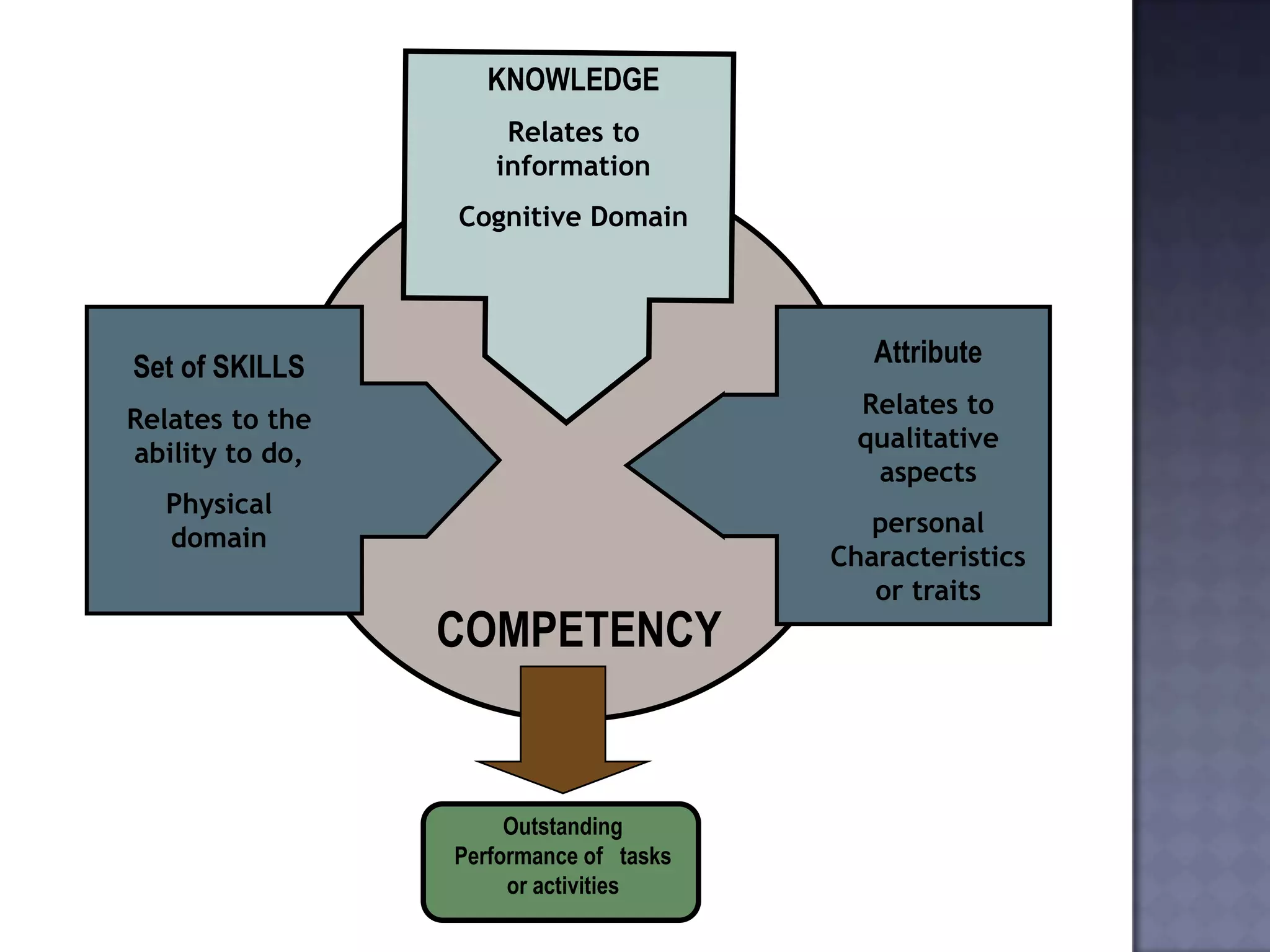
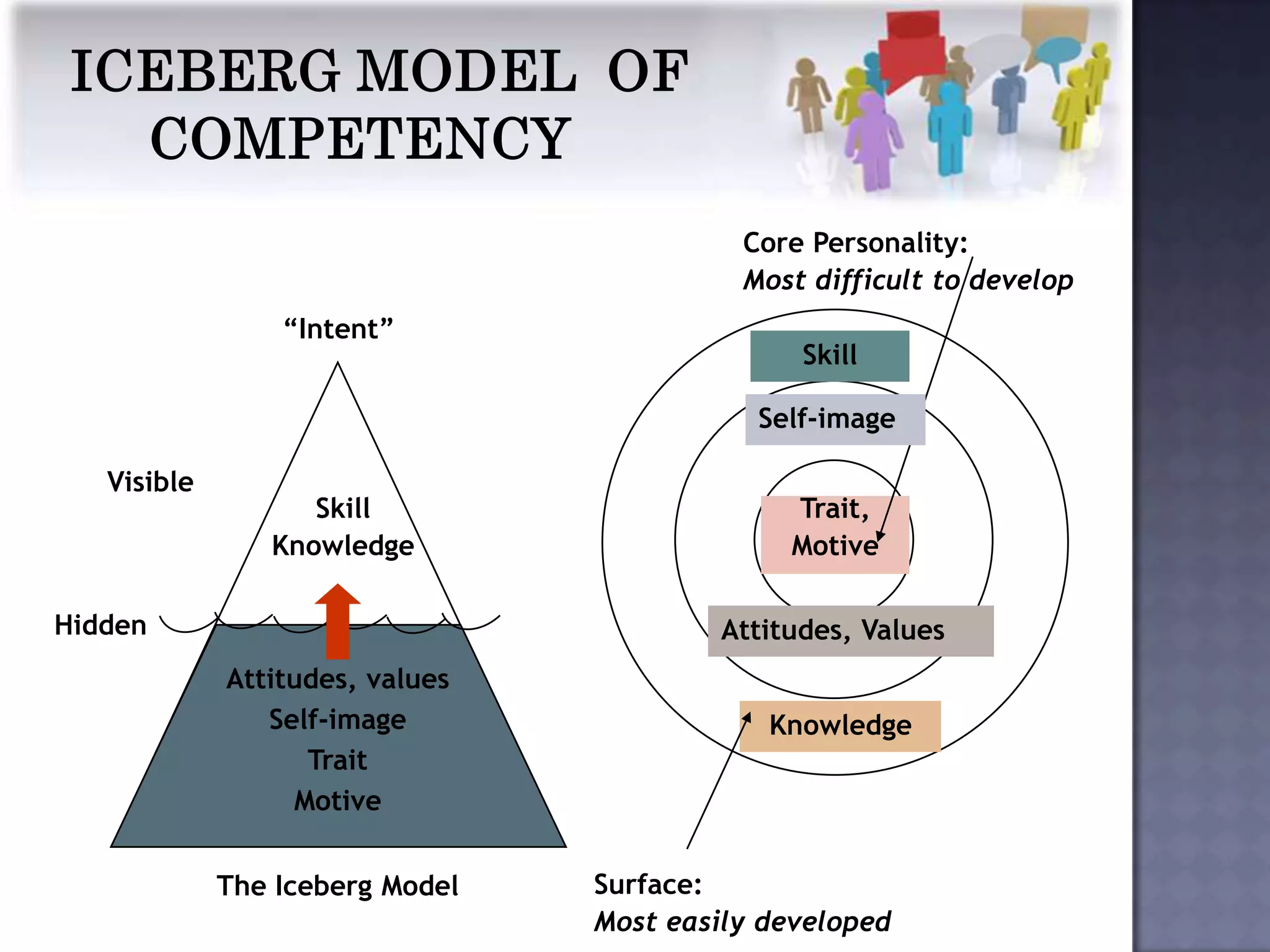
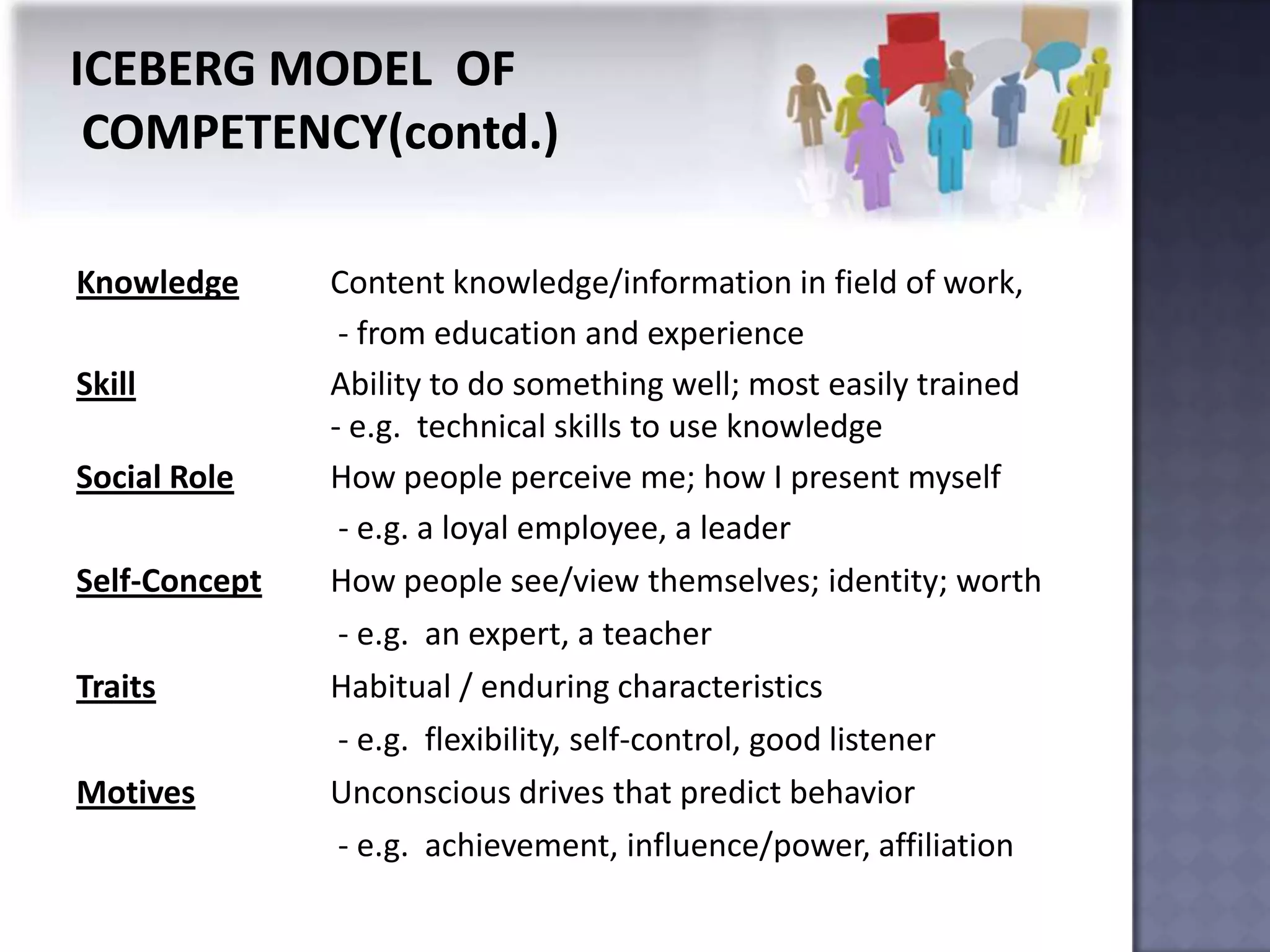
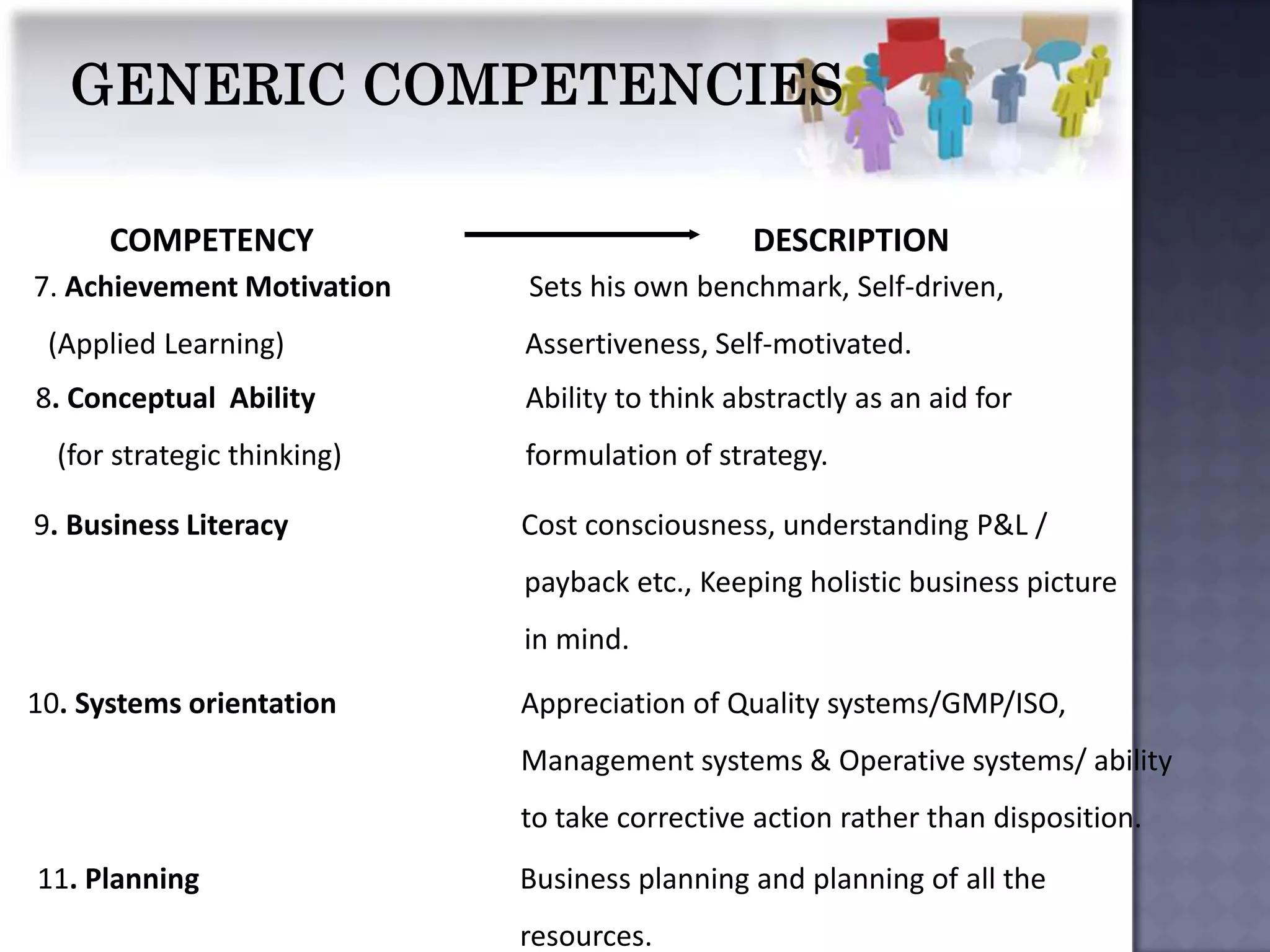
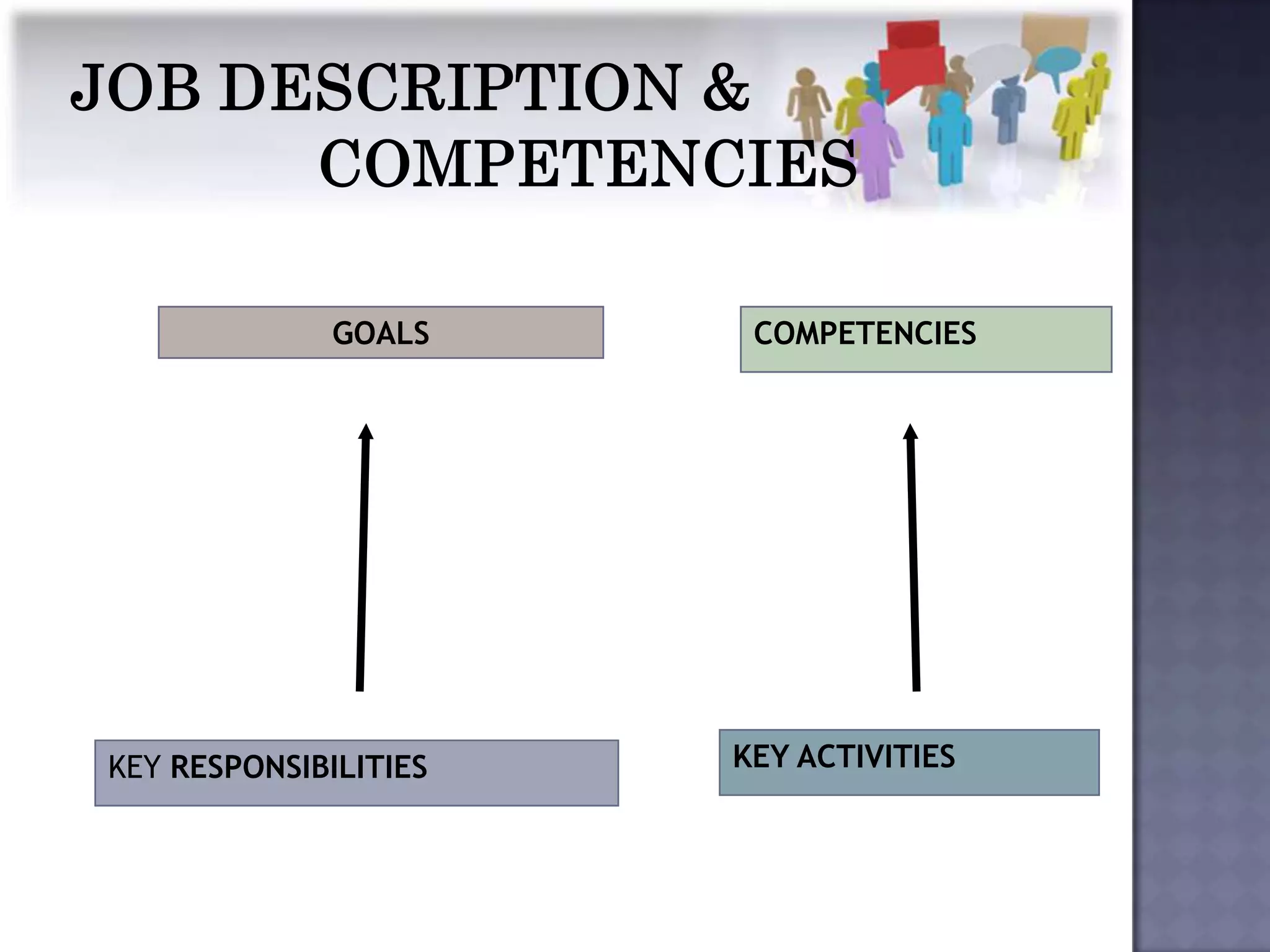
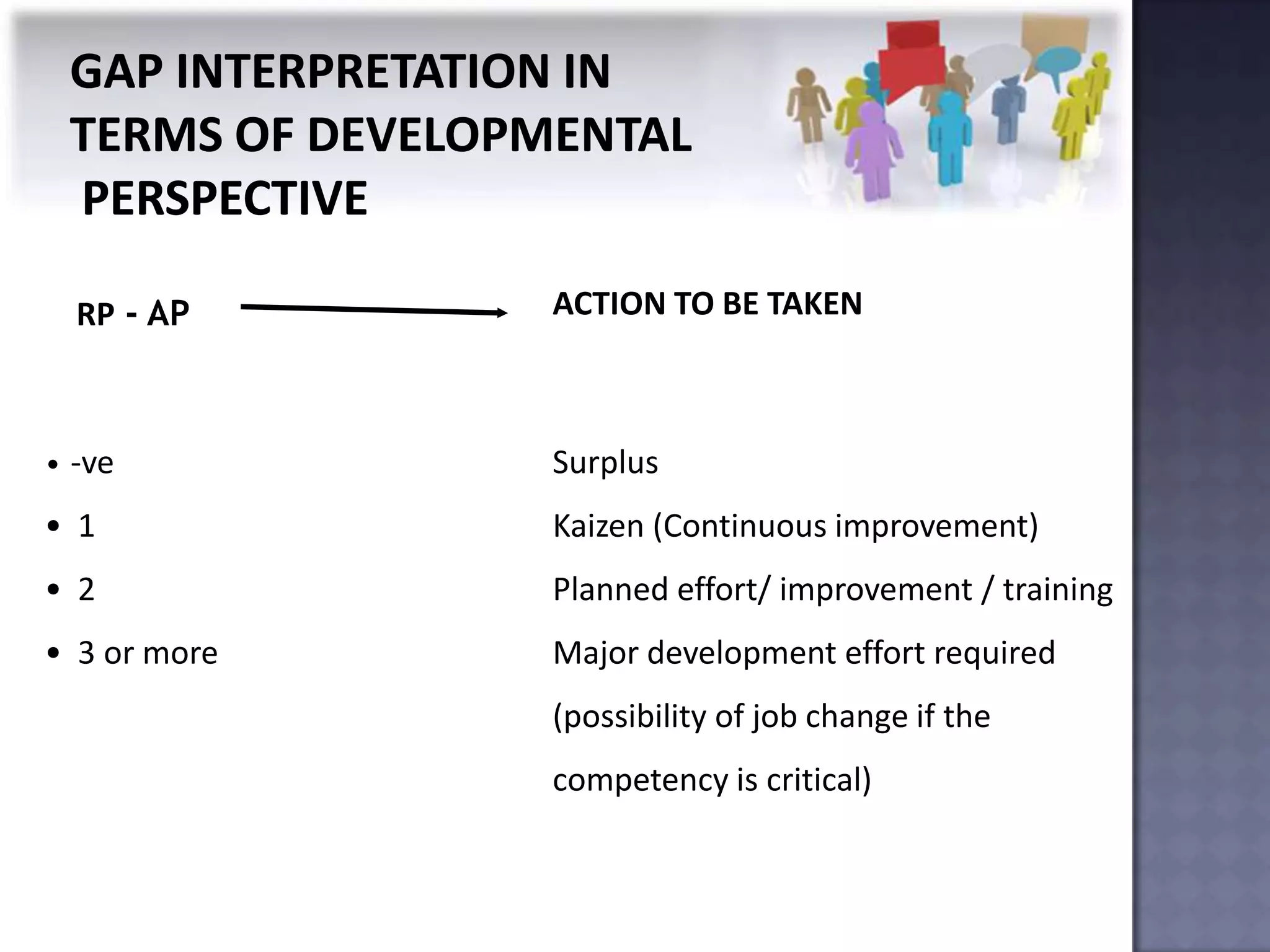
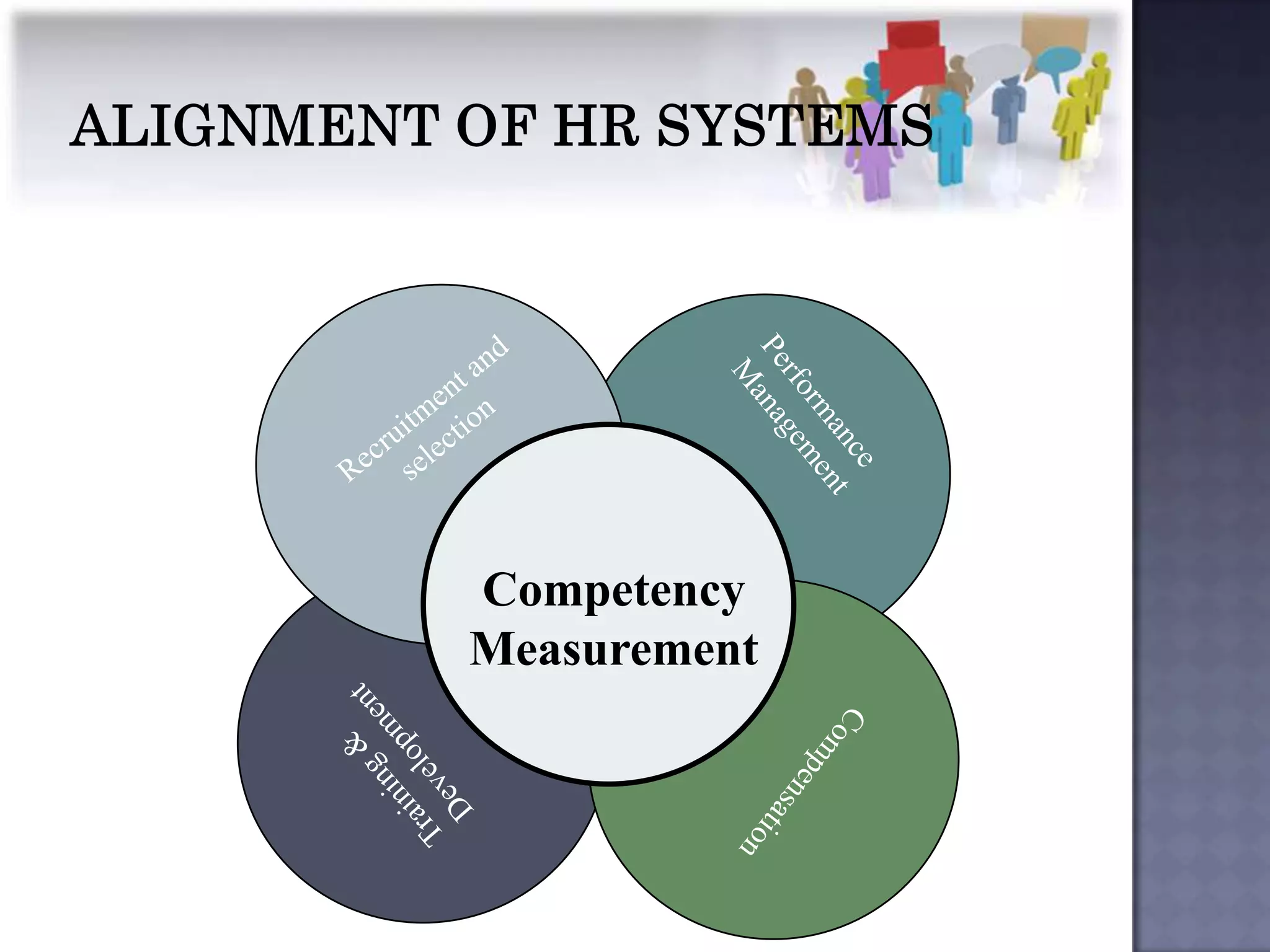
The document discusses competency measurement and its importance. It defines a competency as an underlying characteristic that enables superior job performance. It then outlines various methods for identifying competencies required for roles and measuring individuals' competencies, such as expert panels, surveys, and assessment centers. Competency measurement is important for objectives like performance management, learning and development, assignments, and career planning. It establishes standards and provides fact-based feedback for improvement.