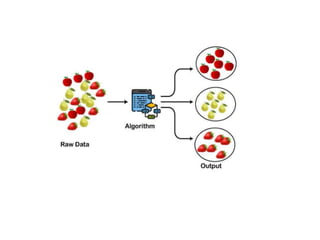
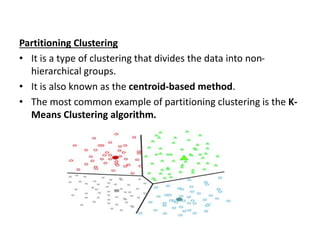
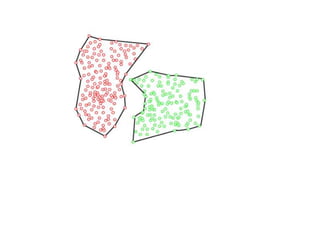
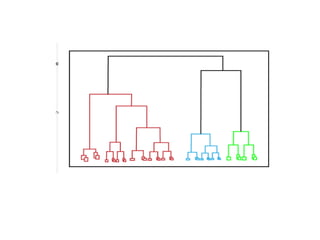
Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) is a dimensionality reduction and classification technique commonly used in machine learning. It projects high-dimensional data onto a lower dimensional space to maximize class separability so that classes are easily distinguishable. LDA is widely applied for tasks like face detection, disease classification, and product recommendation. It is useful for classification problems with labeled data and aims to capture the most important information in the data to effectively separate classes.