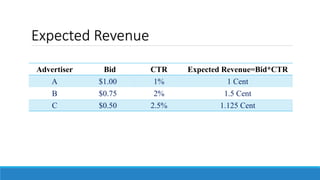
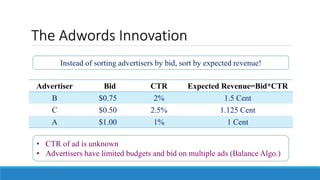
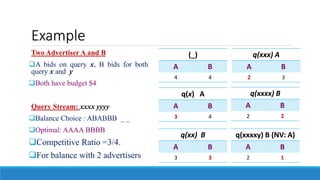
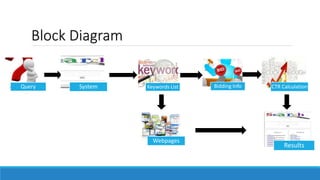
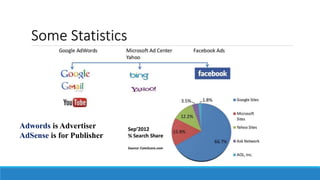
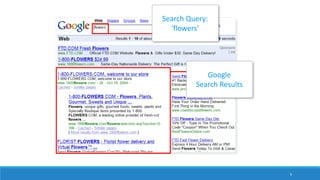
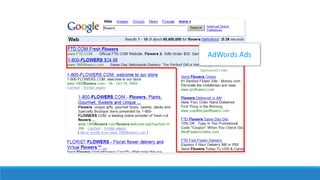
This document discusses online advertisement and the AdWords problem. It begins by describing traditional advertising like posters, magazines and billboards that charge per impression, then describes how online ads use targeting and metrics like clicks. It explains that AdWords is Google's advertising system where advertisers bid on keywords and the highest bidder's ad appears. The document defines the AdWords problem and algorithms like greedy and balance that aim to maximize revenue by sorting ads by expected revenue rather than bid. It provides an example showing the balance algorithm can achieve a better competitive ratio than greedy. Finally, it mentions implementing this on an open advertising dataset.






![Understanding Adwords Technicalities
Keywords:
Ads are continuously matched to internet users interest based on your keywords
Use keywords match types to your advantage
Broad Match
Phrase Match
Exact Match
Negative Keywords
URL:
Two types of URL are used in an Adwords namely
Display URL
Actual URL
Broad Match
Keywords: buy flowers
Queries:
• buy flowers
• buy red flowers
• flowers buy
• New York buy flowers
Phrase Match
Keywords: “buy flowers”
Queries:
Where can I buy flowers
buy flowers in New Delhi
buy red flowers (extra word)
flowers buy (the words are
reversed)
Exact Match
Keywords: [buy flowers]
Queries:
buy flowers
Buy flowers (Capitalization
doesn’t matter)
Negative Match
Keywords: -cheap
Queries:
buy cheap flowers
cheap flowers in New York](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computationaladvertisingandtheadwordsproblem-141226065314-conversion-gate01/85/Online-Advertisements-and-the-AdWords-Problem-11-320.jpg)