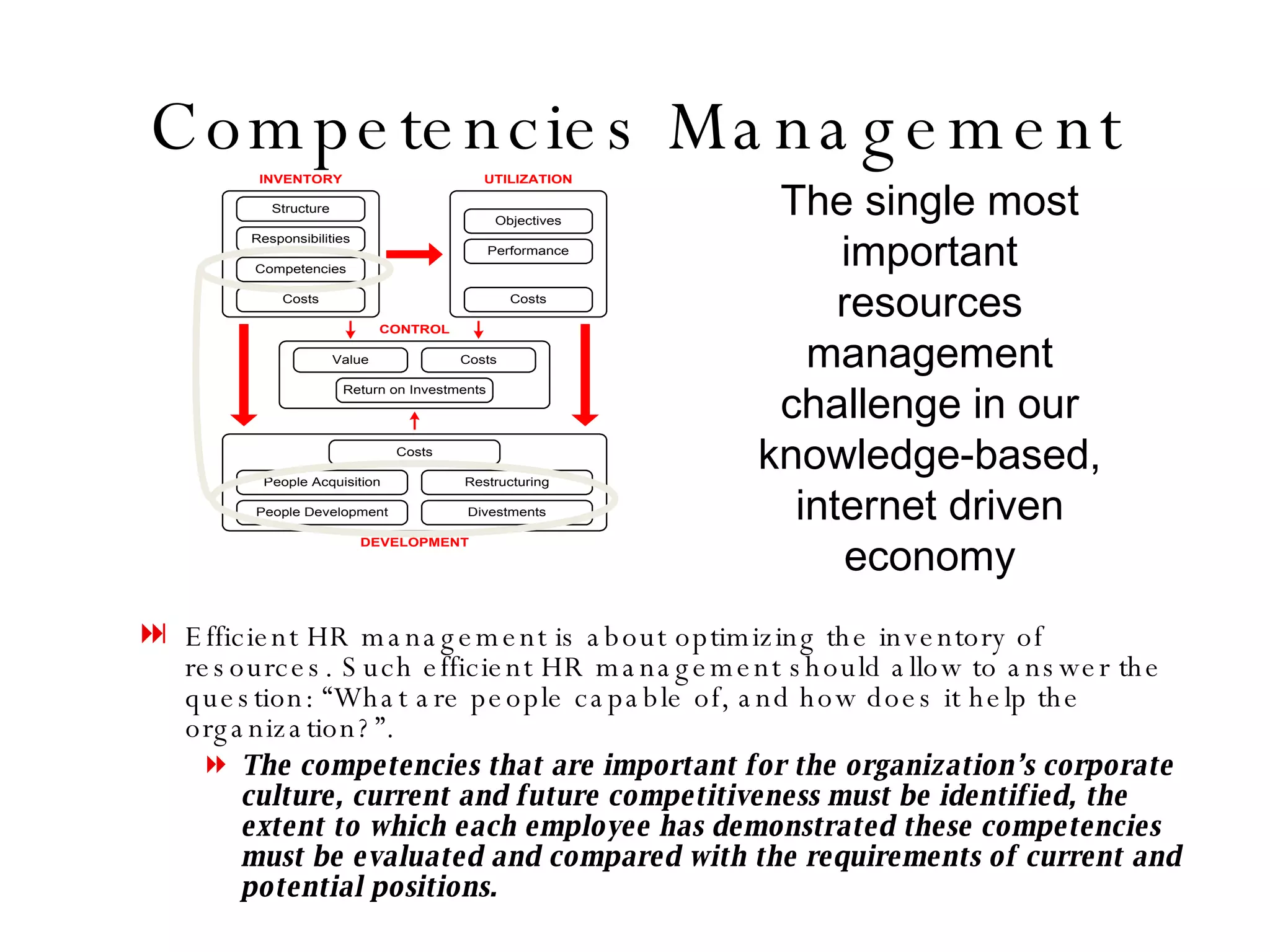
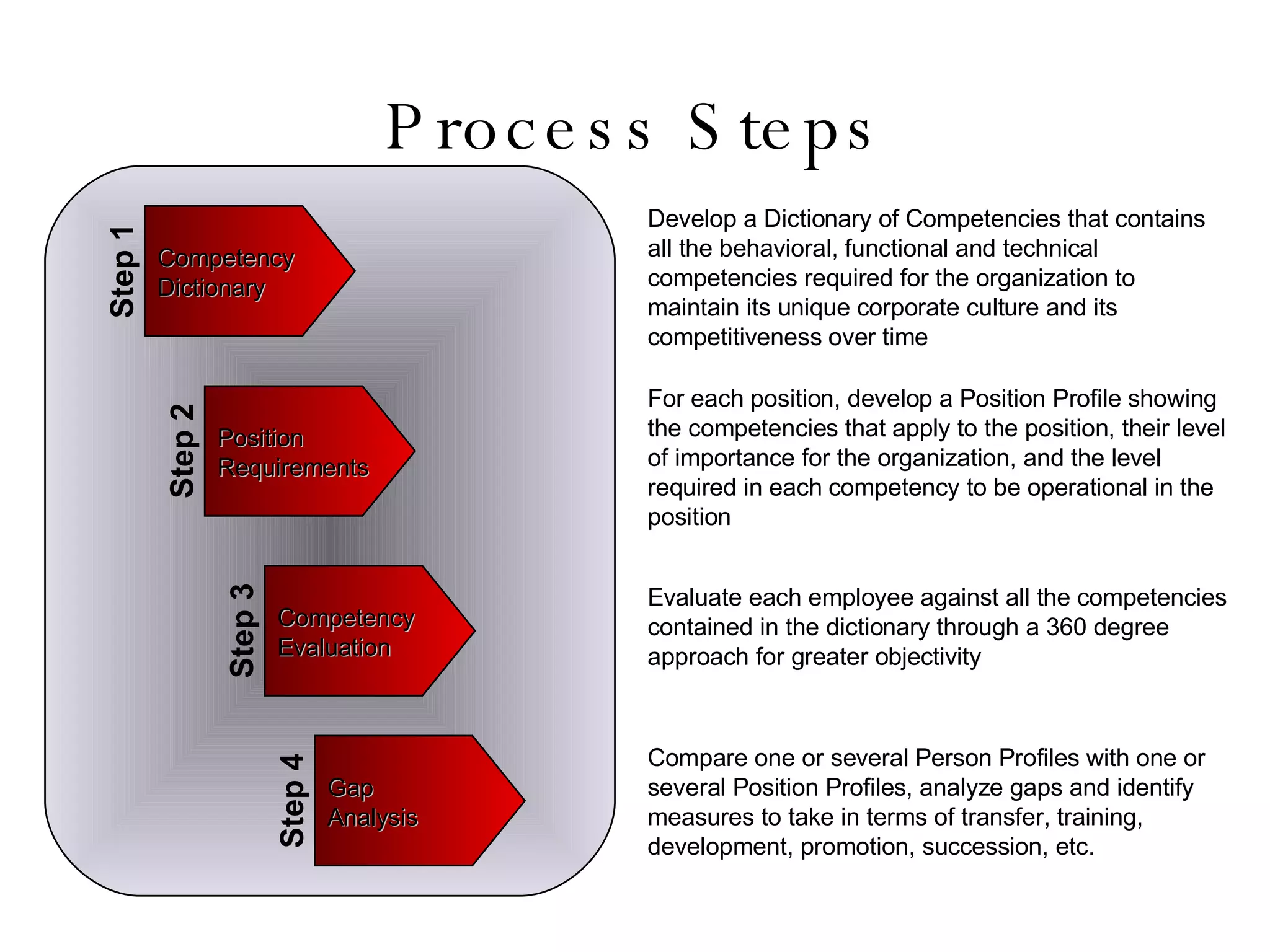
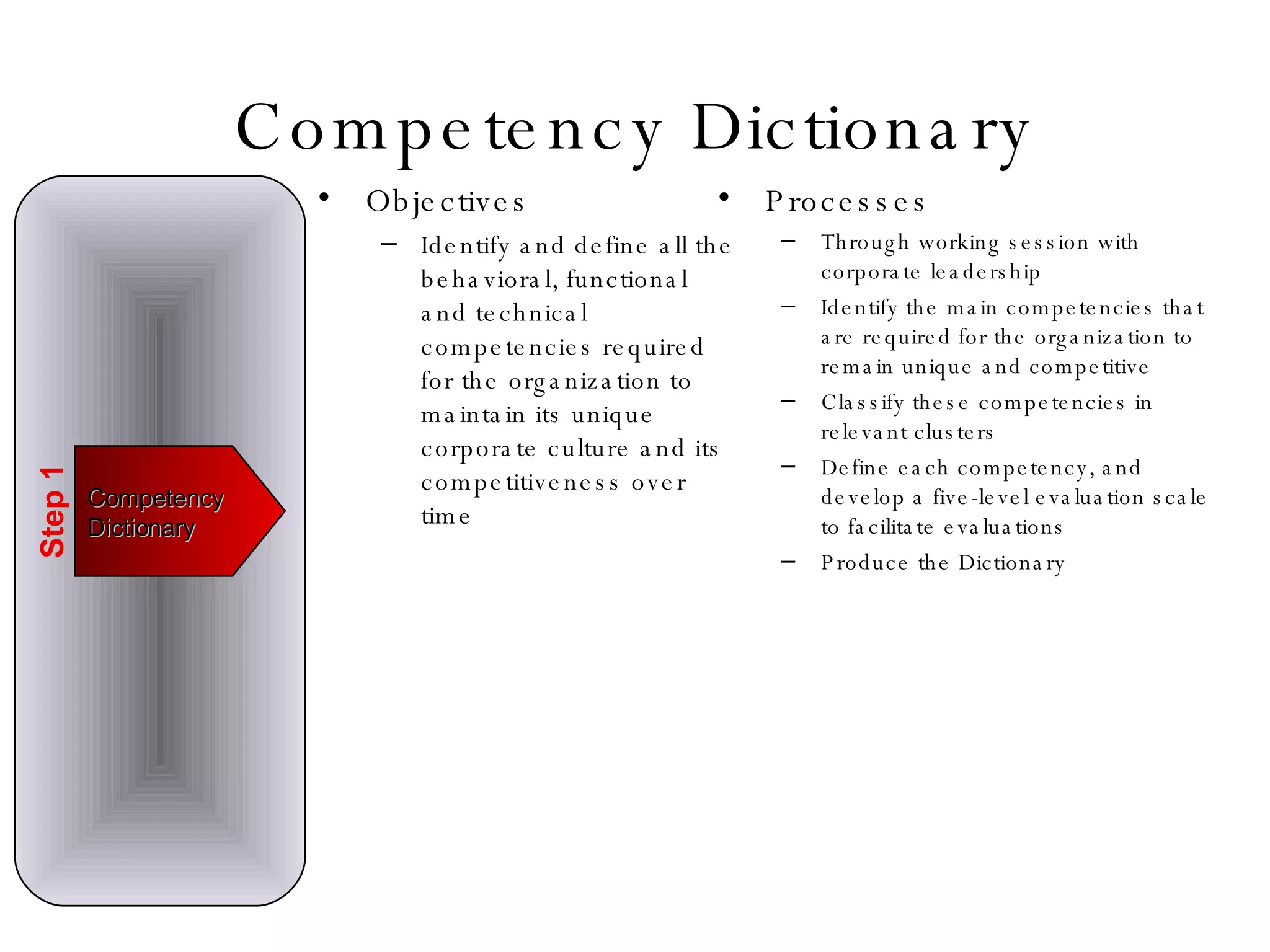
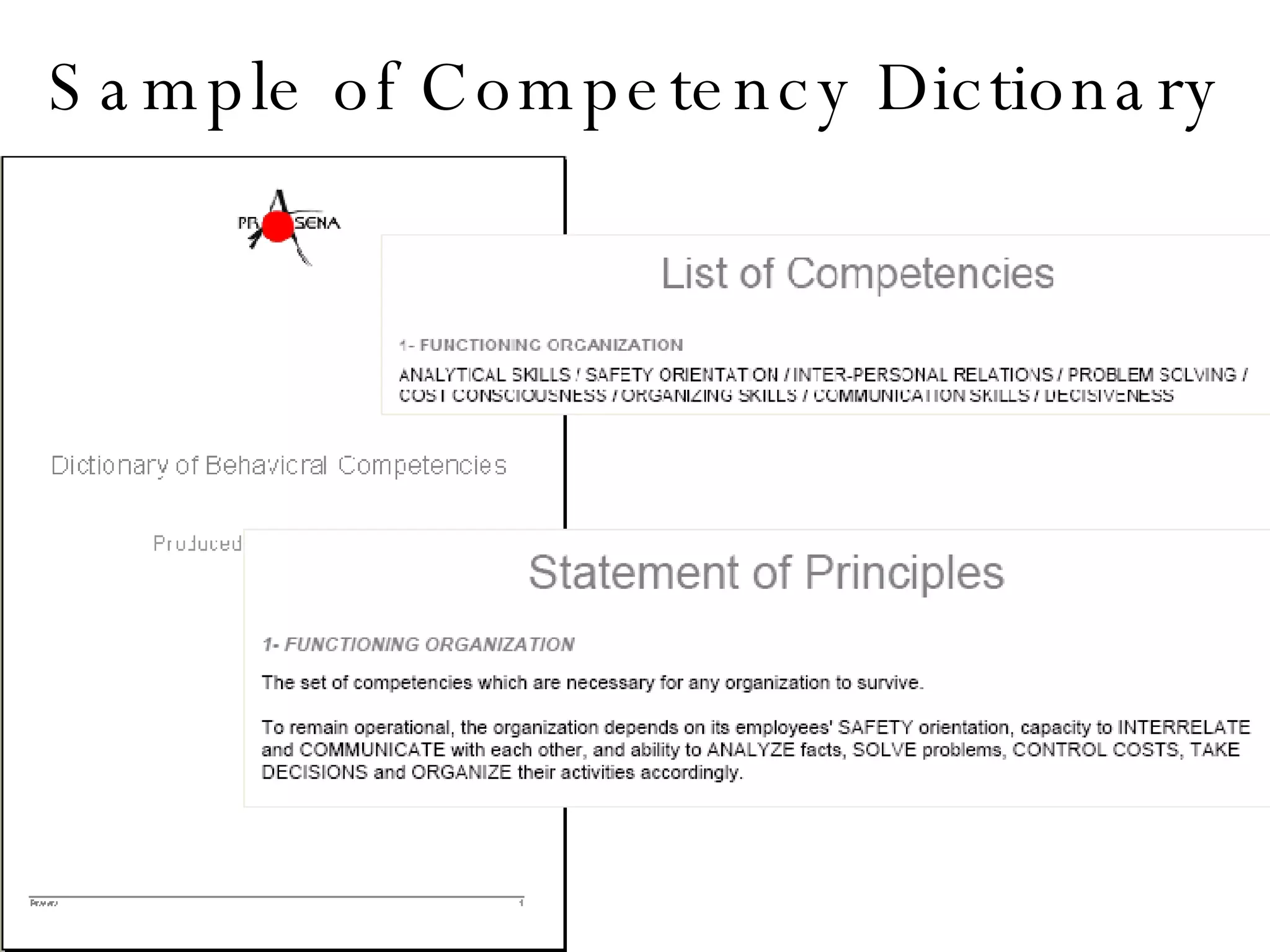
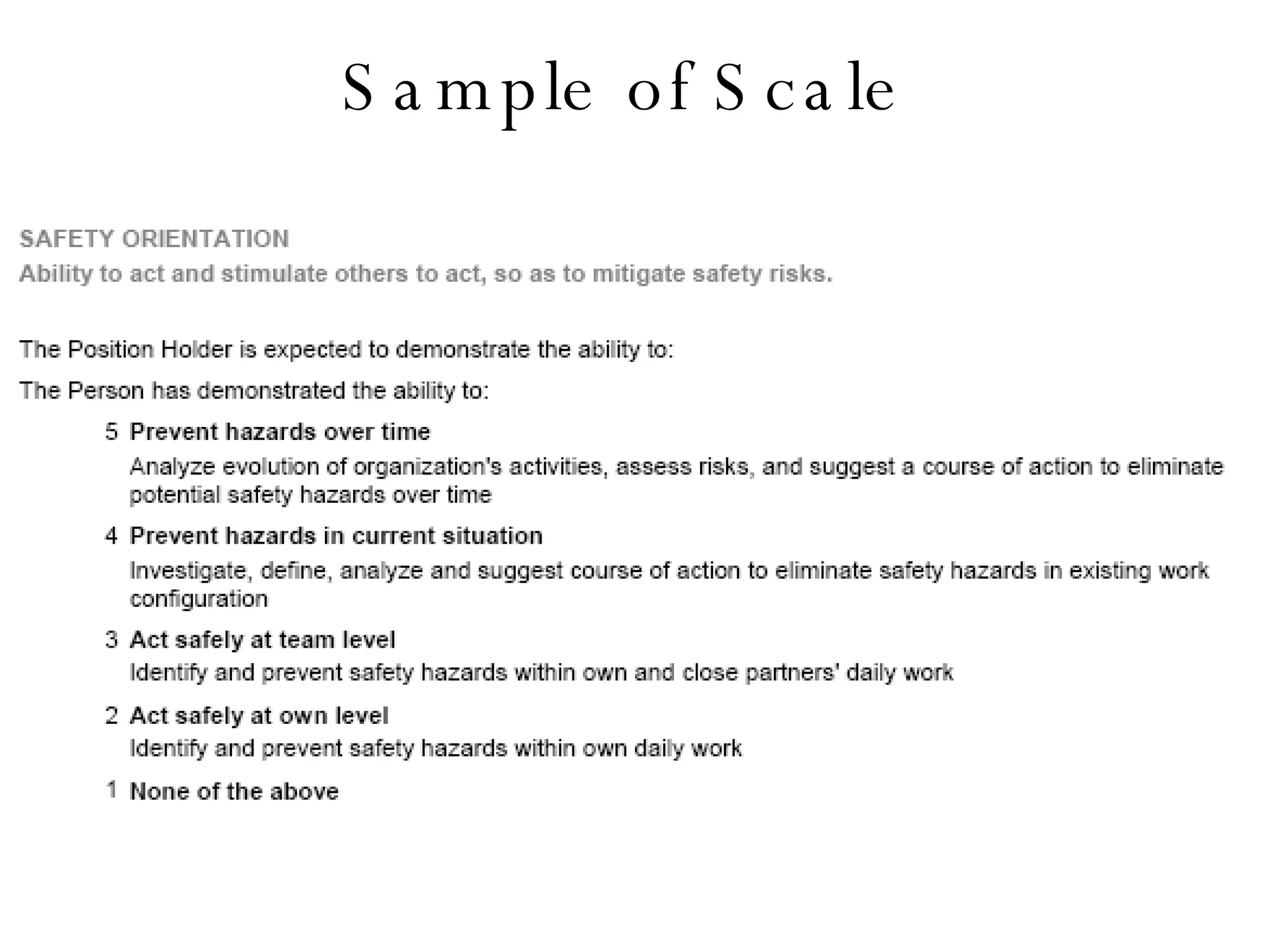
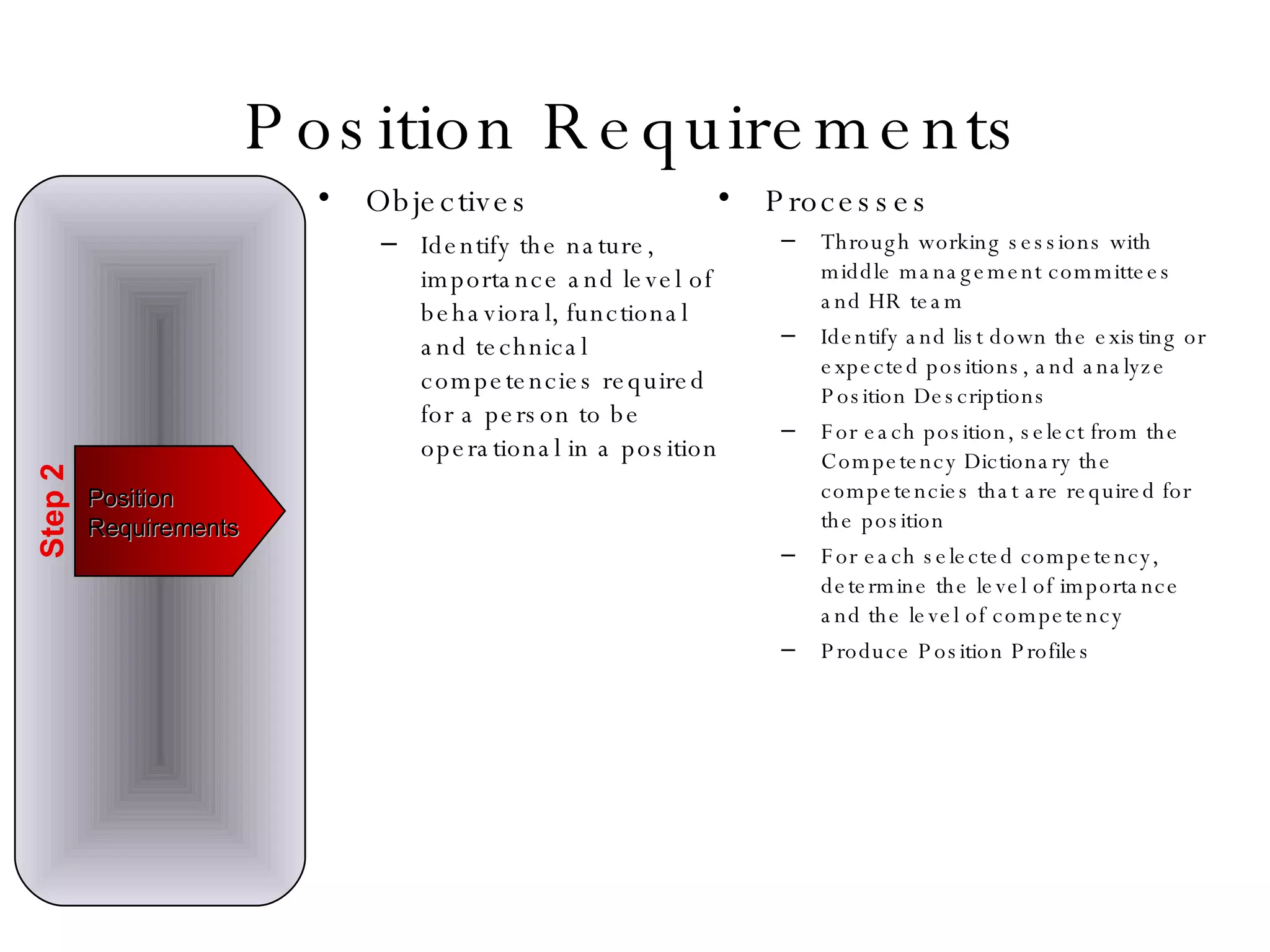
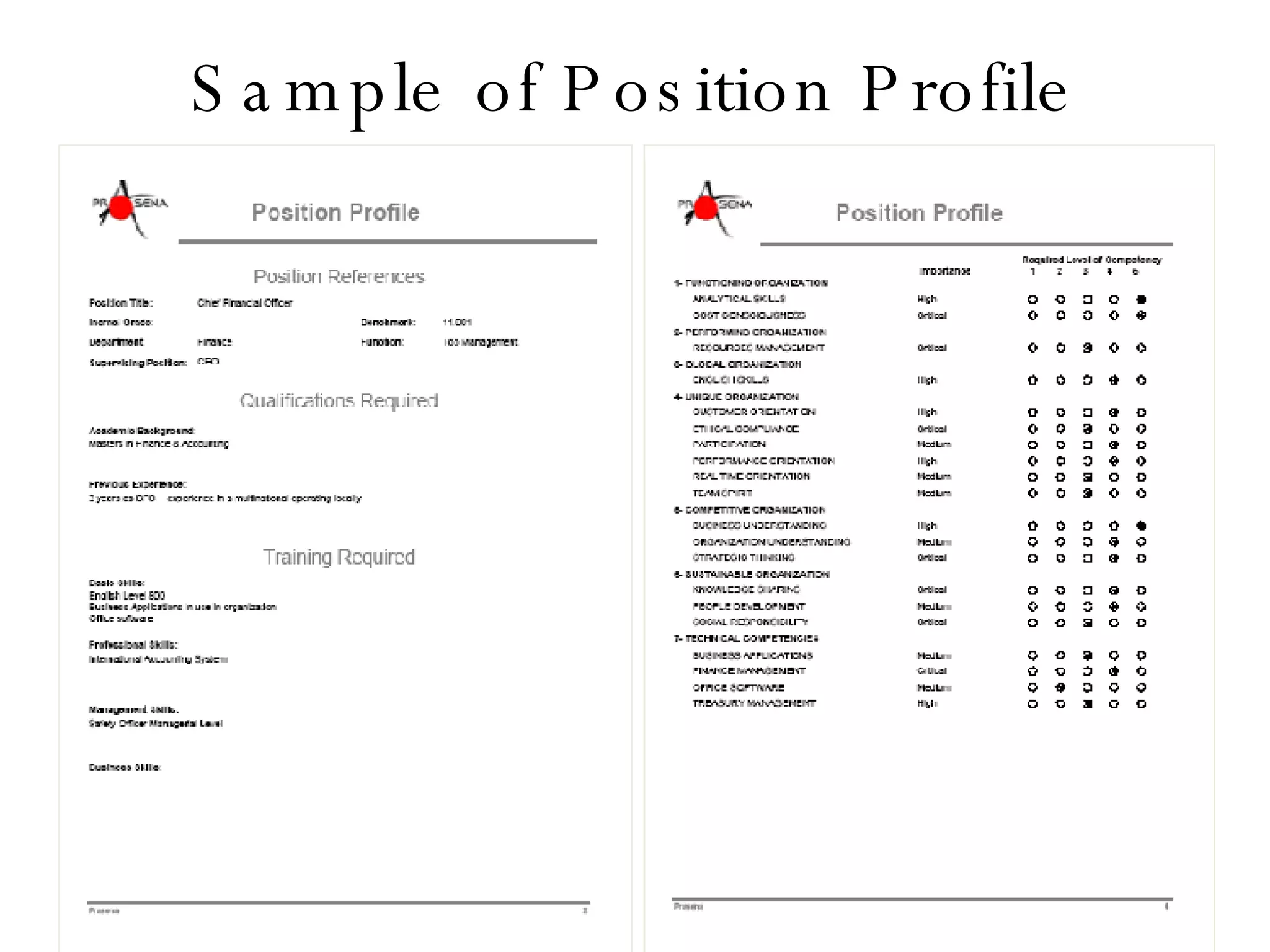
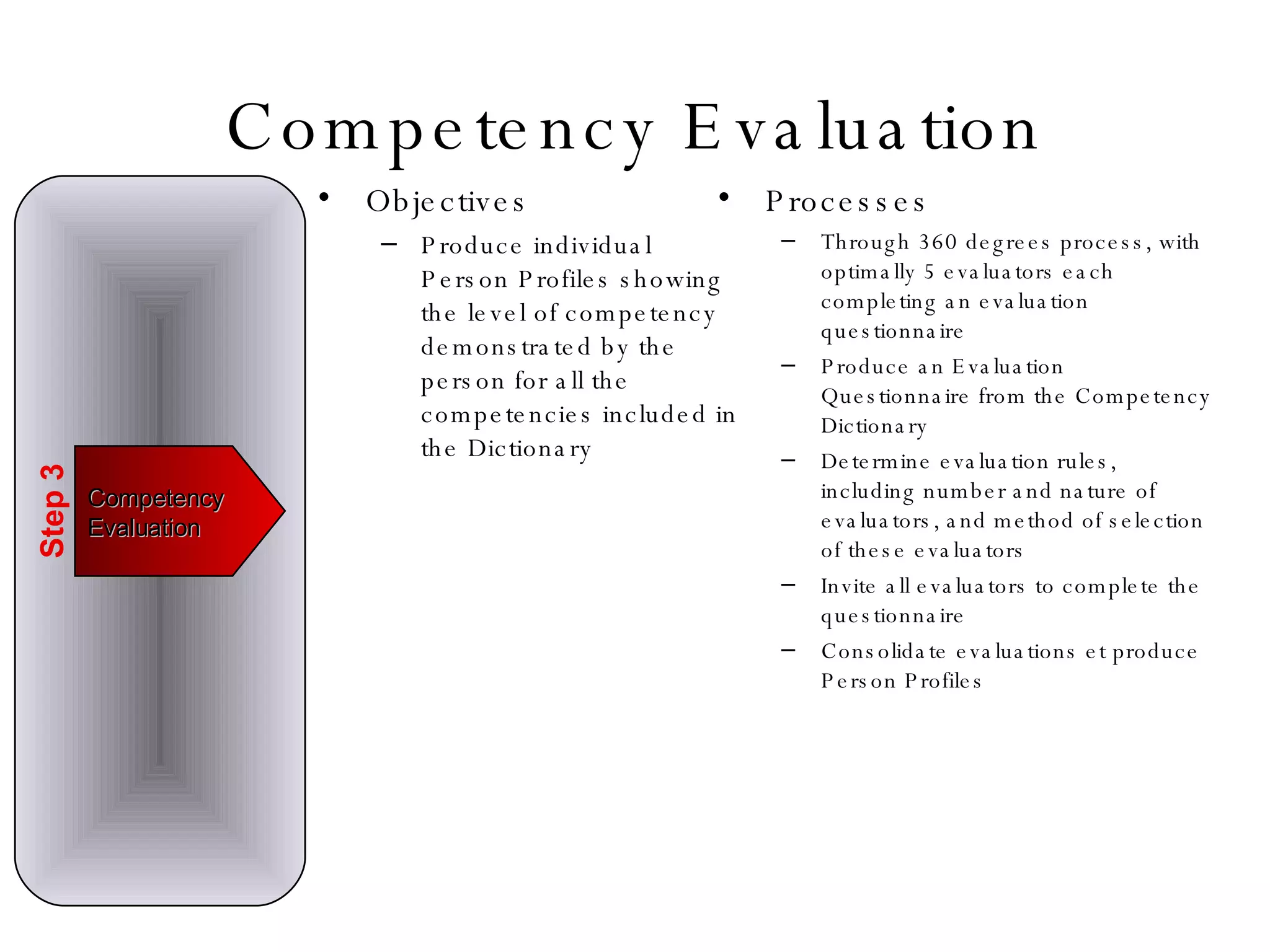
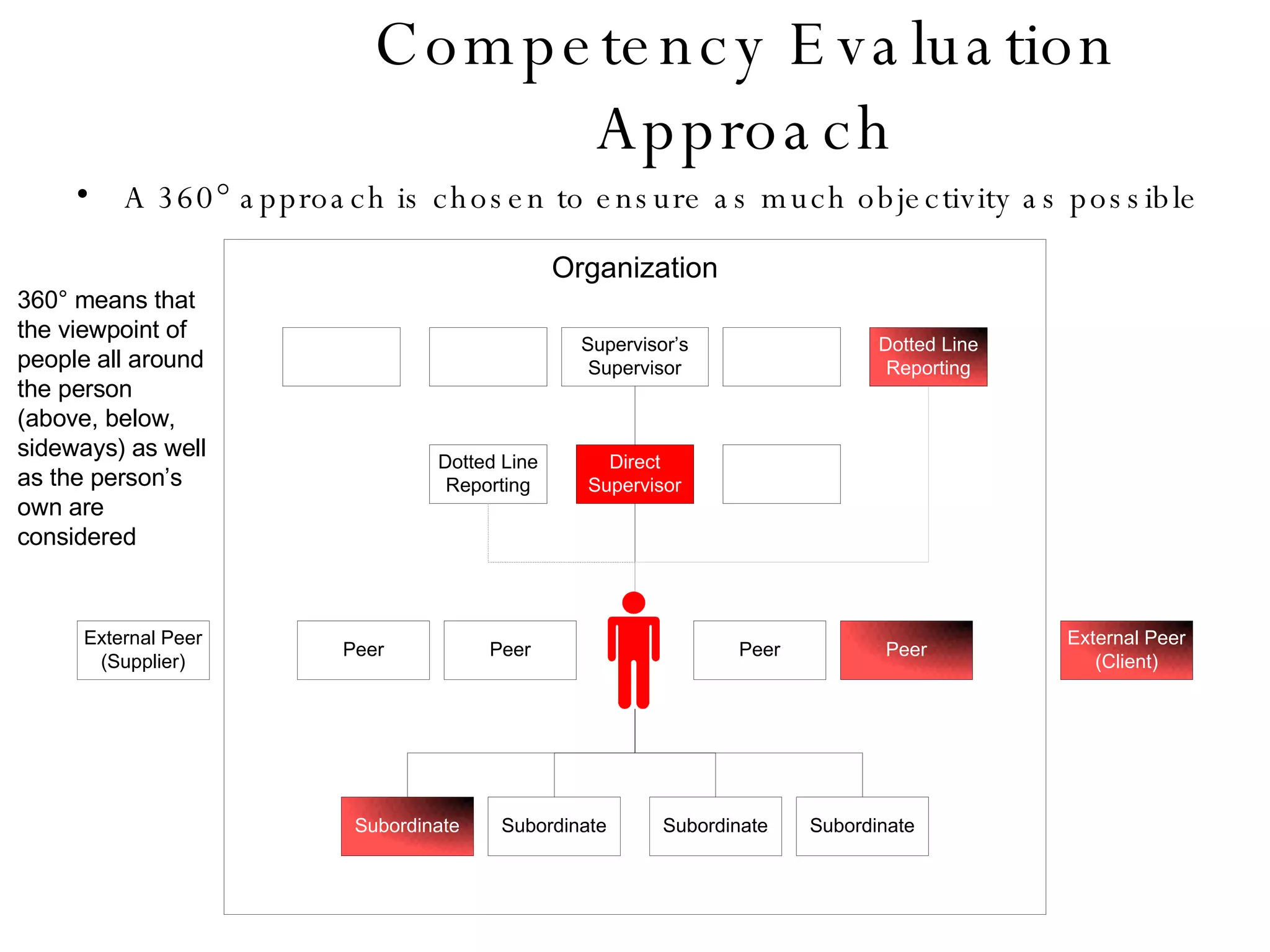
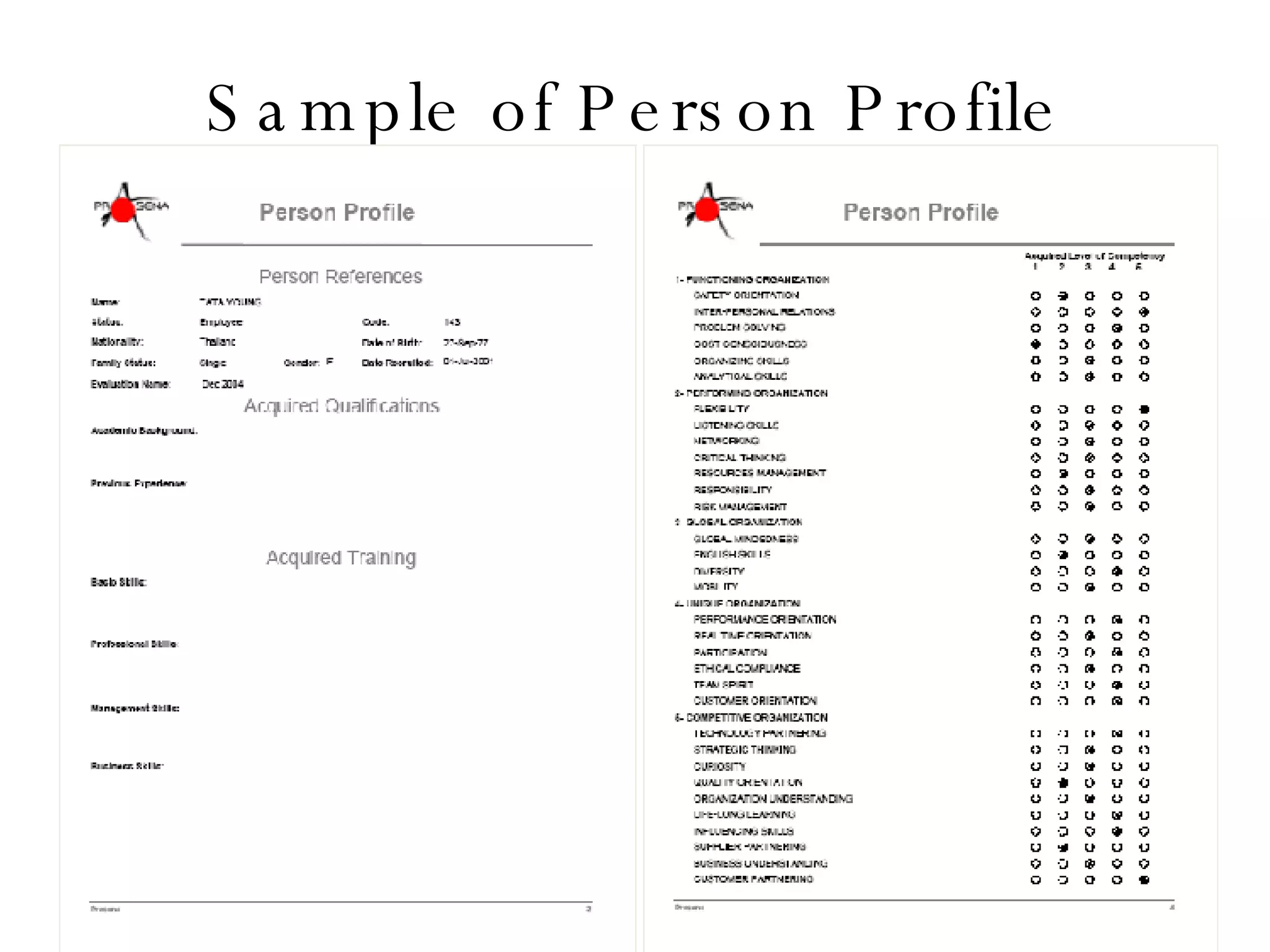
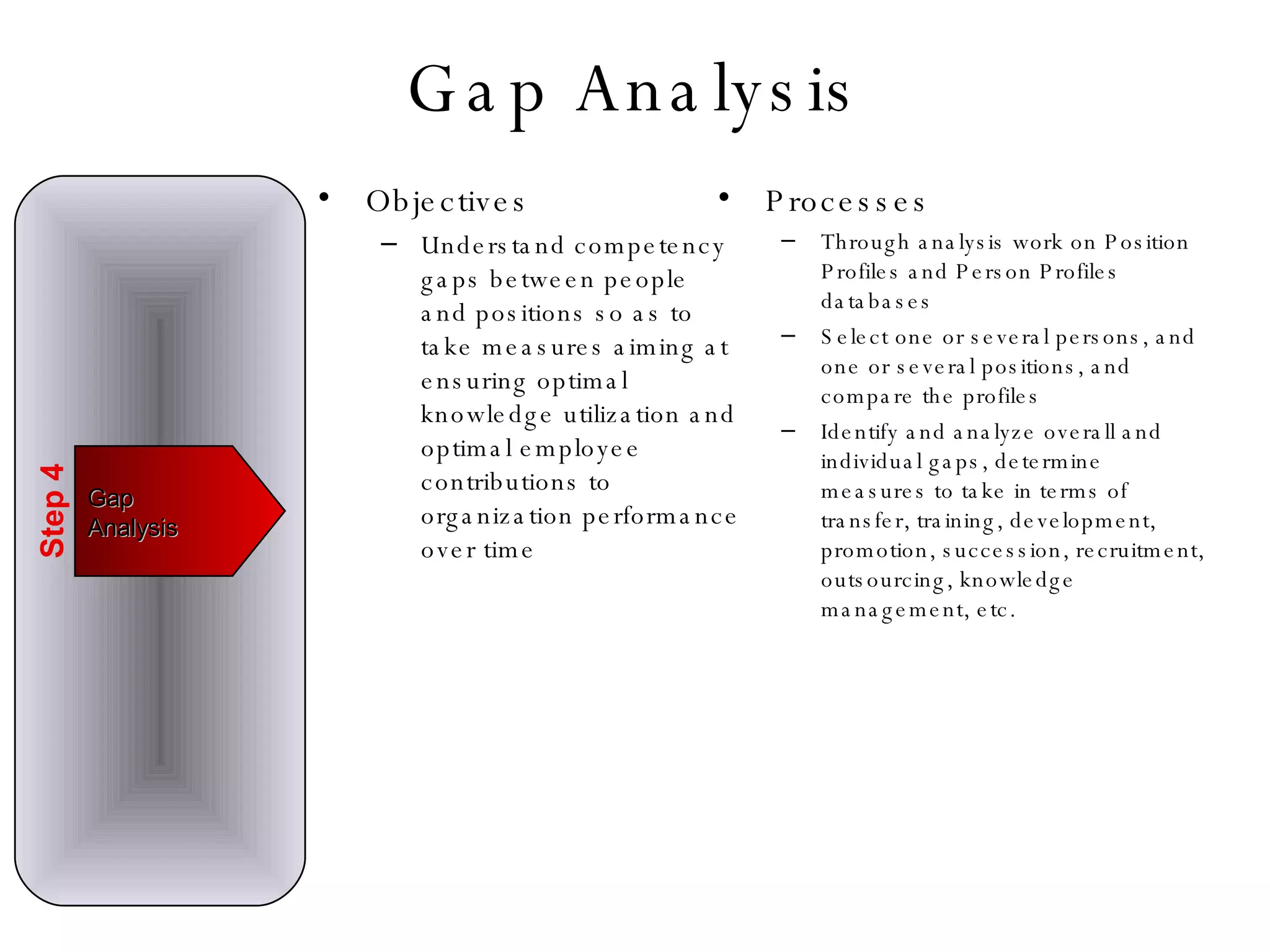
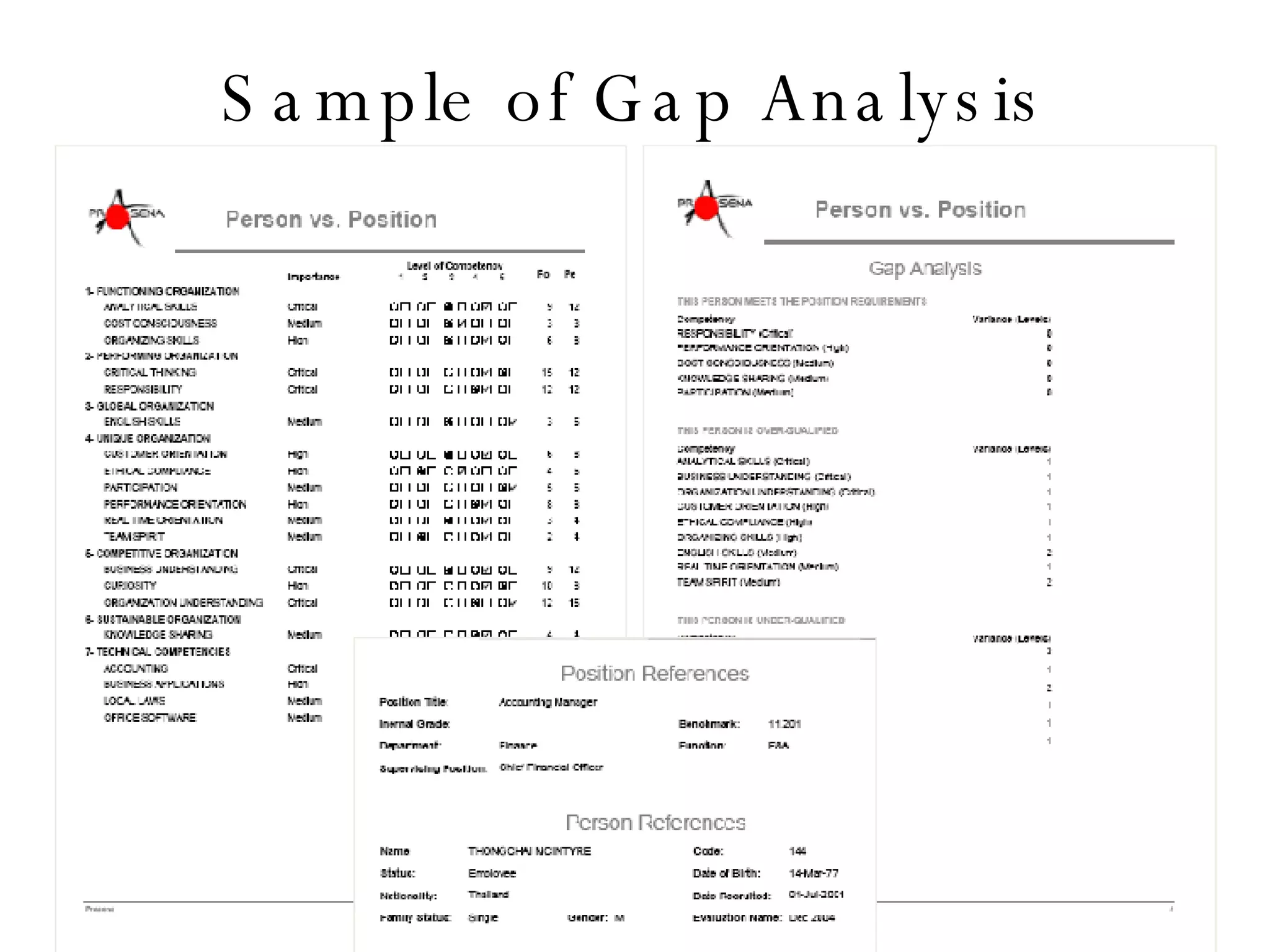
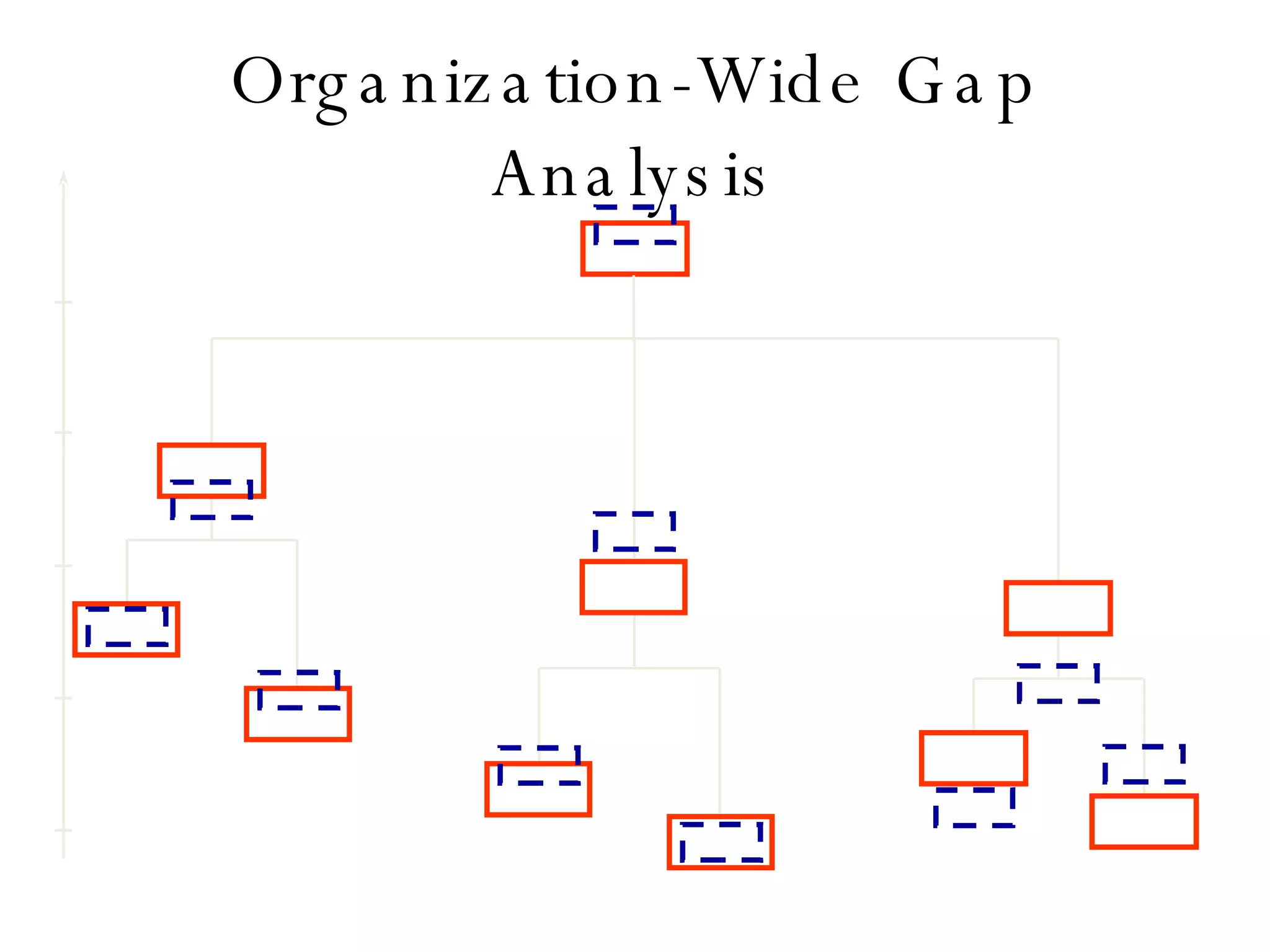
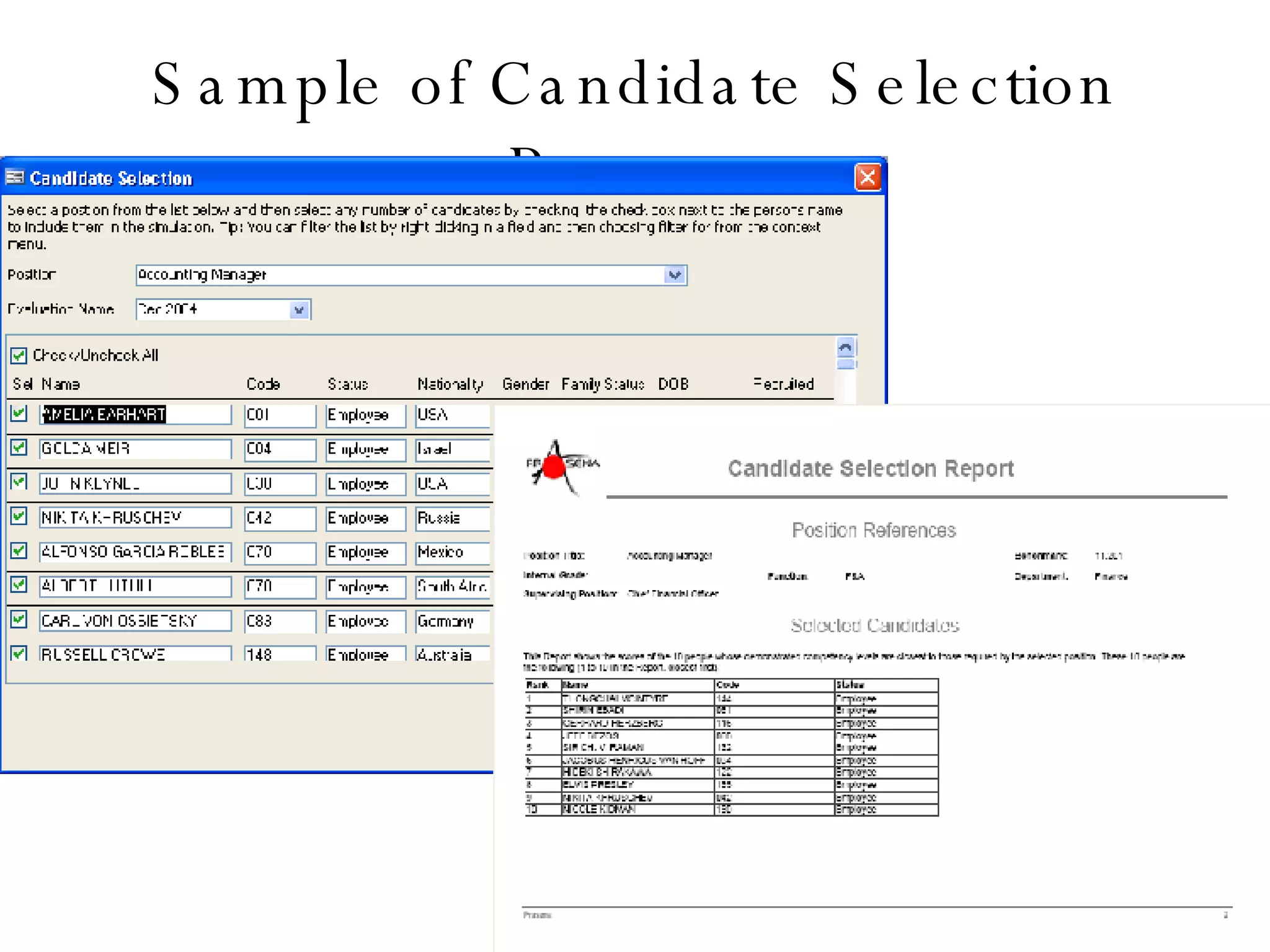
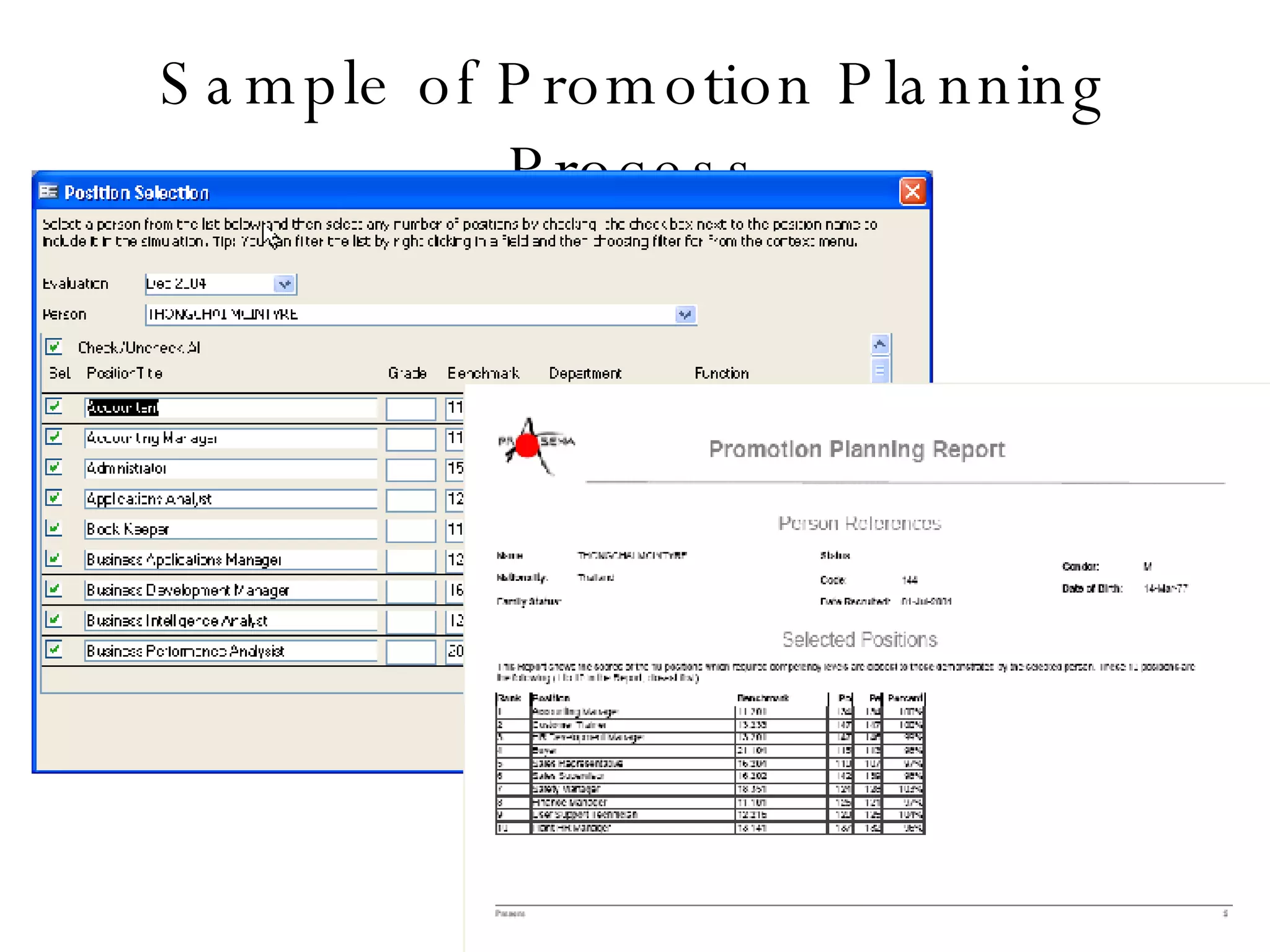
Lukas Ritzel is a management professional with over 20 years of international experience, currently managing ICT at DCT International Hotel & Business Management School and cofounding the change management consulting company Prasena. He emphasizes efficient human resource management to optimize workforce competencies and ensure organizational competitiveness through a structured approach involving competency dictionaries and evaluations. The document outlines processes for identifying, evaluating, and analyzing employee competencies to align individual capabilities with organizational needs.