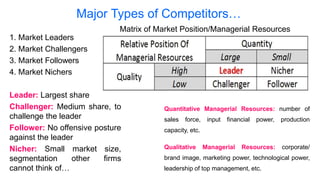
This document discusses strategies for different types of competitors based on Philip Kotler's description of military-style marketing strategies. It describes six competitive positions - dominant, strong, favorable, tenable, weak, and nonviable. It also discusses four major types of competitors - market leaders, challengers, followers, and nichers. The document focuses on strategies for market leaders, including expanding the total market through adding new users, discovering new uses, increasing usage, and increasing frequency of use. It also discusses defending the current market share through position defense, flank defense, preemptive defense, counteroffensive defense, mobile defense, and contraction defense.