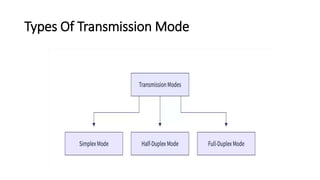
Transmission modes in computer networks specify the direction of data flow between devices. There are three main types: simplex mode allows one-way transmission from sender to receiver; half duplex allows transmission in either direction but not simultaneously; and full duplex allows simultaneous two-way transmission, with the fastest speeds. Examples include keyboards, radio stations, walkie-talkies, and telephone networks.