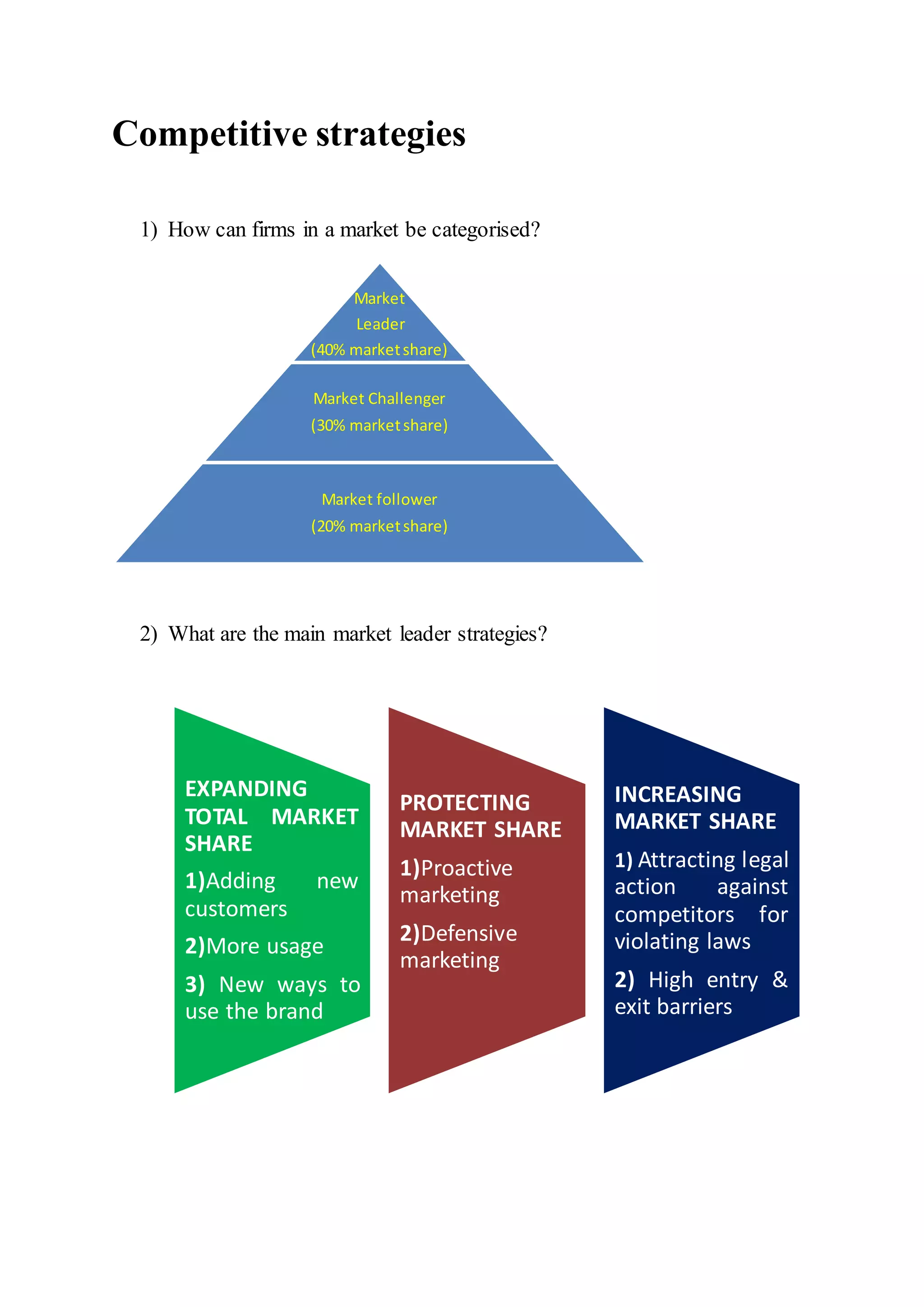
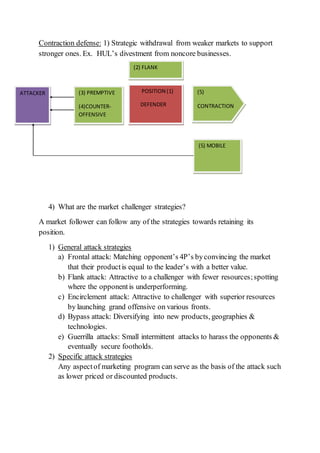
This document outlines different competitive strategies for firms in a market. It categorizes firms as market leaders, challengers, or followers based on their market share. It describes the leader's strategies to expand or protect market share through increasing barriers or legal action against competitors. For protecting share, leaders employ proactive, responsive, anticipative or creative marketing. Challengers aim to increase share through frontal, flank, encirclement, bypass or guerrilla attacks. Followers employ imitation, duplication, emulation or adaptation strategies compared to the market leader.