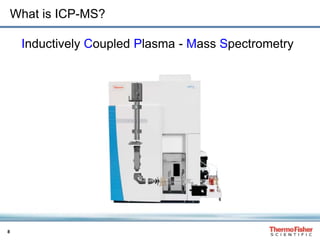
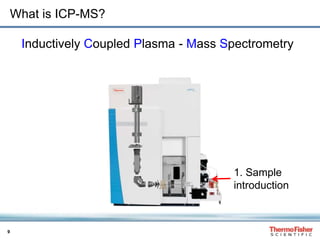
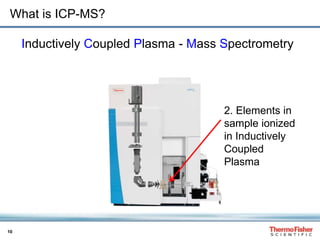
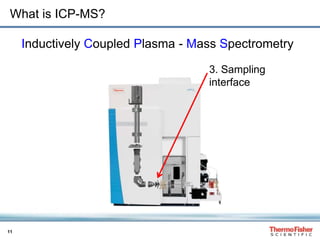
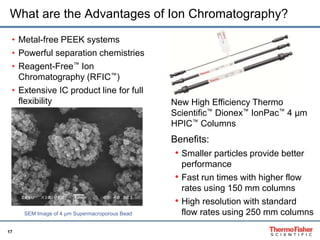
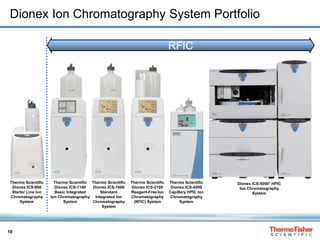
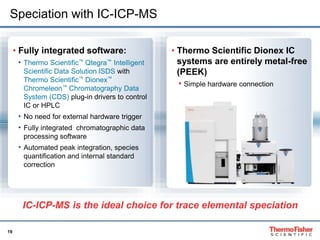
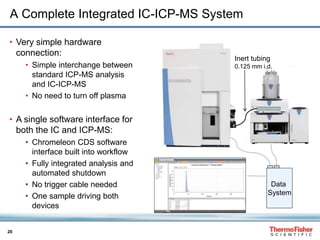
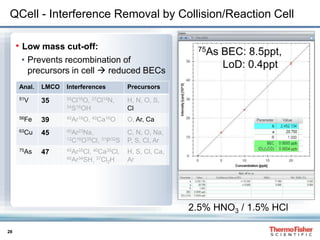
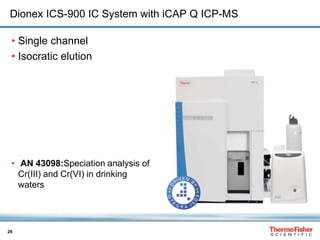
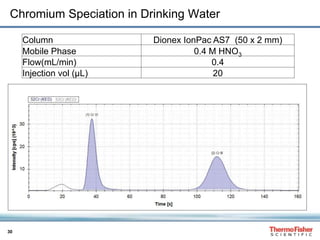
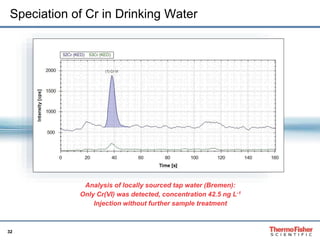
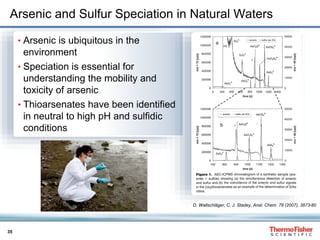
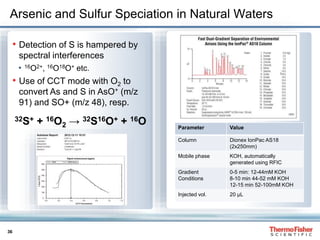
This document discusses speciation analysis using ion chromatography coupled with inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (IC-ICP-MS). It provides an overview of the technique, including separation of species using ion chromatography, detection of elements using ICP-MS, and integration of the two systems. Examples are given of speciation analysis of chromium, arsenic, and sulfur to determine different chemical forms in environmental and drinking water samples. The technique allows sensitive detection of multiple elements and their species simultaneously for applications such as monitoring regulatory compliance and studying environmental processes.
![4
Metals in the Environment and Speciation
HO-As-OH
|
OH
O
||
H3C-As-CH3
|
OH
Environmental Fate
Mobility Toxicity
Bioavailability
Reactivity
[Cr(H2O)6]3+
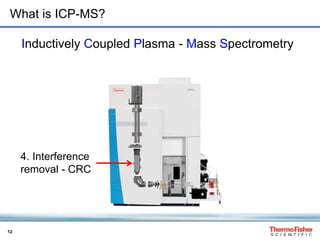
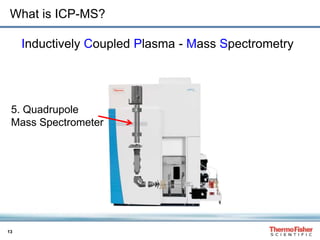
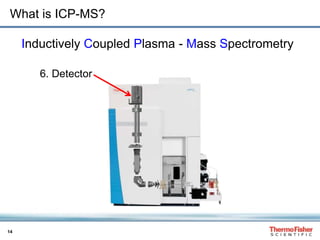
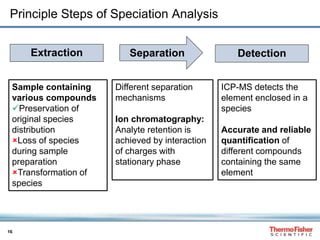
H3C-Hg+
Hg0
Cr2O7
2-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/piproc-ws71159e0614scompleteinorganicelementalspeciationsolutionsforenvironmentalapplications-31101-140819125407-phpapp02/85/Chromatography-Complete-Inorganic-Elemental-Speciation-Analysis-Solutions-for-Environmental-Applications-4-320.jpg)


![25
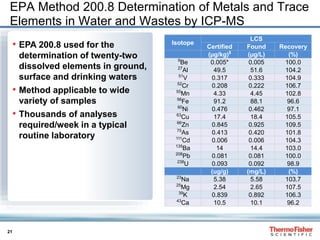
Considerations for HPLC-ICP-MS Parameters
• The determination of Cr by ICP-MS is complicated by
polyatomic interferences:
• 40Ar12C+ on 52Cr
• 37Cl16O+ on 53Cr
• IC and sample preparation parameters need to be chosen
carefully due to the complex redox chemistry of Cr
Chemical forms of Cr as a function of pH and potential
HCrO4
- CrO4
2-
H2CrO4
[Cr(H2O)6]3+
Cr3+
Cr(OH)3(s) Cr(OH)4
-
Cr(OH)2+
Cr(OH)2
+
Cr(OH)3
°
Cr(VI)
Cr(III)
pH
0,7
964
6,5
Eh
Cr2O7
2-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/piproc-ws71159e0614scompleteinorganicelementalspeciationsolutionsforenvironmentalapplications-31101-140819125407-phpapp02/85/Chromatography-Complete-Inorganic-Elemental-Speciation-Analysis-Solutions-for-Environmental-Applications-25-320.jpg)

![31
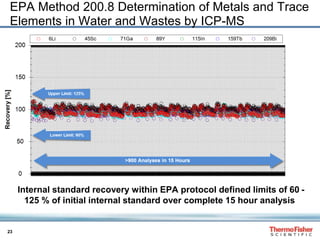
IC-ICP-MS for the Speciation of Cr(III) and Cr(VI)
• Both chromium isotopes, 52, 53Cr,
can be monitored
• Cr(III) and Cr(VI) are completely
baseline separated
• Limits of detection:
• 0.20 ng L-1 [Cr(VI)]
• 0.38 ng L-1 [Cr(III)]
• Isocratic chromatography
performed in less than 3 minutes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/piproc-ws71159e0614scompleteinorganicelementalspeciationsolutionsforenvironmentalapplications-31101-140819125407-phpapp02/85/Chromatography-Complete-Inorganic-Elemental-Speciation-Analysis-Solutions-for-Environmental-Applications-31-320.jpg)

![37
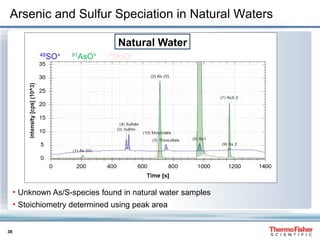
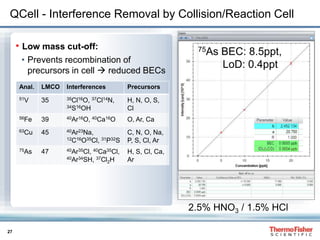
Arsenic and Sulfur Speciation in Natural Waters
• Different As and S containing anions separated and individually detected
• Simultaneously, also metal based species as MoO4
2- can be detected
Instrumental
Performance:
LOD [SO4
2-]:
4.8 ng g-1
BEC: 2.5 ng g-1
LOD [As(III)]:
0.02 ng g-1
BEC: 0.08 ng g-1
48SO+ 91AsO+ 114MoO+
Standards](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/piproc-ws71159e0614scompleteinorganicelementalspeciationsolutionsforenvironmentalapplications-31101-140819125407-phpapp02/85/Chromatography-Complete-Inorganic-Elemental-Speciation-Analysis-Solutions-for-Environmental-Applications-37-320.jpg)