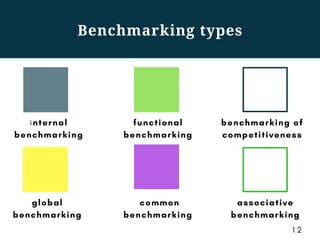
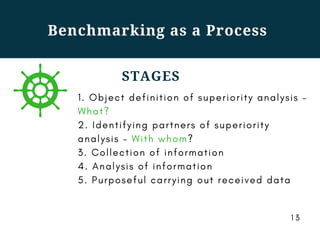
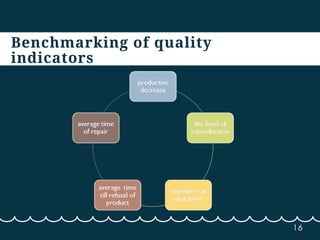
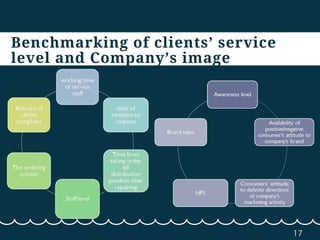
This document discusses competitive intelligence and benchmarking. It describes competitive intelligence as a permanent process of collecting, accumulating, structuring, and analyzing internal and external data about a company to provide high-level management with information. It lists common competitive intelligence tasks like researching competitors, new clients/markets, technologies, and suppliers. Benchmarking is defined as comparing business processes, quality indicators, client service levels, and company image to competitors and leaders in other industries. The document provides examples of benchmarking types and outlines benchmarking as a multi-step process of defining objectives, identifying benchmarking partners, collecting information, analyzing it, and applying learnings.