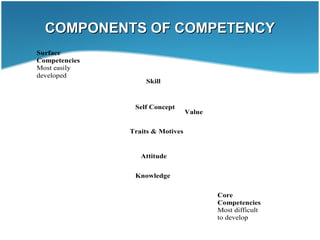
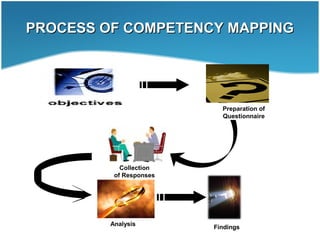
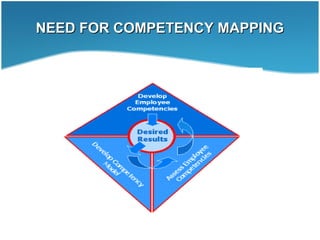
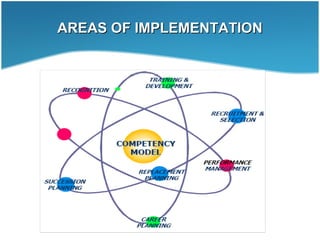
This document discusses competency mapping. It defines competency as an underlying characteristic that enables superior job performance. Competency mapping is the process of assessing individual strengths and how they align with competencies needed for roles. It involves identifying competencies, collecting employee responses on competencies, and analyzing gaps between individual and role competencies. Competency mapping is used for recruitment, training, career planning, performance management, and rewards to improve employee and organizational performance.