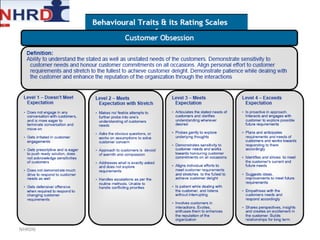
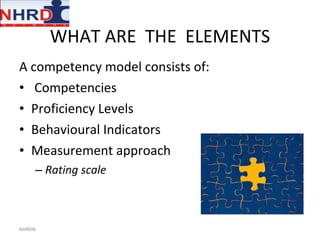
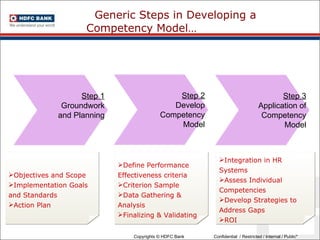
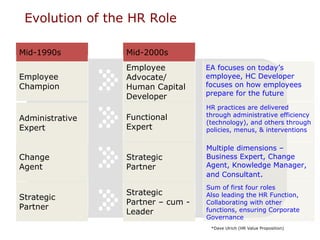
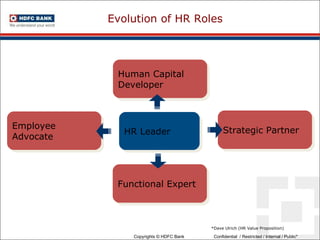
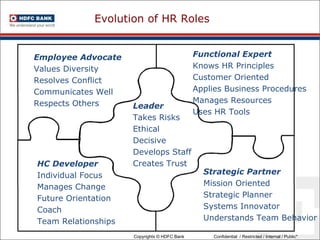
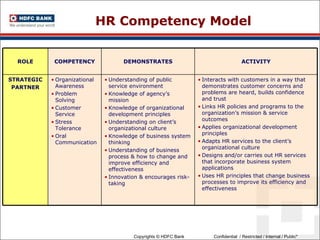
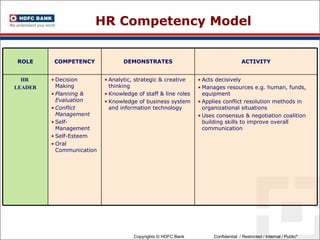
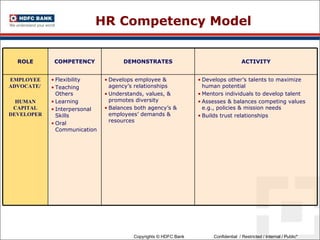
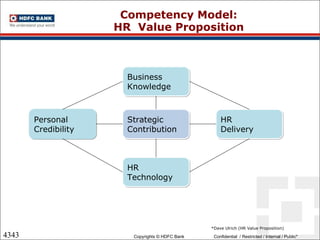
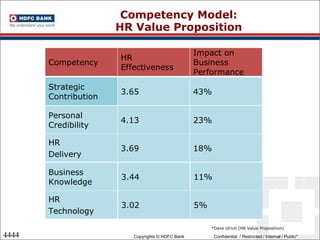
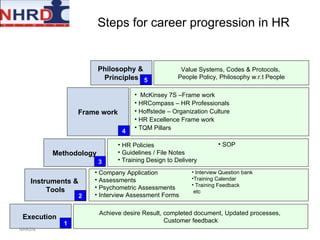
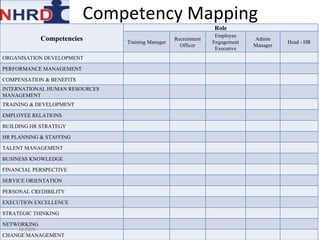
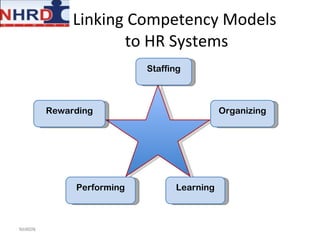
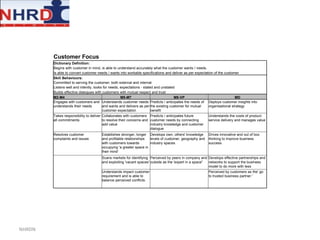
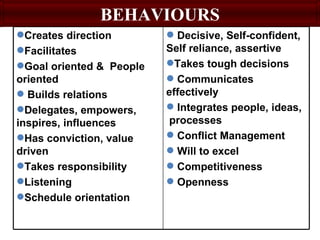
This document discusses developing an HR competency framework. It defines competencies and provides examples. It describes developing a competency model which includes competencies, proficiency levels, behavioral indicators and a measurement approach. Guidelines are provided for assessing the effectiveness of competency models. The HR Compass model is presented as well as an evolution of HR roles. Small group exercises are included to identify competencies for different HR scenarios.





















































![Q& A Contact me: [email_address] Cell +91 9833477278 NHRDN](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/competencyworkshopver3-110401005138-phpapp01/85/HR-Competency-Workshop-Presentation-by-Vijayan-Pankajakshan-84-320.jpg)
