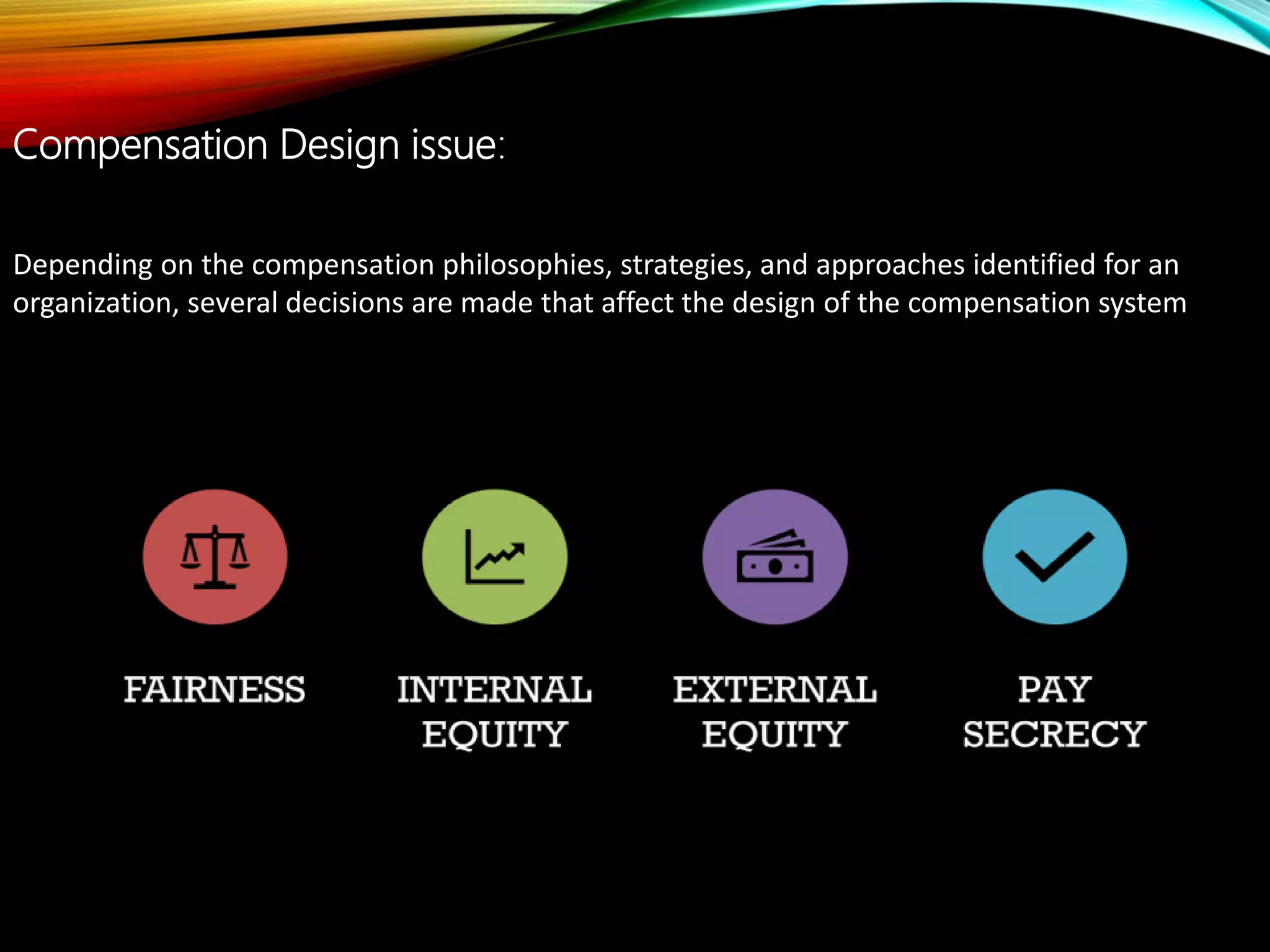
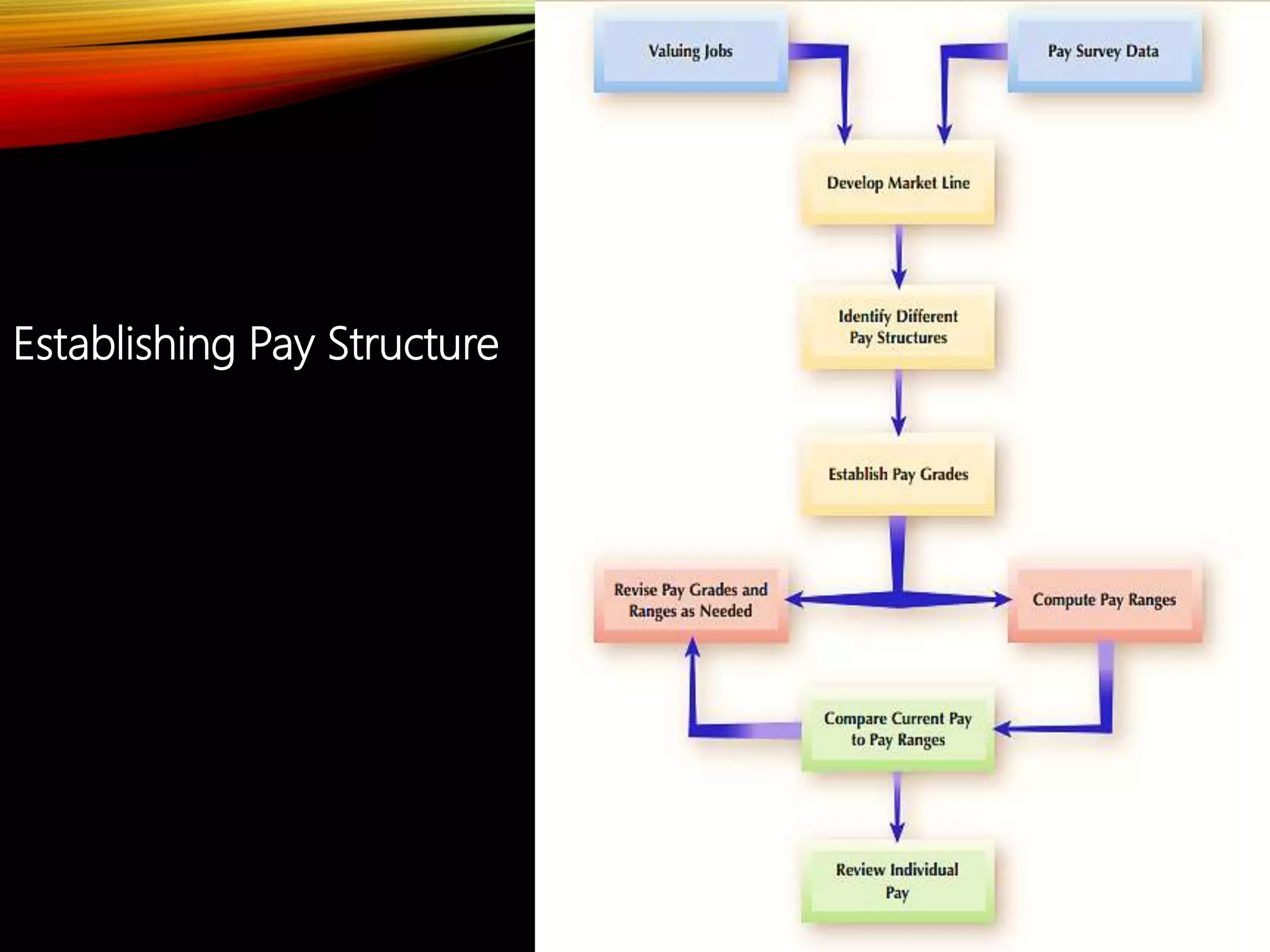
The document provides an overview of total rewards in HR management, emphasizing how they encompass various compensation types, benefits, and performance management strategies aimed at attracting and retaining employees. It details the principles of compensation, including direct and indirect types, equity considerations, and compliance with legal standards like the Fair Labor Standards Act. Additionally, it highlights practical examples of companies implementing innovative compensation strategies to motivate employees.