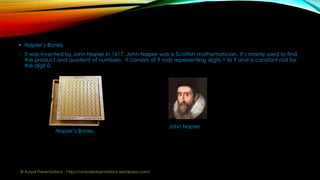
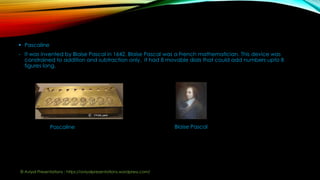
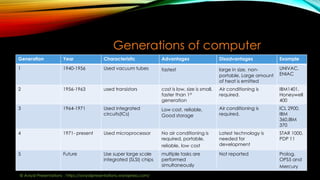
The document provides an overview of computers, including definitions, historical evolution, and key components such as hardware and software. It discusses major inventions that preceded modern computers, highlights the four main functions of computers (input, processing, storage, and output), and categorizes different types of computers and their generations. Additionally, it outlines the advantages and disadvantages of using computers in various applications.