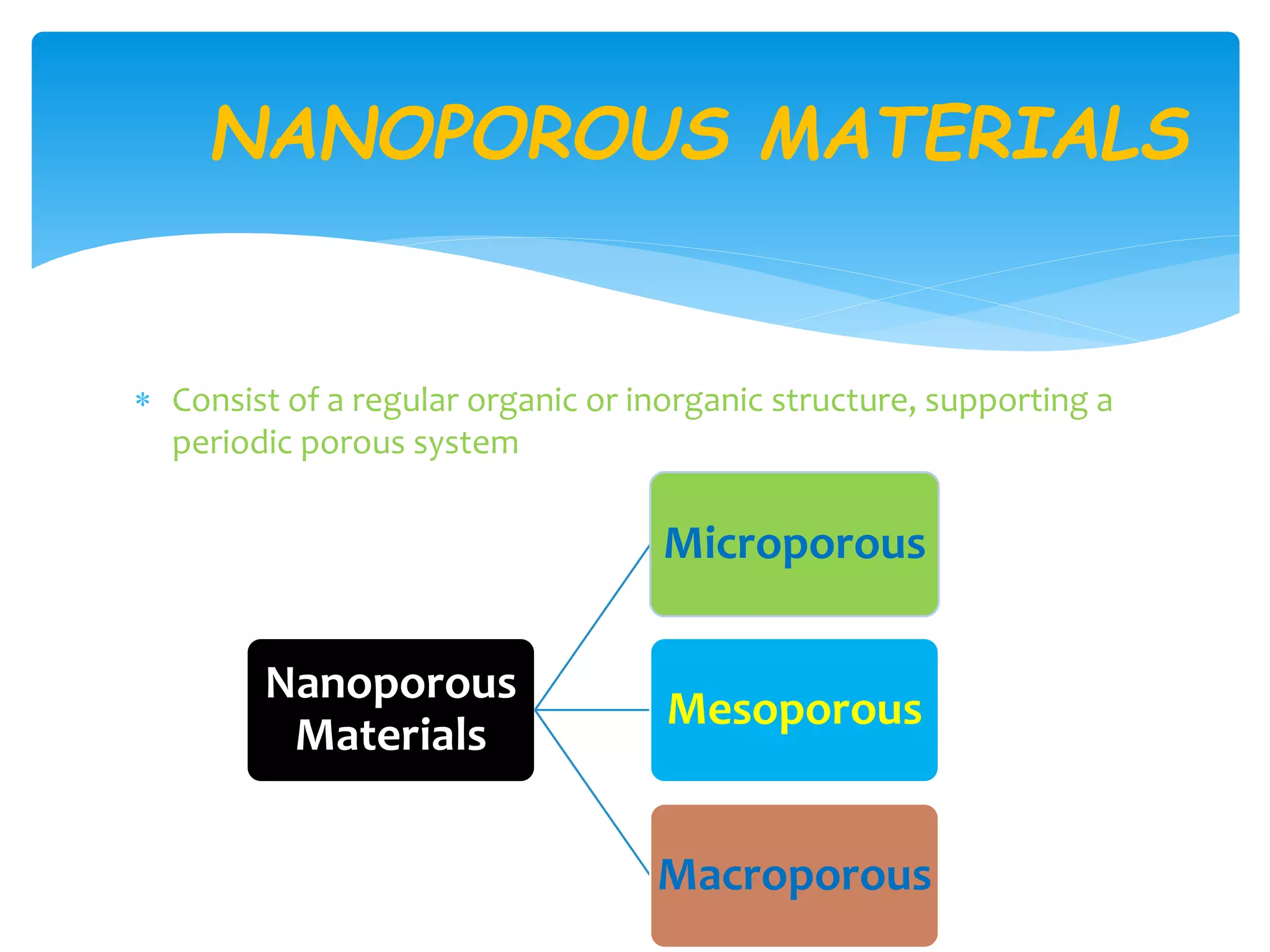
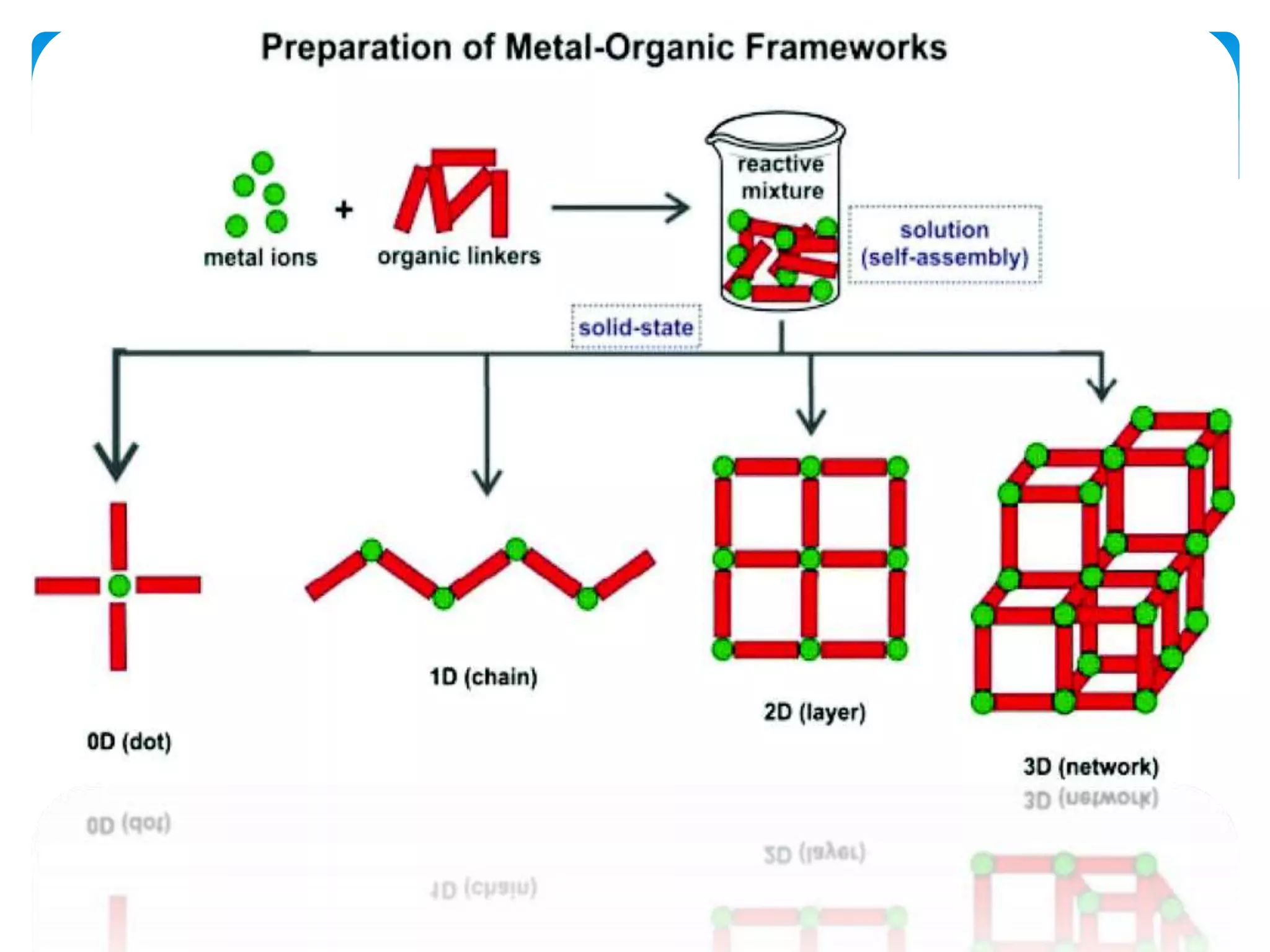
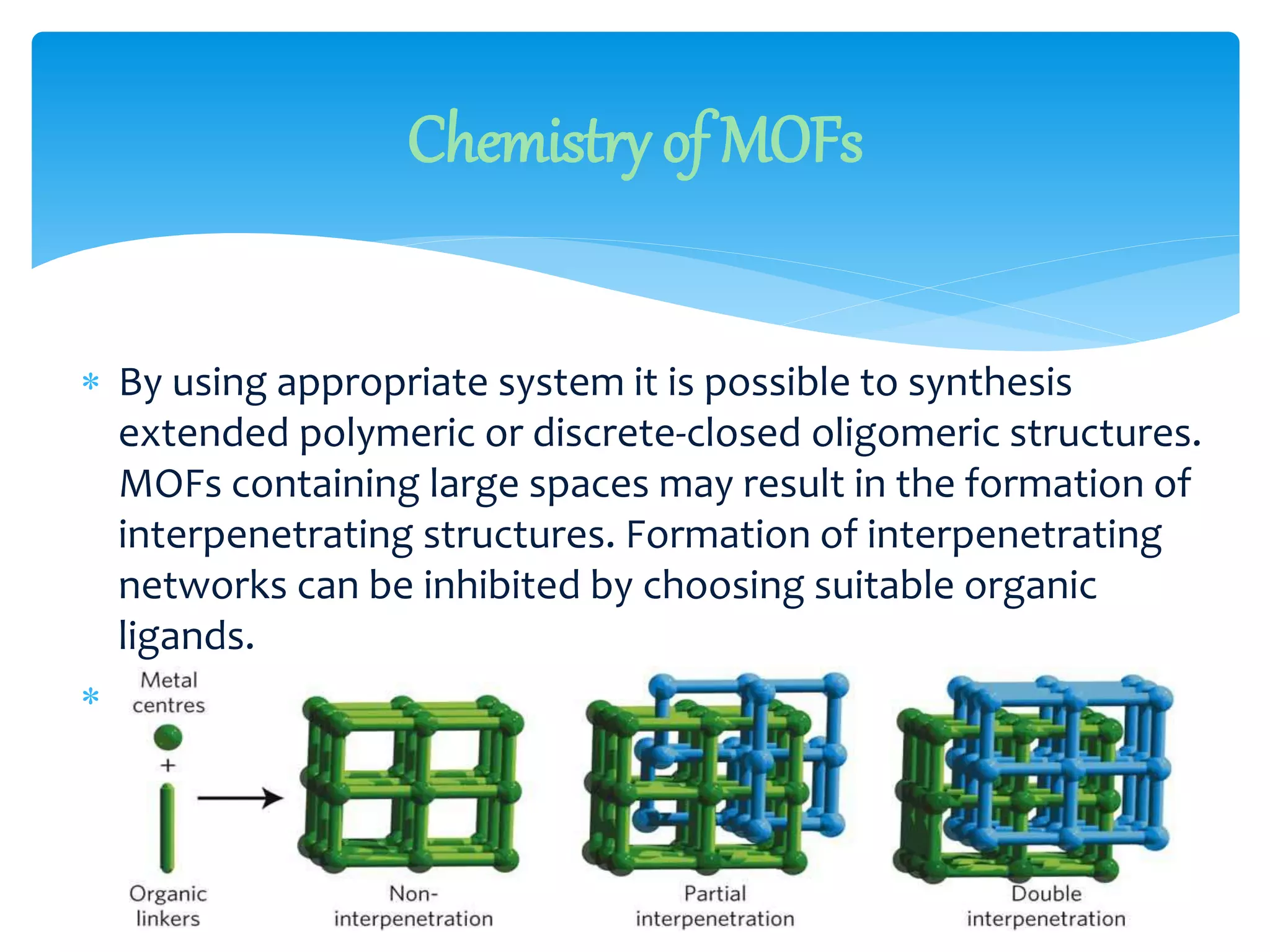
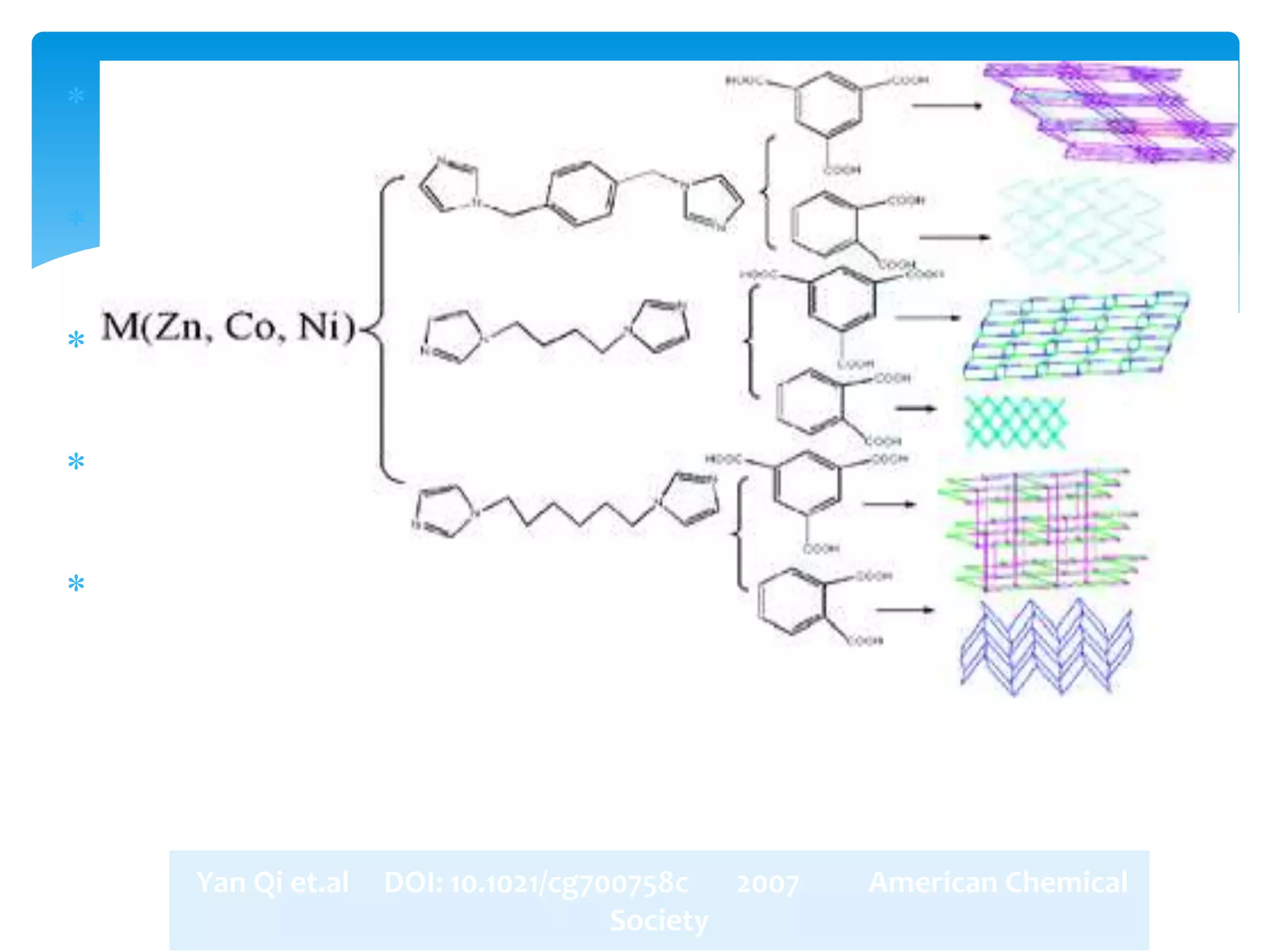
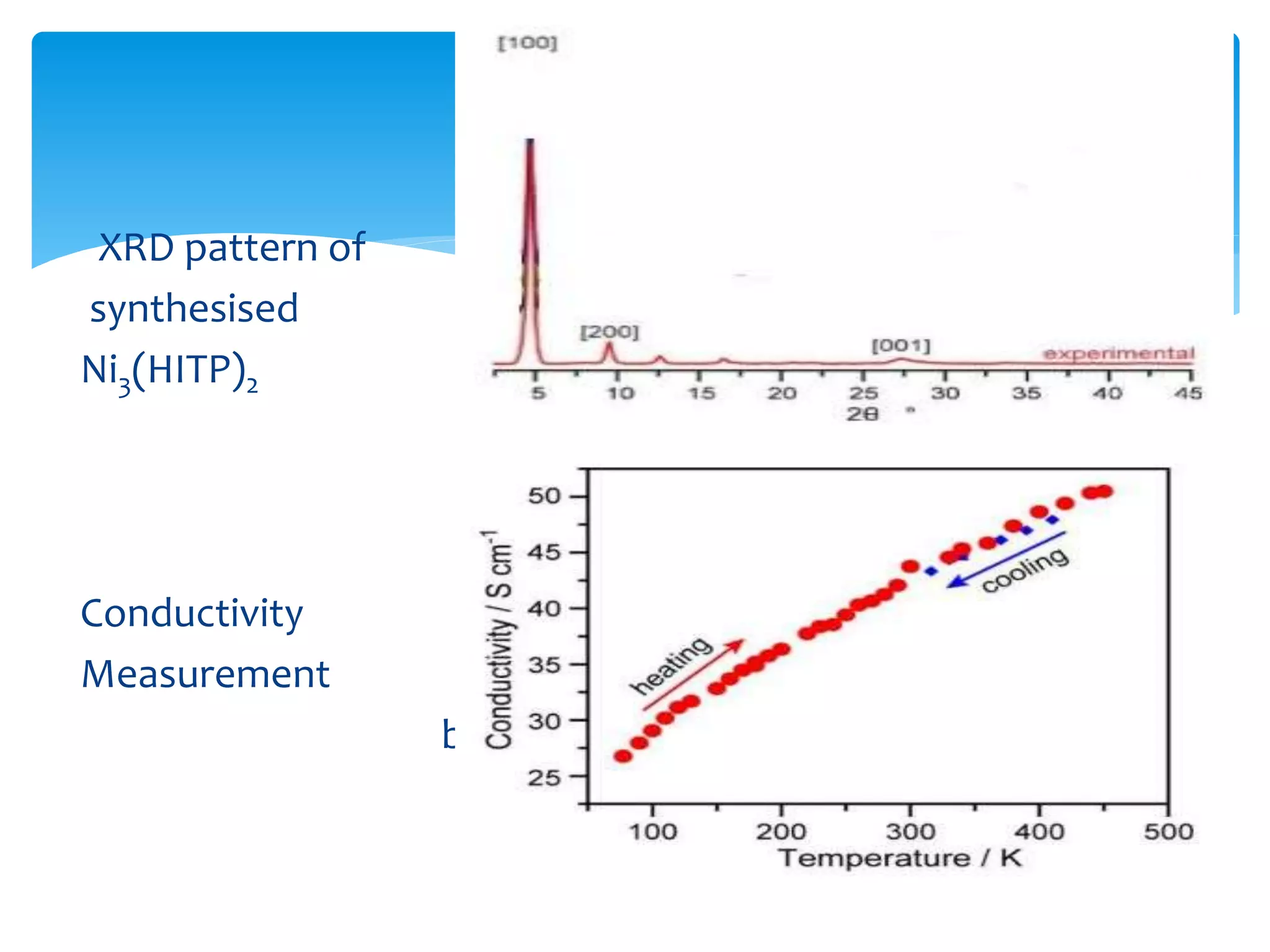
The document discusses metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), a class of materials characterized by their porous structures which consist of metal ions coordinated to organic ligands. It highlights their significant properties, such as tunability, thermal stability, and potential applications in gas storage, catalysis, and energy storage. The synthesis methods and structural features of MOFs are also examined, emphasizing their importance in material science and engineering.