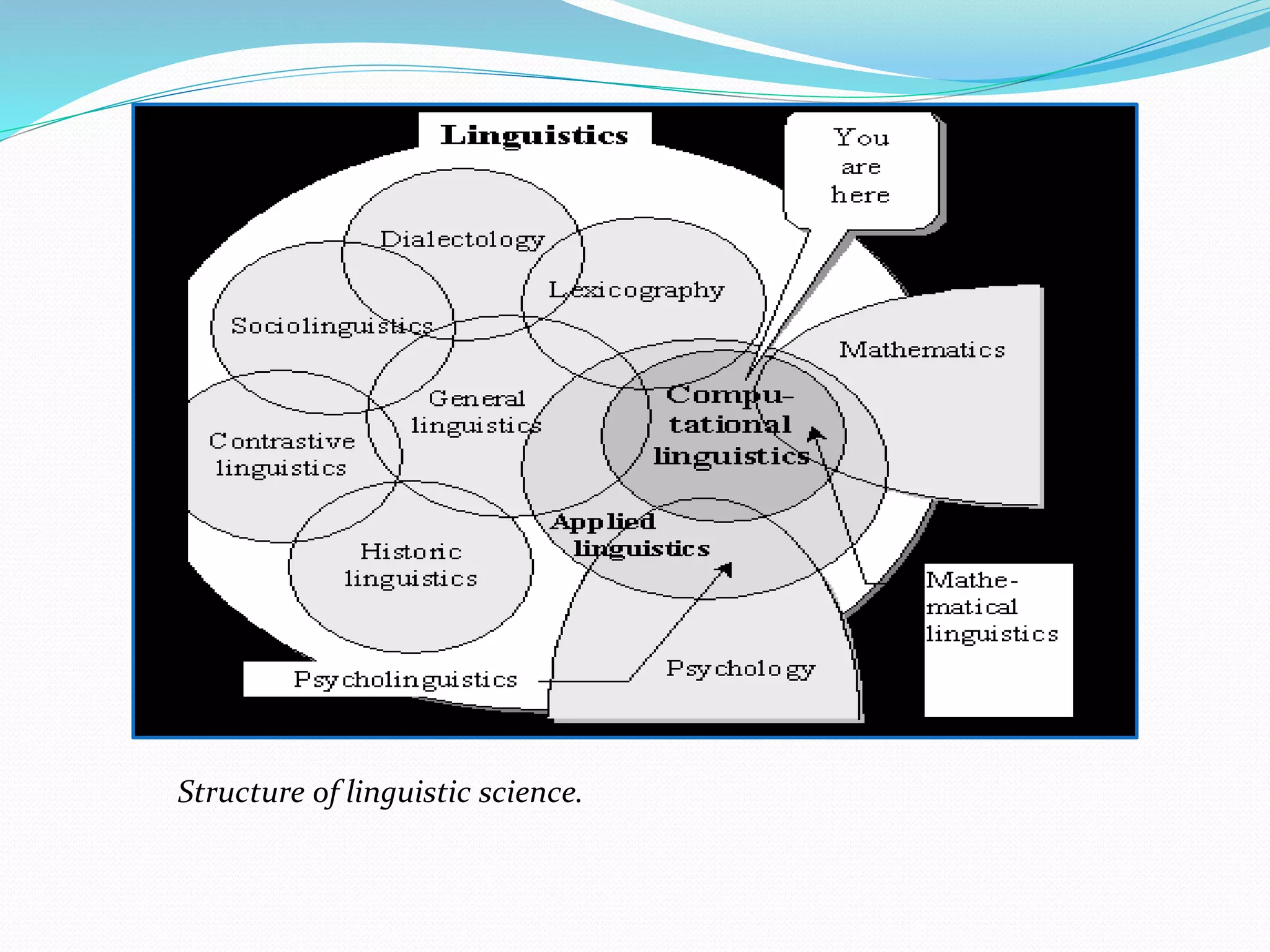
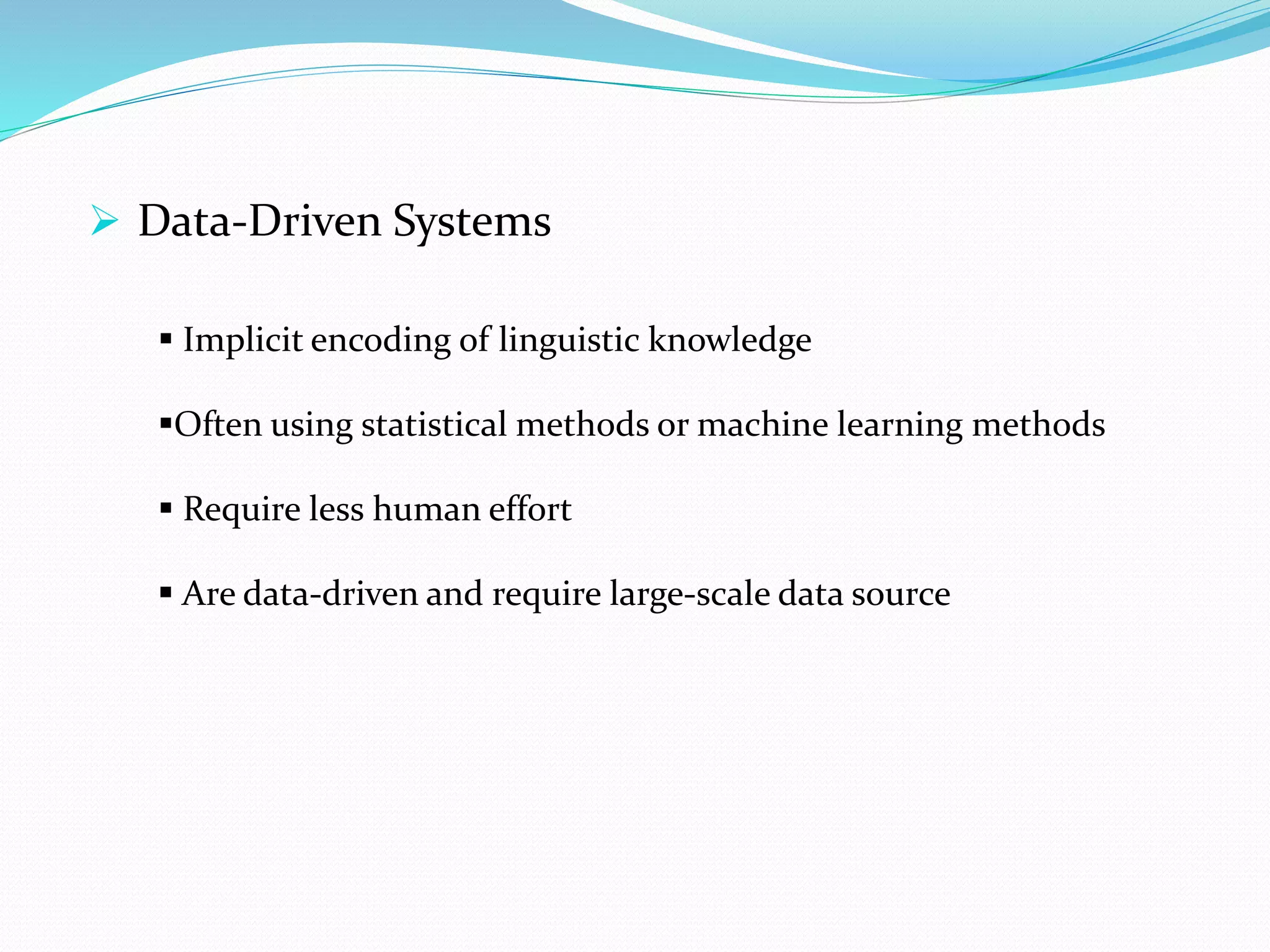
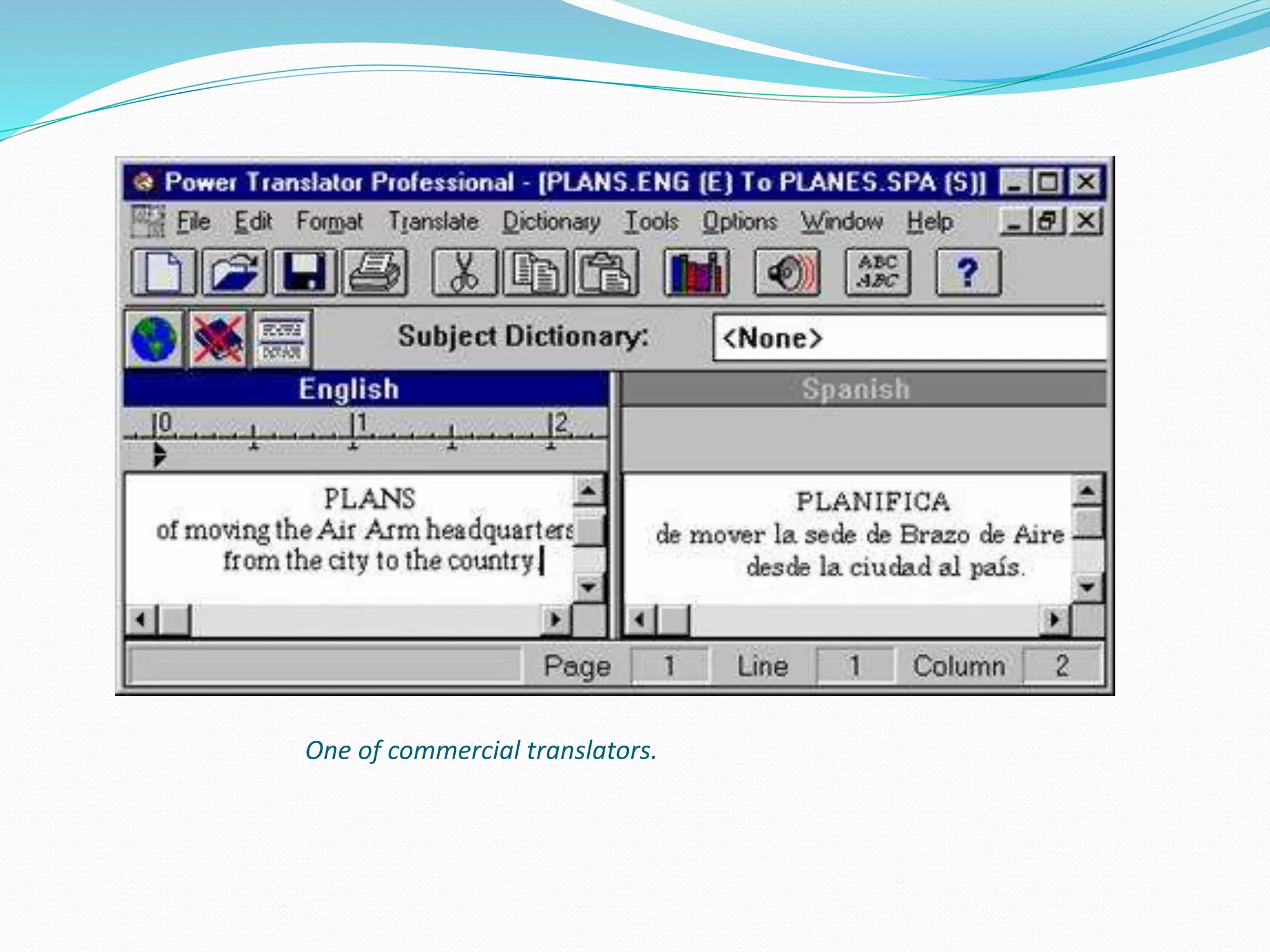
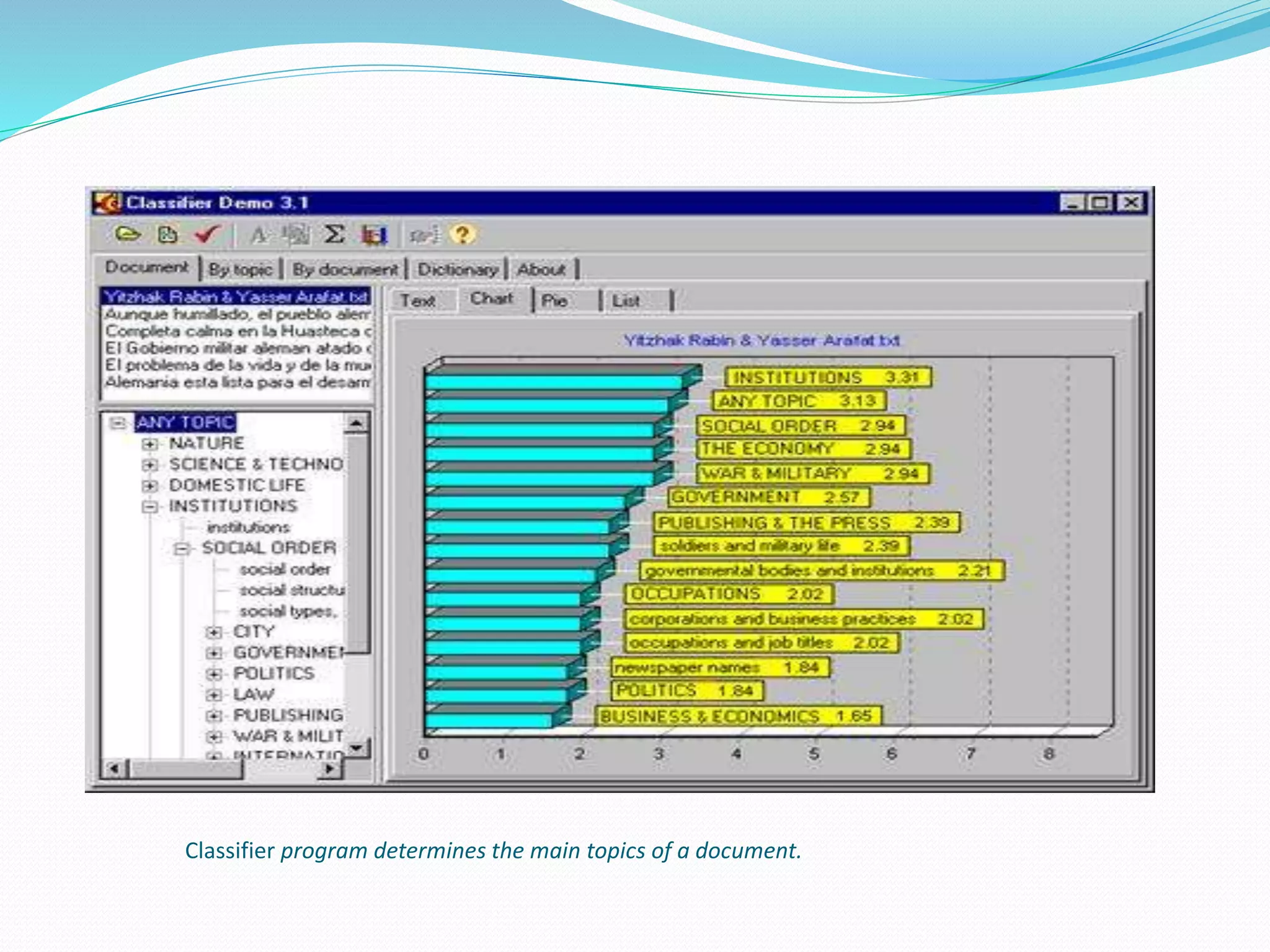
Computational linguistics is defined as the scientific study and engineering of language from a computational perspective. It originated in the 1950s with the goal of using computers to automatically translate texts between languages. There are two main approaches: rule-based systems which explicitly encode linguistic rules and data-driven systems which use statistical and machine learning methods on large datasets. Computational linguistics is applied in many areas including machine translation, speech recognition, natural language interfaces, and information extraction from text documents.