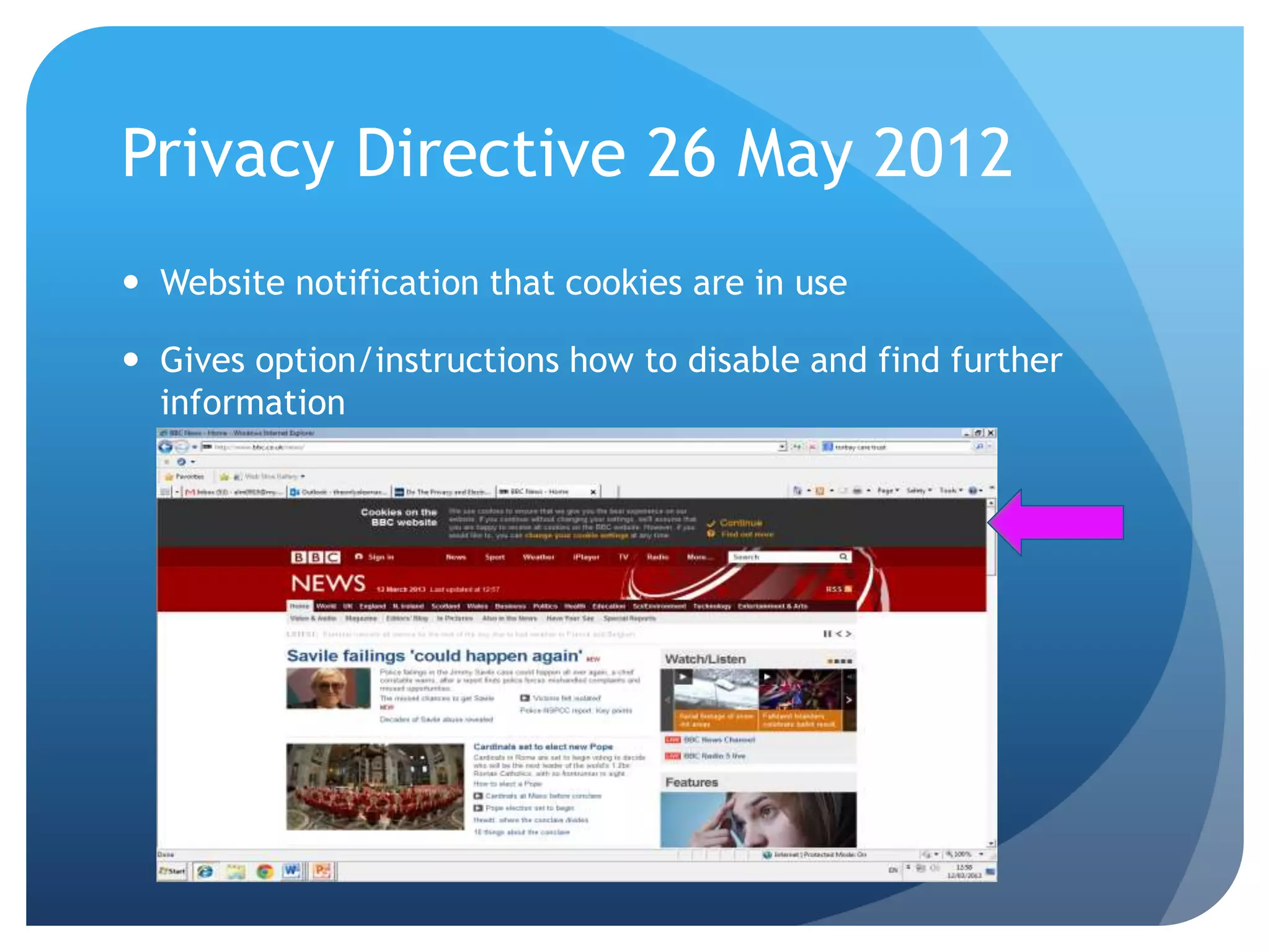
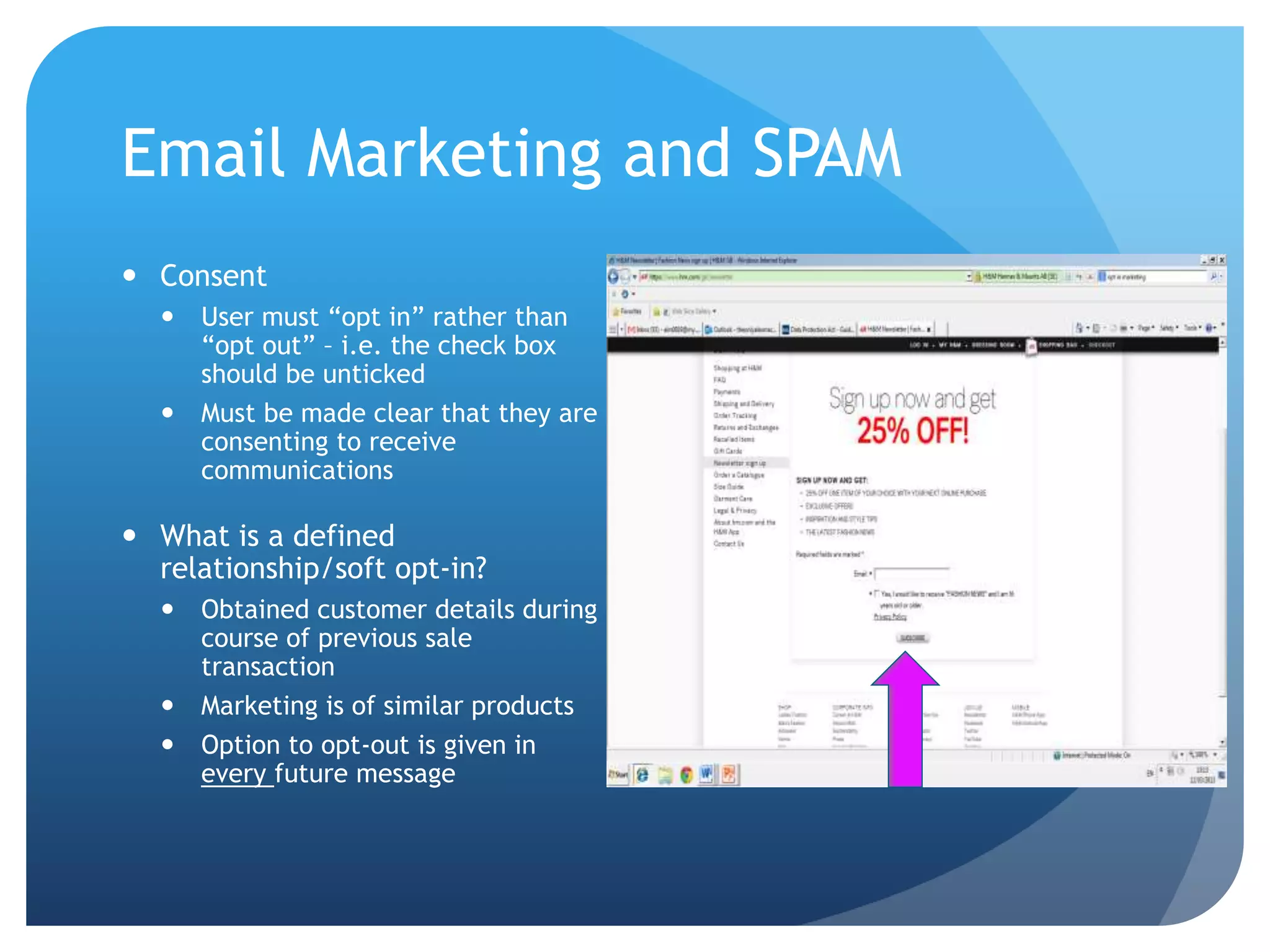
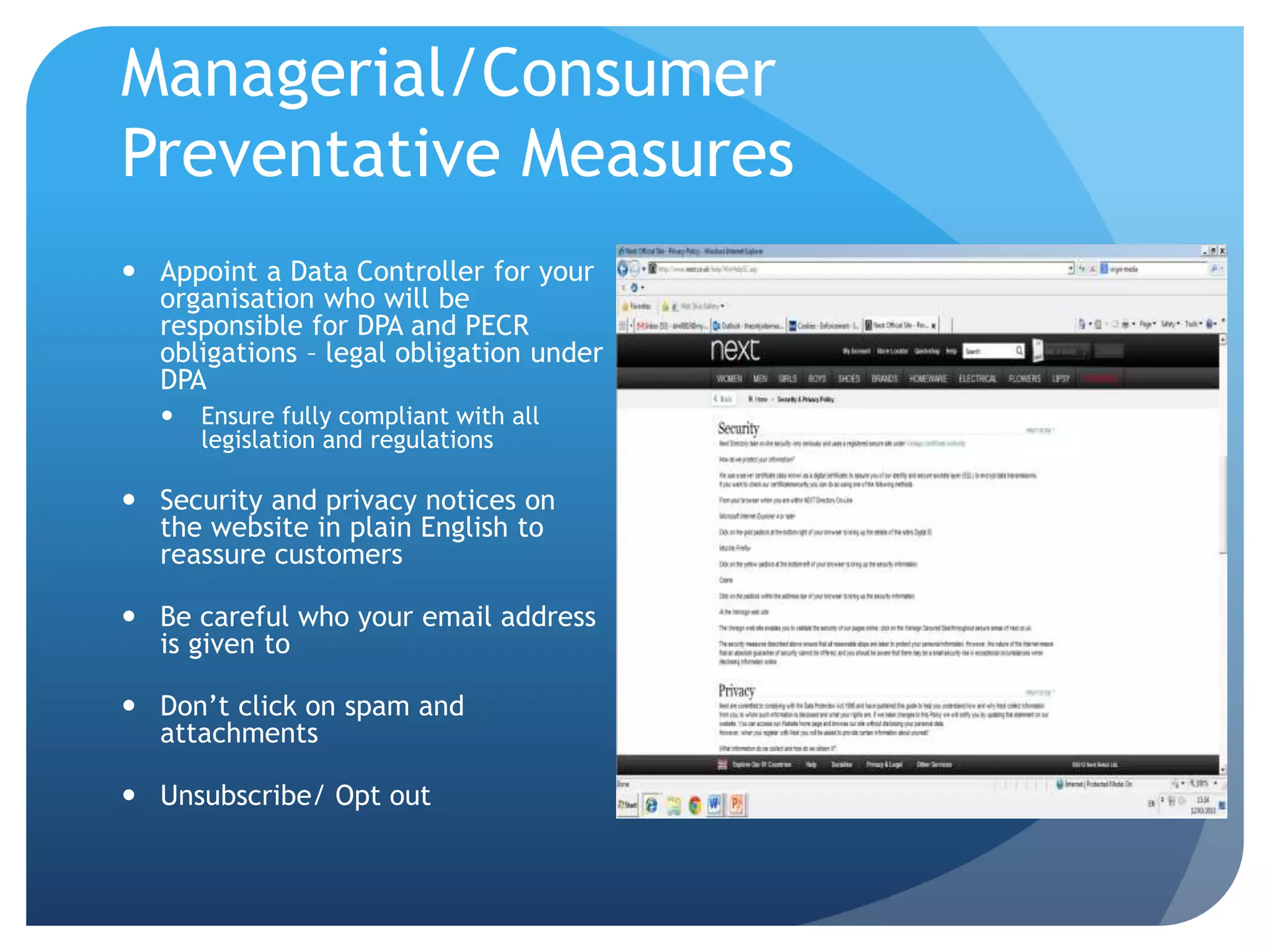
This document discusses security and privacy issues for both consumers and website owners. It covers topics such as types of security risks like hacking and viruses, privacy laws like the Data Protection Act, and how to implement preventative measures. The key implications are reputational damage and fines for non-compliance, so both groups benefit from measures to reassure users and protect their data/systems.



















![References
Chaffey, D., 2013. Website Security Requirements. [online]. Available at:
http://www.smartinsights.com/ecommerce/payment-security/website-security-
requirements/ [accessed 28 February 2013]
Chaffey, D., 2012. Research on consumer attitudes to online privacy. [online]. Available
at: http://www.smartinsights.com/marketplace-analysis/customer-analysis/research-on-
consumer-attitudes-to-online-privacy/ [accessed 28 February 2013]
Chaffey, D., Mayer, R., Johnston, K. and Ellis-Chadwick, F., 2000. Internet Marketing.
Essex: Pearson.
Financial Ombudsman Service, 2013. Disputed technical transaction. [online]. Available at:
http://www.financial-ombudsman.org.uk/publications/technical_notes/disputed-
transactions.htm [accessed 10 March 2013]
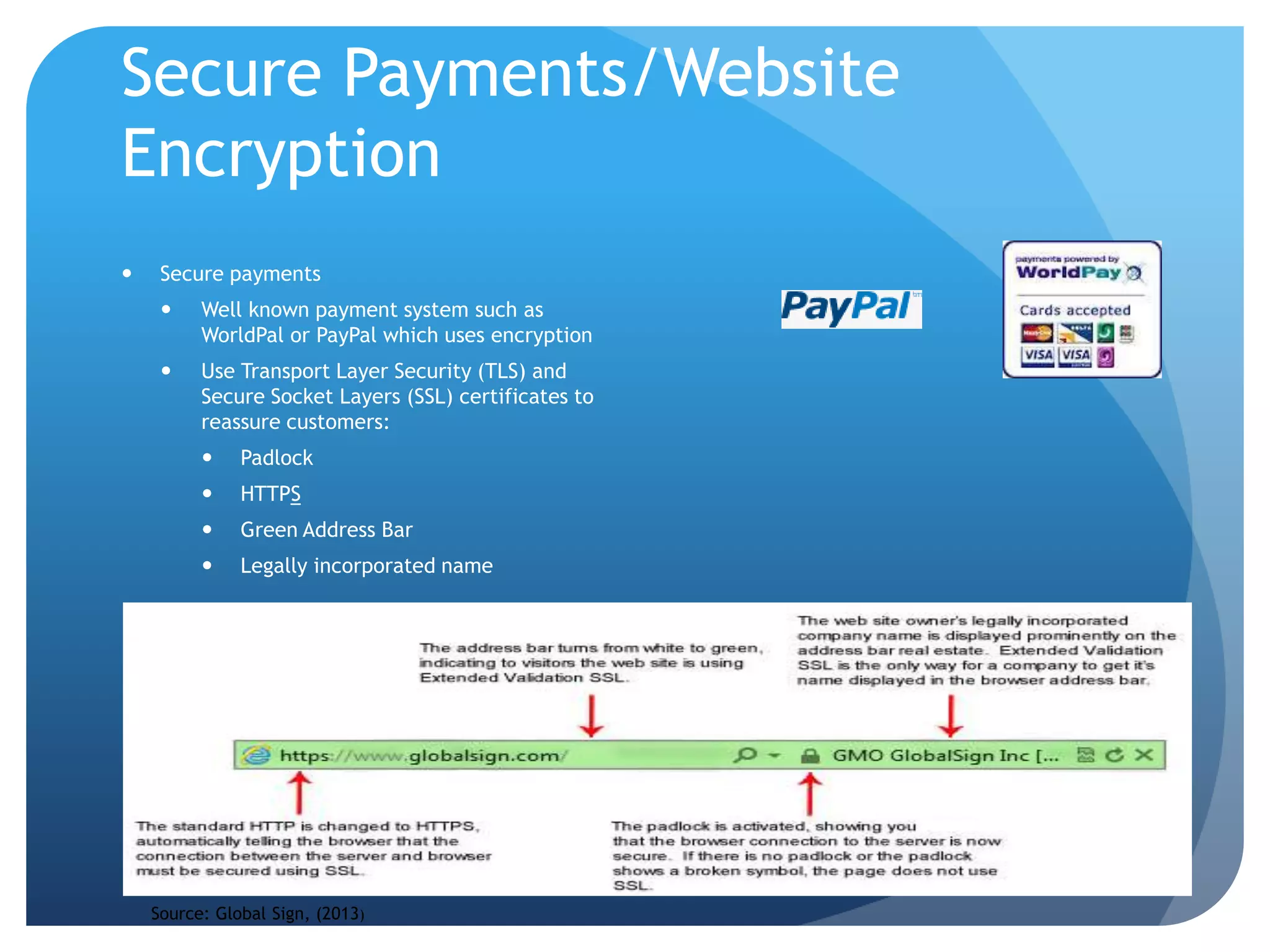
Global Sign, 2013. Security Certificates. [Online]. Available at:
https://www.globalsign.co.uk/ssl/domain-ssl/ [accessed 18 March 2013]
Halliday, J., 2012. The Guardian reaches nearly 9 million readers across print and online.
[online]. Available at: http://www.guardian.co.uk/media/2012/sep/12/guardian-9-
million-readers-nrs [accessed 10 March 2013]
Information Commissioner’s Office, 2013. Data Protection Act Claiming Compensation.
[online] available at:
http://www.ico.gov.uk/upload/documents/library/data_protection/practical_application/c
laiming_compensation.pdf [accessed 12 March 2013]
Information Commissioner’s Office, 2013. Electronic Mail (Regulations 22 and 23). [online]
available at:
http://www.ico.gov.uk/for_organisations/privacy_and_electronic_communications/the_gui
de/electronic_mail.aspx [accessed 10 March 2013]
Information Commissioner’s Office, 2013. Privacy and Electronic Communications
Regulations. [online] available
at:http://www.ico.gov.uk/for_organisations/privacy_and_electronic_communications.aspx
[accessed 3 March 2013]
Information Commissioner’s Office, 2013. Sensitive details of NHS staff
published by Trust in Devon. [online] available at:
http://www.ico.gov.uk/news/latest_news/2012/sensitive-details-of-nhs-staff-
published-by-devon-trust-06082012.aspx
Information Commissioner’s Office, 2013. Viral Marketing. [online] available at:
http://www.ico.gov.uk/for_organisations/privacy_and_electronic_communications/the_gui
de/viral_marketing.aspx [accessed 3 March 2013]
Oremus, W., 2013. Unprotected Sects. [online] Available at:
http://www.slate.com/articles/technology/technology/2012/05/malware_and_computer_vi
ruses_they_ve_left_porn_sites_for_religious_sites_.html [accessed 12 March 2013]
Norton, 2013. Phishing [online]. Available at:
http://uk.norton.com/security_response/phishing.jsp [accessed 10 March 2013]
Paypal, 2013. Security. [online]. Available at:
https://www.paypal.com/uk/webapps/mpp/paypal-safety-and-security [accessed 10 March
2013]
Perlroth, N, 2012. Six big banks targeted in online attacks. [online. Available at:
http://www.bostonglobe.com/business/2012/09/30/banks-hits-wave-computer-attacks-
group-claiming-middle-east-ties/gsE6W3V57nBAYrko1ag8rN/story.html [accessed 10 March
2013]
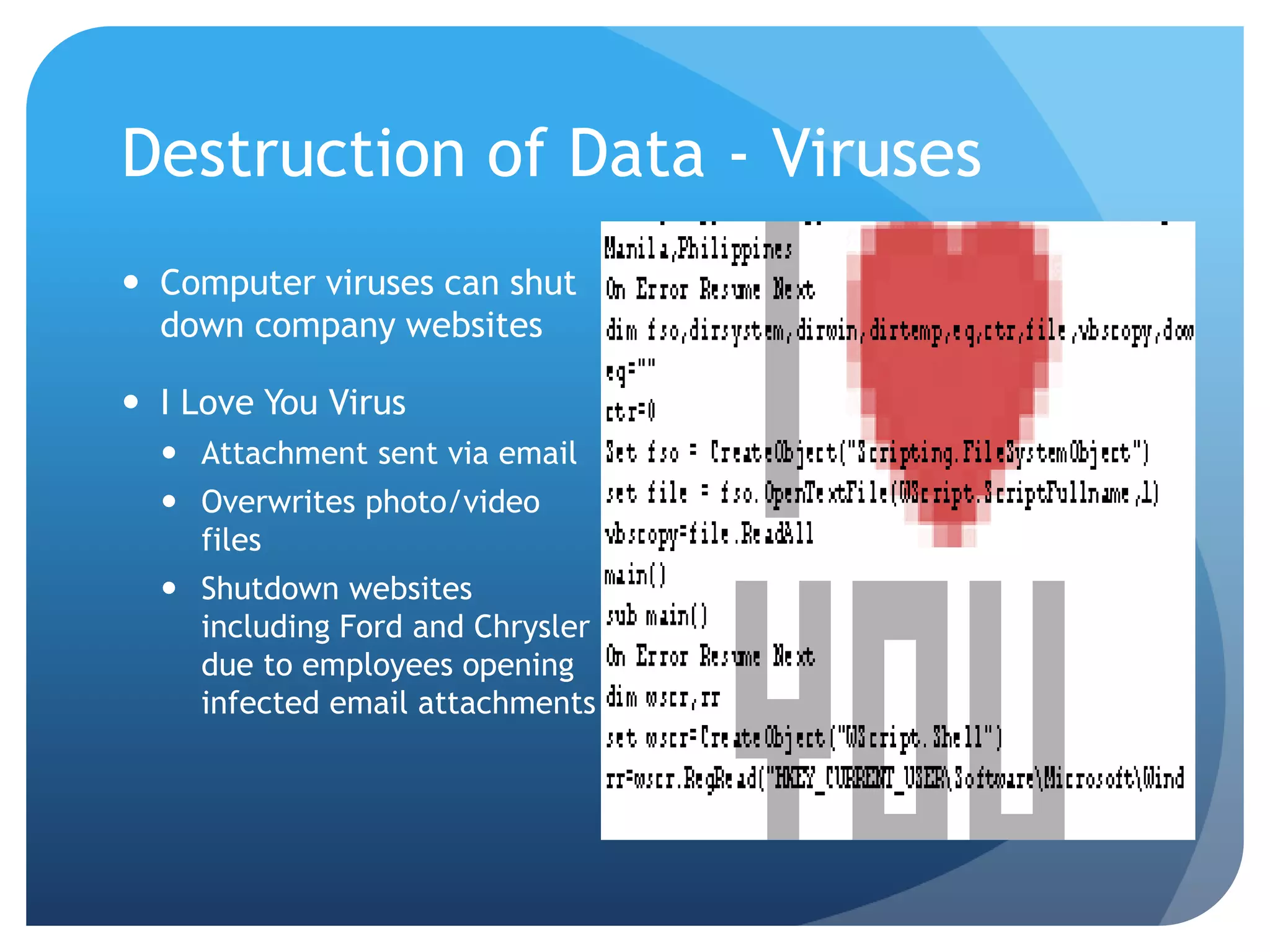
Seltzer, L, 2010. ‘I Love You’ virus turns ten: what have we learned? [online]. Available
at: http://www.pcmag.com/article2/0,2817,2363172,00.asp [accessed 28 February 2013]
Symantec, (2012). Internet Security Threat Report 2011{online]. Available at:
http://www.symantec.com/content/en/us/enterprise/other_resources/b-
istr_main_report_2011_21239364.en-us.pdf [ accessed 12 March 2013]
Teixera, R, 2007. Top five small business internet security threats. [online]. Available at:
http://smallbiztrends.com/2007/06/top-five-small-business-internet-security-threats.html
[accessed 3 March 2013].
Watson Hall, 2013. Top 10 Website Security Issues. [online]. Available at:
https://www.watsonhall.com/resources/downloads/top10-website-security-issues.pdf
[accessed 28 February 2013]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalmarketingfinal-151111124851-lva1-app6891/75/Digital-marketing-presentation-security-risks-for-websites-28-2048.jpg)