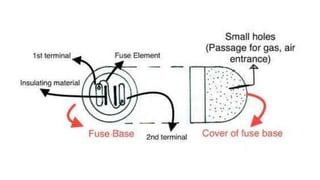
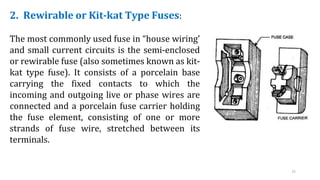
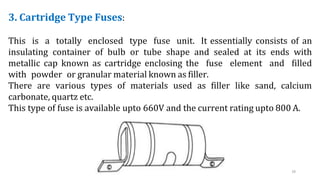
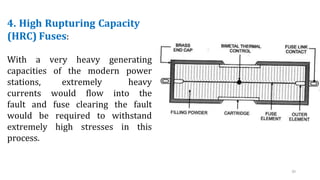
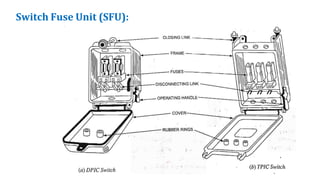
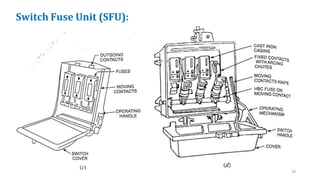
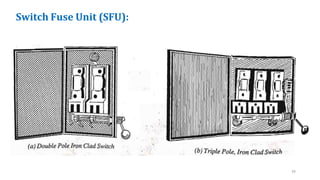
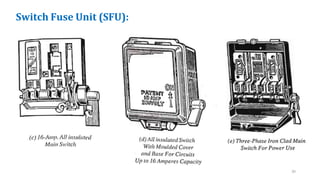
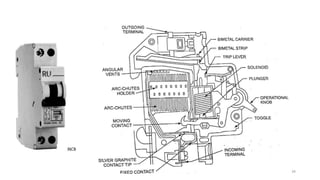
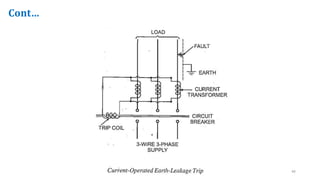
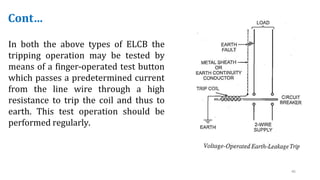
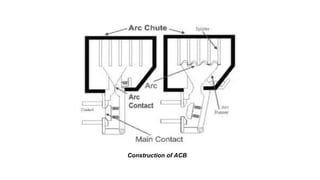
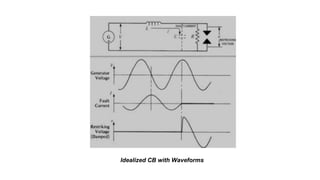
The document discusses various components of low voltage switchgear used in electrical installations, including:
- Switch fuse units, miniature circuit breakers, earth leakage circuit breakers, molded case circuit breakers, and air circuit breakers.
- It describes the working and construction of fuses, MCBs, MCCBs, ELCBs, and air circuit breakers.
- The key components and operating mechanisms that provide overload and short circuit protection in low voltage electrical distribution systems are explained.