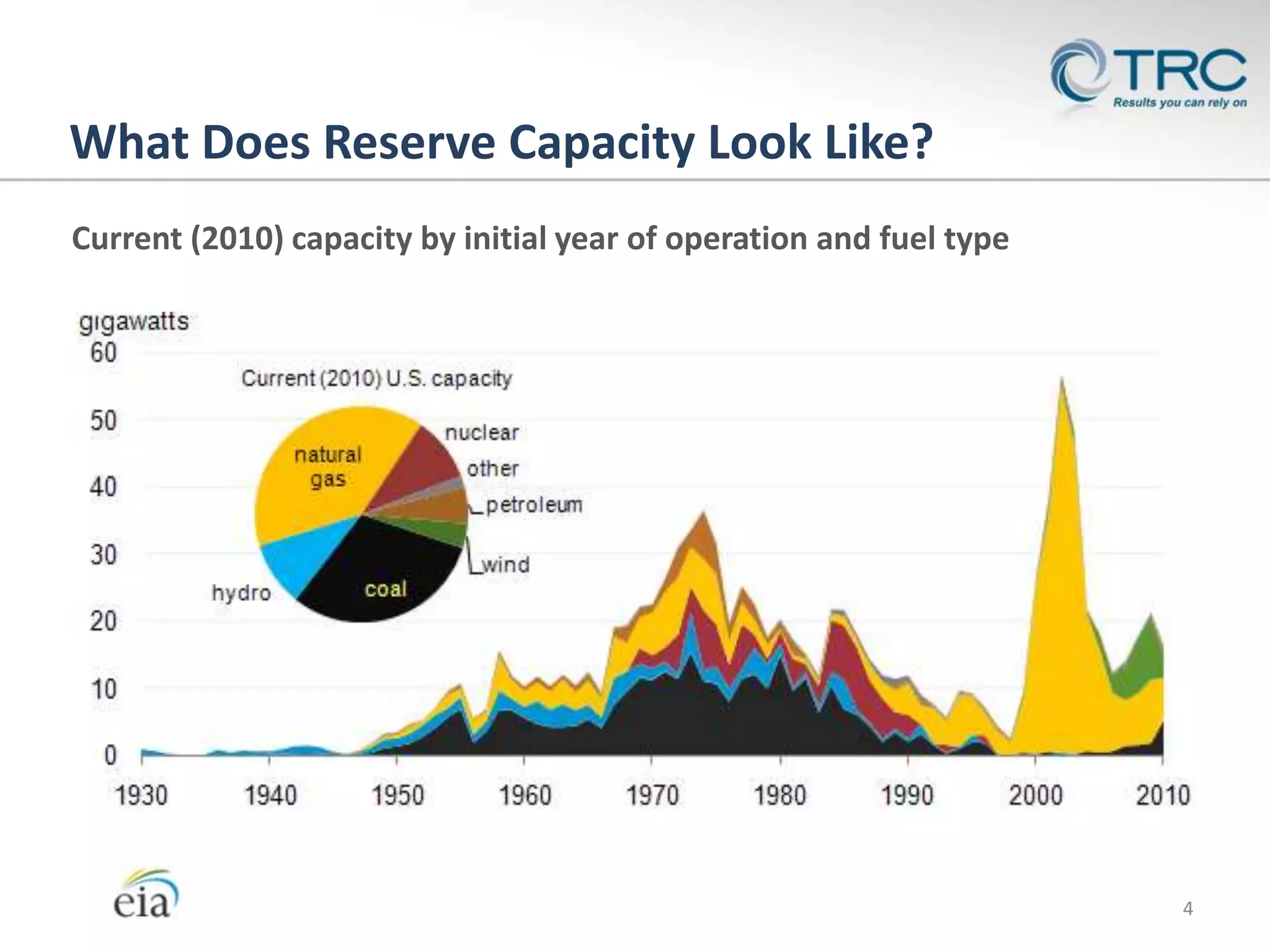
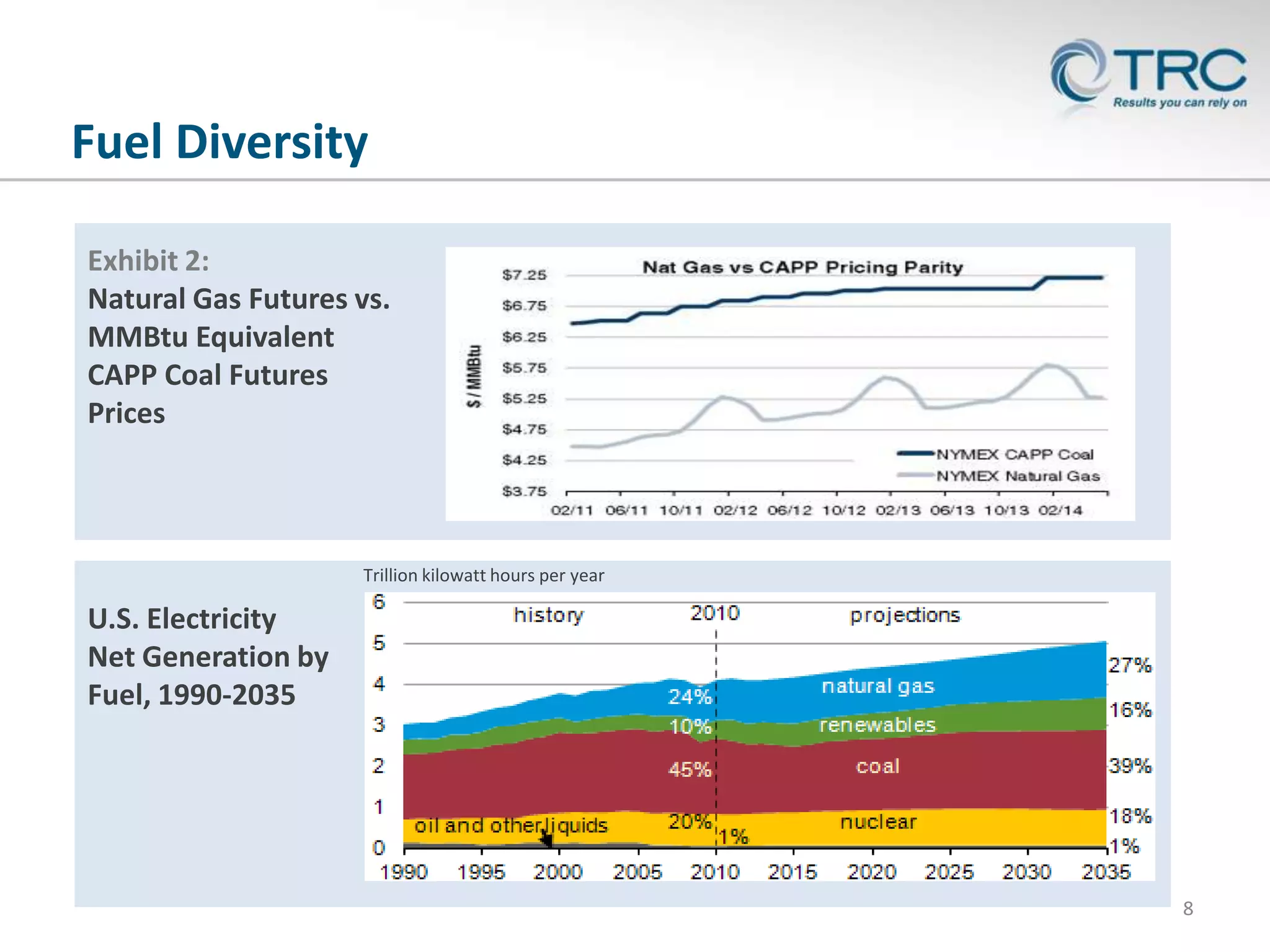
The document discusses the changing dynamics of the U.S. power generation sector regarding compliance with the Clean Air Act, emphasizing the transition from coal to gas turbine plants due to economic and regulatory factors. It outlines projected retirements, retrofitting, and replacement estimates for coal plants, with significant capital expenditure forecasts. The content highlights the importance of optimizing costs, maintaining compliance, and the implications of decommissioning on future energy infrastructure.