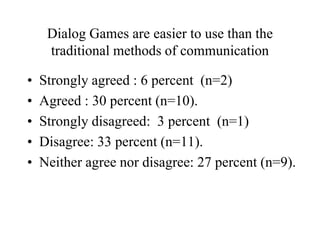
The document discusses a study on the application of dialog games as collaborative learning tools among computer engineering students, highlighting their potential to enhance knowledge development and social interactions. Results indicate that a significant majority of students are aware of collaborative learning concepts and prefer dialog games over traditional face-to-face communication, citing easier usability and better impacts on learning. Overall, students express a positive readiness to adopt dialog games in their educational practices.