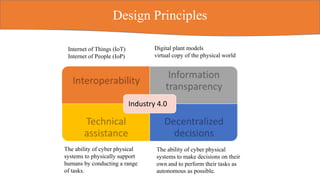
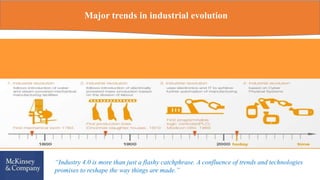
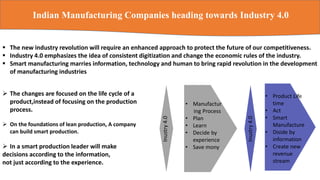
The document discusses Industry 4.0, emphasizing the integration of intelligent products and cyber-physical systems to transform traditional manufacturing into smart factories. It highlights the current challenges and opportunities in Indian manufacturing, including the need for digitization, overcoming infrastructure issues, and embracing new technologies. The conclusion stresses the importance of developing comprehensive digital ecosystems to enhance product and service offerings in the evolving industrial landscape.








![References
[1] K. Linsu, “Stages of development of industrial technology in a developing country: A model,”
Res. Policy, 2002.
[2] M. Blanchet, T. Rinn, G. Von tharden, and G. De Thieulloy, “Industry 4.0 The new industrial
revolution how europe will succeed,” Think Act, 2014.
[3] H. Kagermann, W. Wahlster, and J. Helbig, “Recommendations for implementing the
strategic initiative INDUSTRIE 4.0,” 2013.
[4] M. Hermann, T. Pentek, and B. Otto, “Design Principles for Industrie 4.0 Scenarios: A
Literature Review,” 2015.
[5] H. Lasi, P. Fettke, and T. Feld, “Industry 4.0,” Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng., vol. 4, pp. 239–242,
2014.Plattform Industrie 4.0, “Industrie 4.0 - Whitepaper FuE Themen,” 2013. [Online].
Available: http://www.plattformi40.de/sites/default/files/Whitepaper_Forschung Stand 3. April
2014_0.pdf.
[6] P. Adolphs, H. Bedenbender, and D. Dirzus, “Reference Architecture Model Industrie 4.0
(RAMI4.0),” 2015.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hu501pptgroup-191106162356/85/INDUSTRY-4-0-Economics-for-Engineers-12-320.jpg)