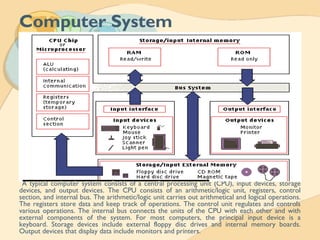
This document provides an introduction to PC operations and computer education. It discusses the basic components and functions of a computer system including hardware such as the CPU, memory, and I/O devices. It also covers software types like operating systems, applications, and system software. The document outlines the three basic operations of input, processing, and output and characteristics of modern computers like electronic storage and stored programs. It concludes with advantages and limitations of computer systems.