Types of Computer Networks
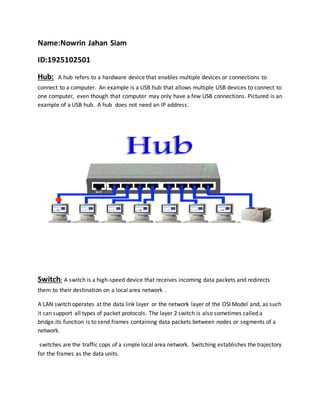
- 1. Name:Nowrin Jahan Siam ID:1925102501 Hub: A hub refers to a hardware device that enables multiple devices or connections to connect to a computer. An example is a USB hub that allows multiple USB devices to connect to one computer, even though that computer may only have a few USB connections. Pictured is an example of a USB hub. A hub does not need an IP address. Switch: A switch is a high-speed device that receives incoming data packets and redirects them to their destination on a local area network . A LAN switch operates at the data link layer or the network layer of the OSI Model and, as such it can support all types of packet protocols. The layer 2 switch is also sometimes called a bridge.its function is to send frames containing data packets between nodes or segments of a network. switches are the traffic cops of a simple local area network. Switching establishes the trajectory for the frames as the data units.
- 2. routing takes place at layer 3, there data gets sent between networks or from one network to another. Router: A router is a device that connects two or more packet-switched networks . The function of router is managing traffic between these networks by forwarding data packets to their intended IP addresses, and allowing multiple devices to use the same Internet connection.
- 3. NIC CARD: A network interface controller.NIC, also known as a network interface card, network adapter . NIC card is a computer hardware component that connects a computer to a computer network.
- 4. IP ADRESS: IP full form is internet protocol. IP address is a unique identifier. Any time that you use the internet you’re requesting access to a specific online destination, and in return, information is sent back to you. IP lays out the standards and rules for routing data and connecting to the internet. There are two types of IP addresses: 1. IPv4 2. IPv6 IPv4 and IPv6: 1. IPv4 is 32-Bit IP address and IPv6 is a 128-Bit IP address. 2. IPv4 is a numeric addressing method whereas IPv6 is an alphanumeric addressing method. 3. IPv4 binary bits are separated by a dot(.) and IPv6 binary bits are separated by a colon(:). 4. IPv4 supports broadcast. on the otherhand, IPv6 doesn’t support broadcast. 5. IPv4 has checksum fields while IPv6 doesn’t have checksum fields 6. When we compare IPv4 and IPv6, IPv4 supports VLSM (Variable Length Subnet Mask) and IPv6 doesn’t support VLSM. 7. IPv4 uses ARP to map to MAC address whereas IPv6 uses NDP to map to MAC address.
- 5. IP ADDRESS RANGES: Class A: 1-126 Class B: 128-191 Class C: 192-223 Class D: 224-239 Class E: 240-255 Transmission Mode In Computer Network: Data Transmission mode defines the direction of the flow of information between two communication devices. The data transmission modes ar three types based on the direction of exchange of information: 1. Simplex 2. Half-Duplex 3. Full Duplex 1. Simplex It is a one directional data transmissiom mode. The communication is unidirectional. A sender can only send data but can not receive it.
- 7. This transmission mode is not so popular because we cannot perform two-way communication between the sender and receiver in this mode. It is mainly used in the business field as in sales that do not require any corresponding reply. It is similar to a one-way street. For Example, Radio and TV transmission, keyboard etc. Advantages of a Simplex transmission mode: 1. It utilizes the full capacity of the communication channel during data transmission. 2. It has no data traffic issues as it is one way transmission mode. Disadvantages of a Simplex transmission mode: 1. It is unidirectional in nature having no inter-communication between devices. 2. There is no mechanism for information to be transmitted back to the sender. 2. Half-Duplex Half-Duplex is the data transmission mode in which the data can flow in both directions but in one direction at a time. Each station can both transmit and receive the data but not at the same time. This type of data transmission mode can be used in cases where there is no need for communication in both directions at the same time. It can be used for error detection when the sender does not send or the receiver does not receive the data properly. The data needs to be transmitted again by the receiver. For Example, Walkie-Talkie, Internet Browsers, etc.
- 8. Advantages of a half-duplex transmission mode: 1. It facilitates the optimum use of the communication channel. 2. It is a two-way communication. Disadvantages of using a half-duplex transmission mode: 1. The two-way communication can not be performed at the same time. 2. Delay in transmission may occur as only one way communication can be possible at a time.
- 9. 3. Full-Duplex Full-Duplex is the data transmission mode in which the data can flow in both directions at the same time. It is two-way communication in which both the stations can transmit and receive the data simultaneously. Full-Duplex mode has double bandwidth as compared to the half-duplex. Its capacity of the channel is divided between the two directions of communication. This mode is used when communication in both direction simultaneously. Example, a Telephone Network beacause the persons can talk and listen to each other simultaneously.
- 10. Advantages of a full-duplex transmission mode: 1. The two-way communication can be work simultaneously in both directions. 2. Fastest mode of communication between devices. Disadvantages of a half-duplex transmission mode: 1. The capacity of the communication channel is divided into two parts. 2. It has improper channel bandwidth utilization because it’s a two way transmission. Types Of Computer Network: