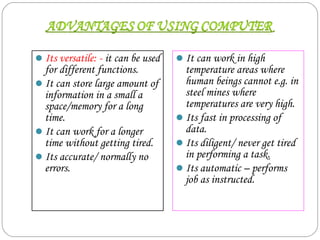
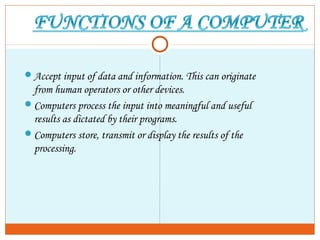
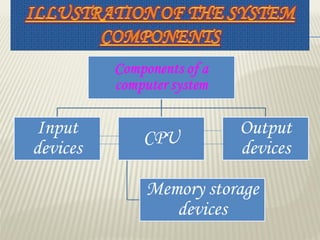
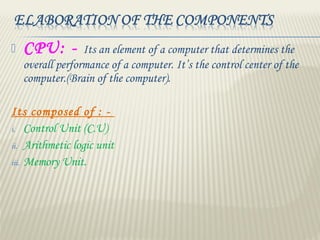
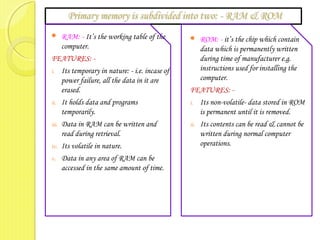
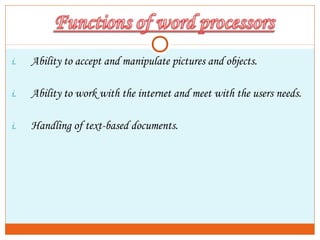
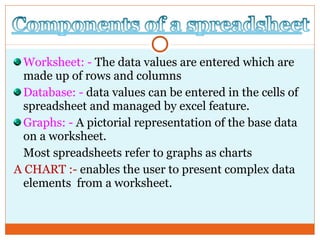
This document provides an introduction to using computers. It aims to equip trainees with basic computer knowledge, skills, and attitudes. It will cover defining computer terms, the different types of computers, computer components, operating systems, and common software applications. Trainees will learn about input/output devices, how computers process and store data, computer maintenance, and security issues like viruses. The goal is for trainees to gain practical skills that could enable self-employment opportunities using computer skills.