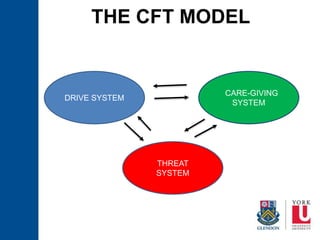
The document discusses Compassion-Focused Therapy (CFT) as a treatment method designed to alleviate shame and self-criticism by fostering compassion towards oneself and others. It presents case studies illustrating the impact of trauma and mental health issues, highlights the interplay of internal and external shame, and explains how CFT draws on evolutionary psychology to develop emotional regulation systems. The therapy aims to enhance the care-giving system, promoting qualities such as empathy and non-judgment to support individual well-being.