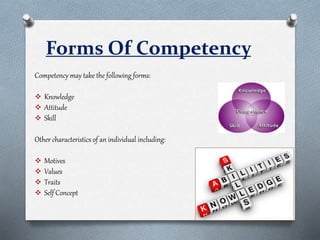
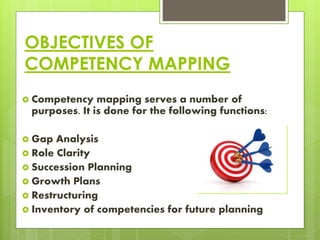
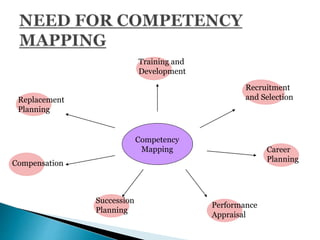
Competencies refer to a cluster of knowledge, skills, and attributes that affect a major part of one's job. Competency mapping is the process of identifying these key competencies for a particular position and using them for tasks like recruitment, training, and development. It involves determining an individual or organization's strengths through assessments. Competency mapping has several objectives like gap analysis, role clarity, succession planning, and growth strategies. There are various tools that can be used to develop competencies, such as literature reviews, focus groups, structured interviews, surveys, and observations.