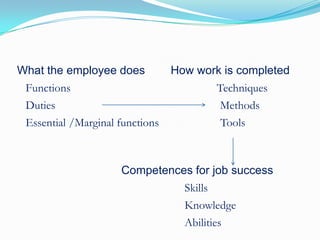
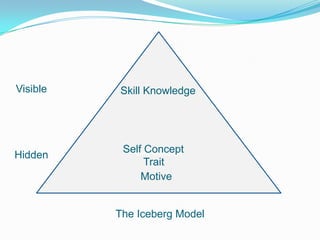
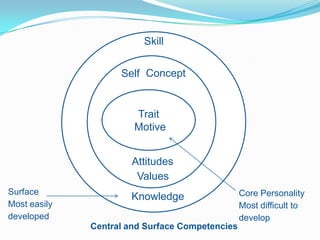
This document discusses competency-based selection systems and competency models. It defines competencies as skills, knowledge, abilities and behaviors that distinguish high performers and relate to effective job performance. The document outlines different approaches to developing competency models, including identifying core competencies required for roles aligned with business strategy. It also discusses how competency models can be used to improve human resource management systems like training, performance evaluation, and succession planning.