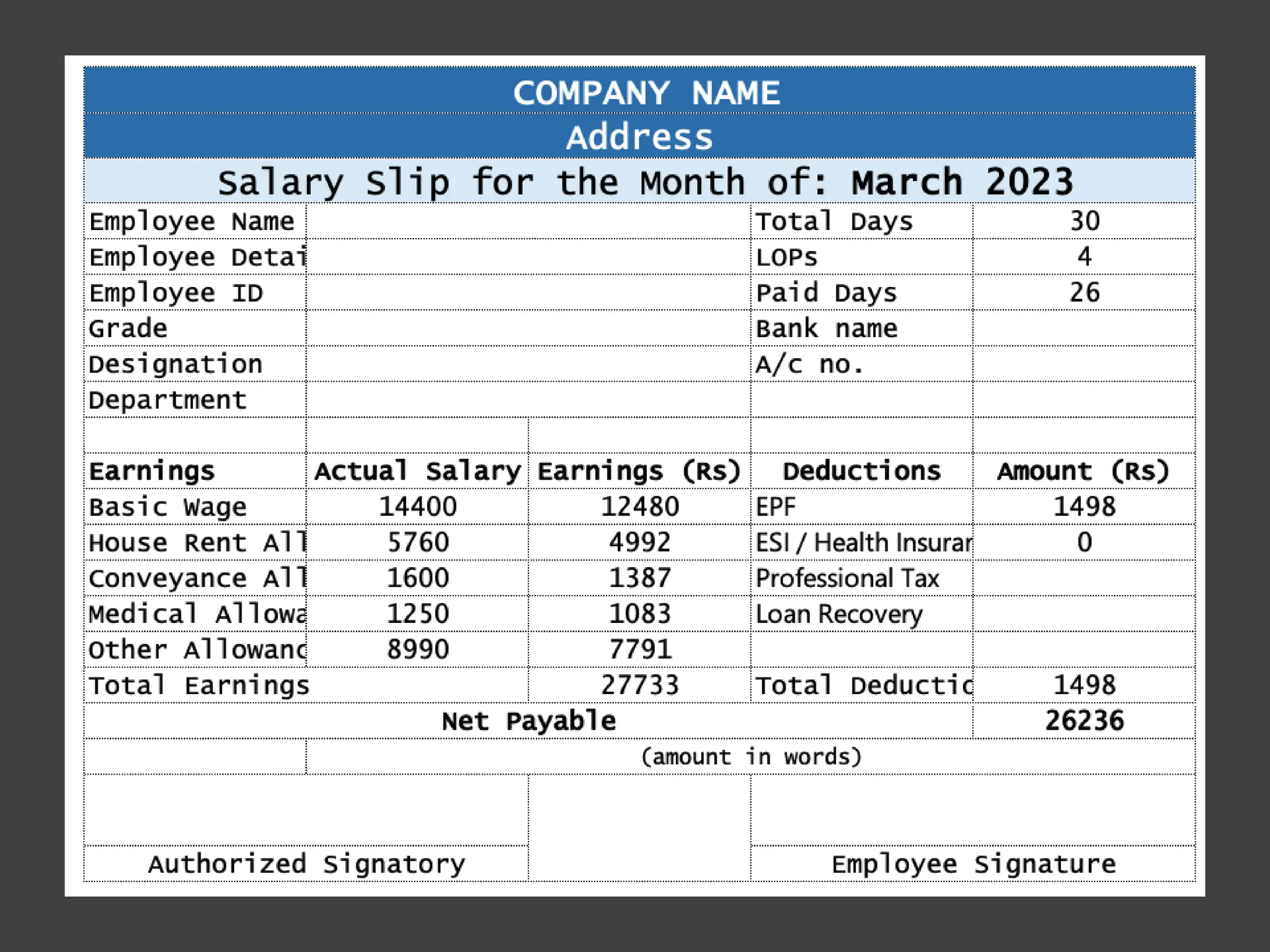
The document outlines the significance of compensation and reward management in HRM, focusing on designing effective pay and benefits programs to attract, retain, and motivate employees. It discusses components of salary, financial and non-financial incentives, and employee separation processes, including retirement and golden handshake strategies. Furthermore, it emphasizes the importance of maintaining internal and external equity in compensation to enhance employee satisfaction, motivation, and organizational performance.