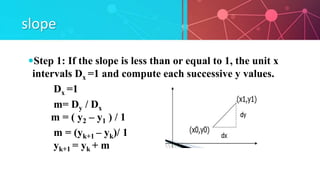
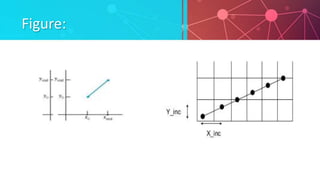
This presentation introduces the Digital Differential Analyzer (DDA) algorithm for line generation in computer graphics. It discusses the algorithm, which calculates either the change in x or y at unit intervals to determine the integer coordinates of the line. The algorithm is simple to implement but uses floating point operations, which can be expensive. It is best for lines with slopes less than or equal to 1 and is limited to the first quadrant. The presentation covers the algorithm steps, advantages of being simple and fast, disadvantages of using floating points, and applications in computer graphics.