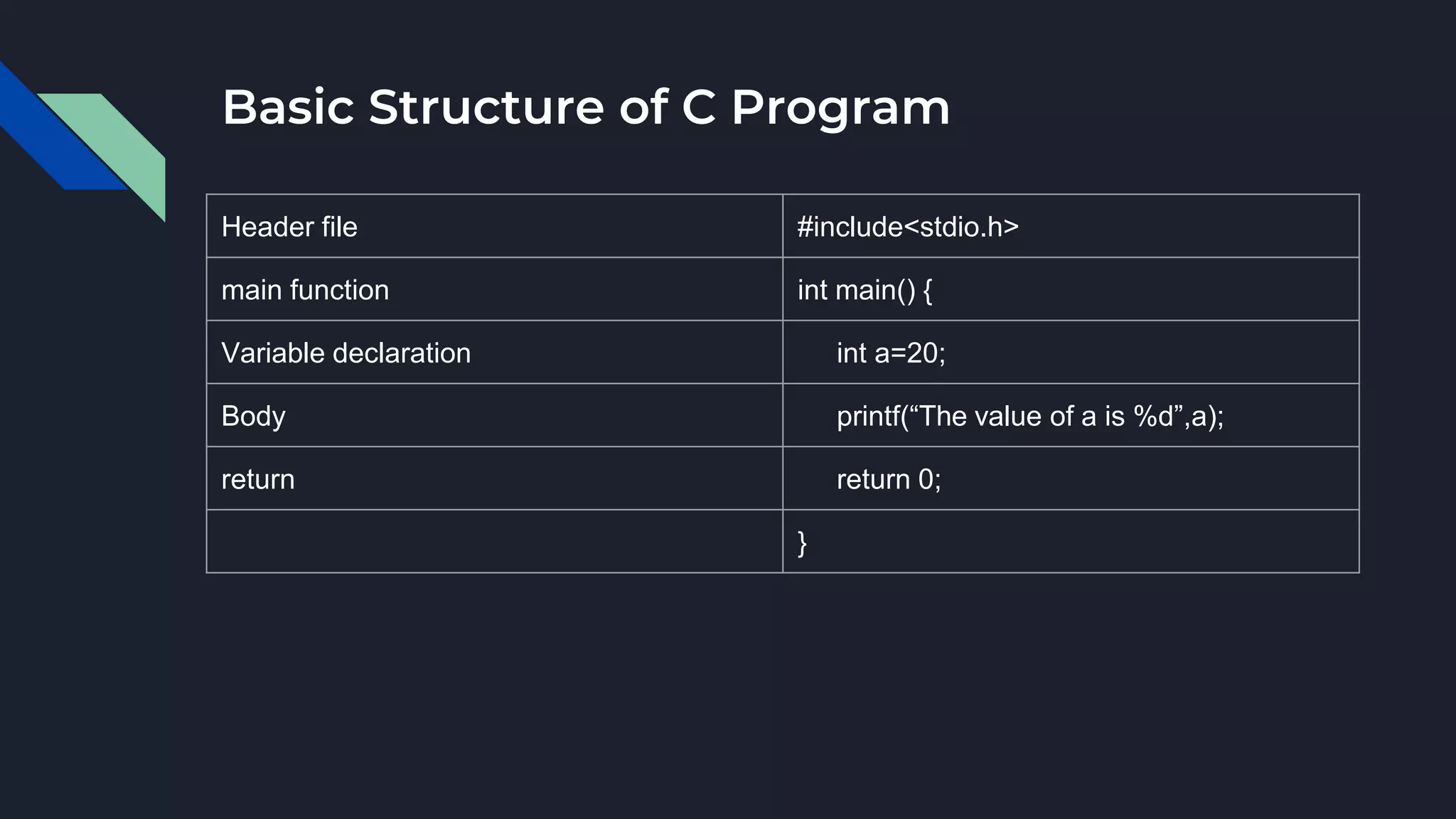
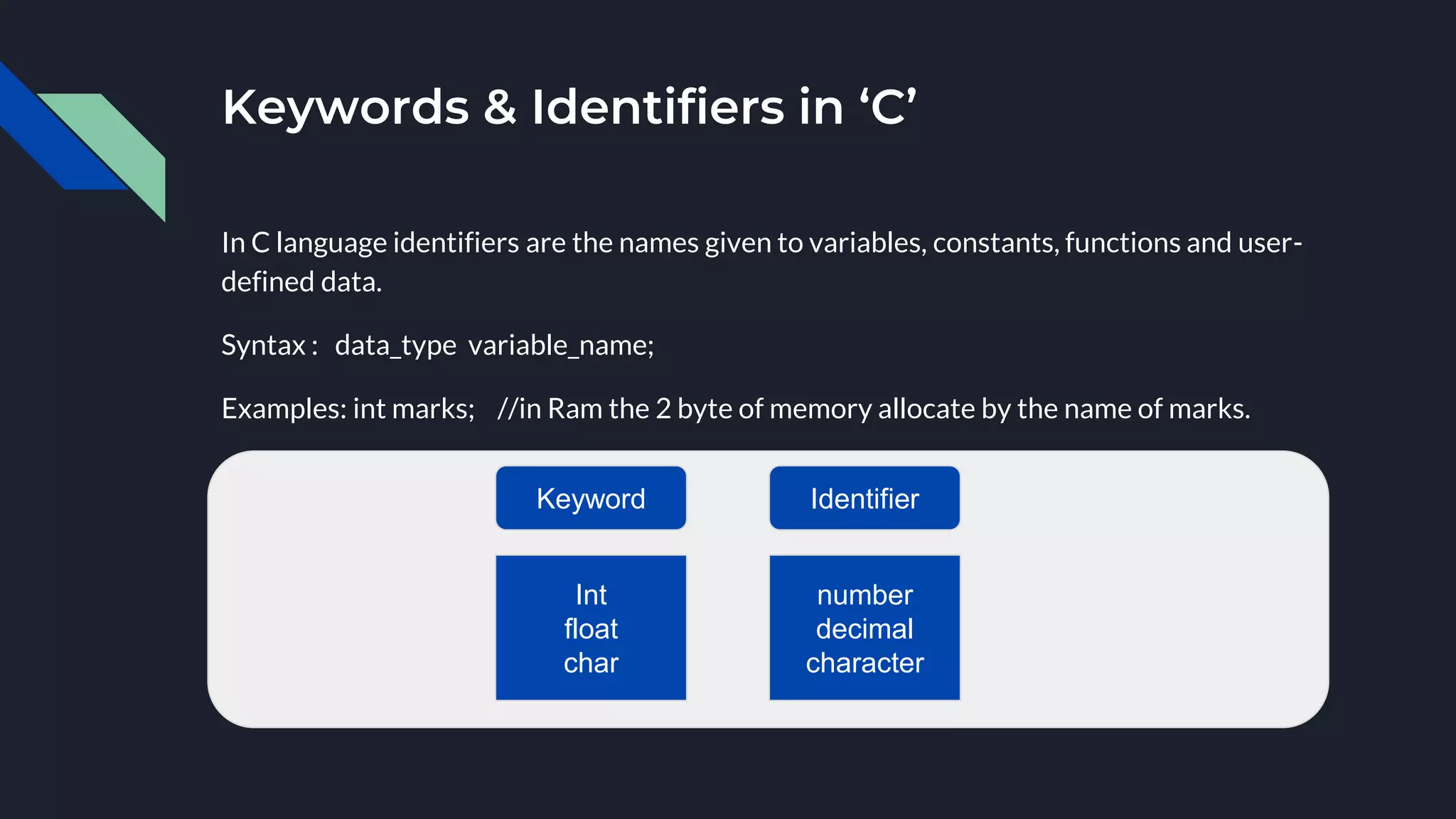
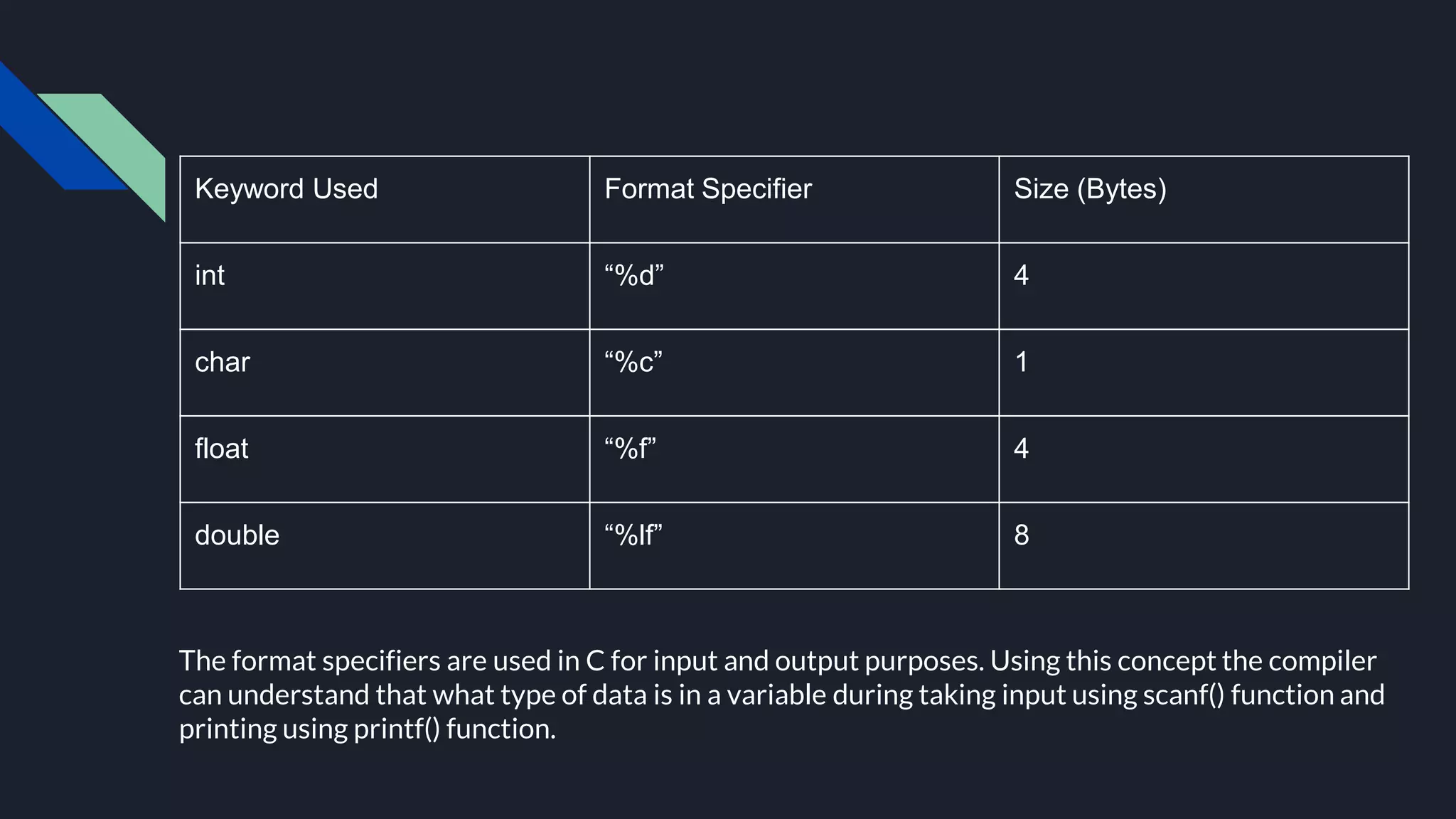
The document provides an overview of the C programming language, highlighting its procedural orientation, key features, and standard library header files. It explains the structure of a basic C program, including data types, operators, and input/output functions like scanf() and printf(). Additionally, it discusses various operators in C, such as arithmetic, relational, and logical operators, and their usage in programming.





![C Input
In C programming, scanf() is one of the commonly used function to take input from the user.
The scanf() function read formatted input from the standard input such as keyboards.
Example:
#include<stdio.h>
int main() {
int age; // variable declaration of type integer.
char name[7];
scanf(“%d”, &age);
scanf(“%s”,name);
printf(“Age= %d”, age); // printf() function used to display the output to
the user.
return 0;
}
Note: & represent the memory address and &age denotes the memory address of age.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsofcprogramming-220904114358-0a2f93c4/75/Basic-of-C-Programming-2022-Updated-By-Shamsul-H-Ansari-9-2048.jpg)