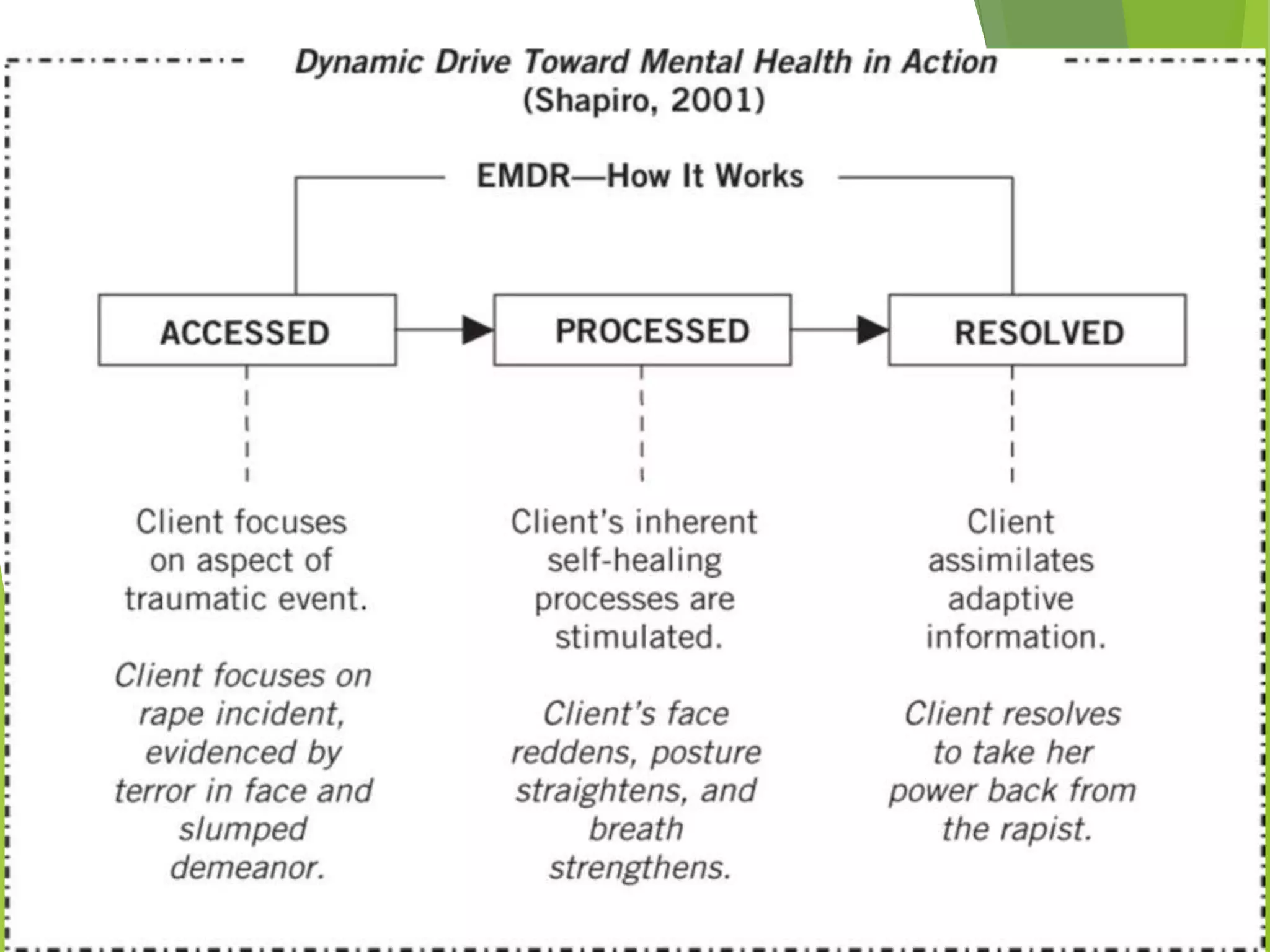
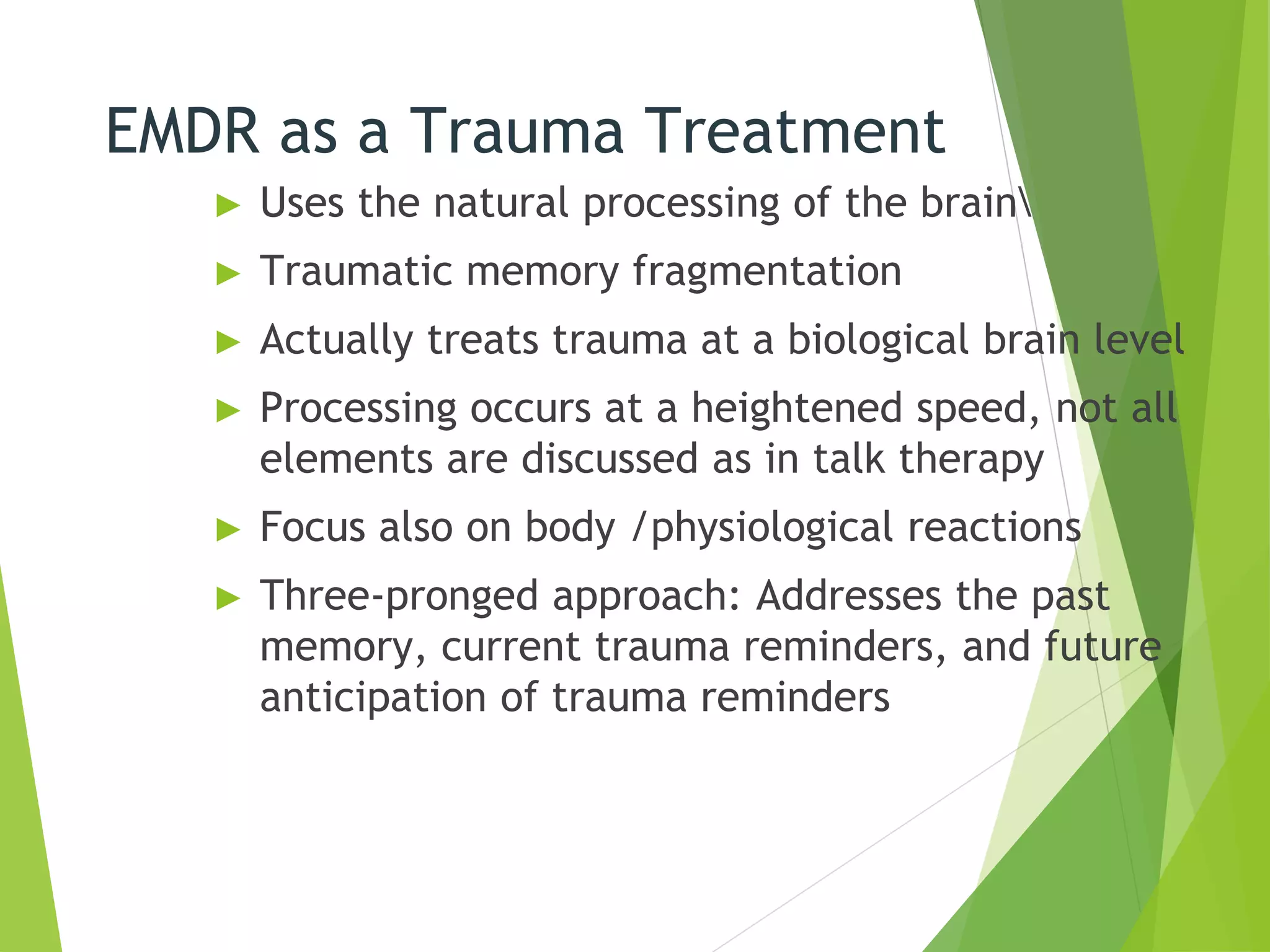
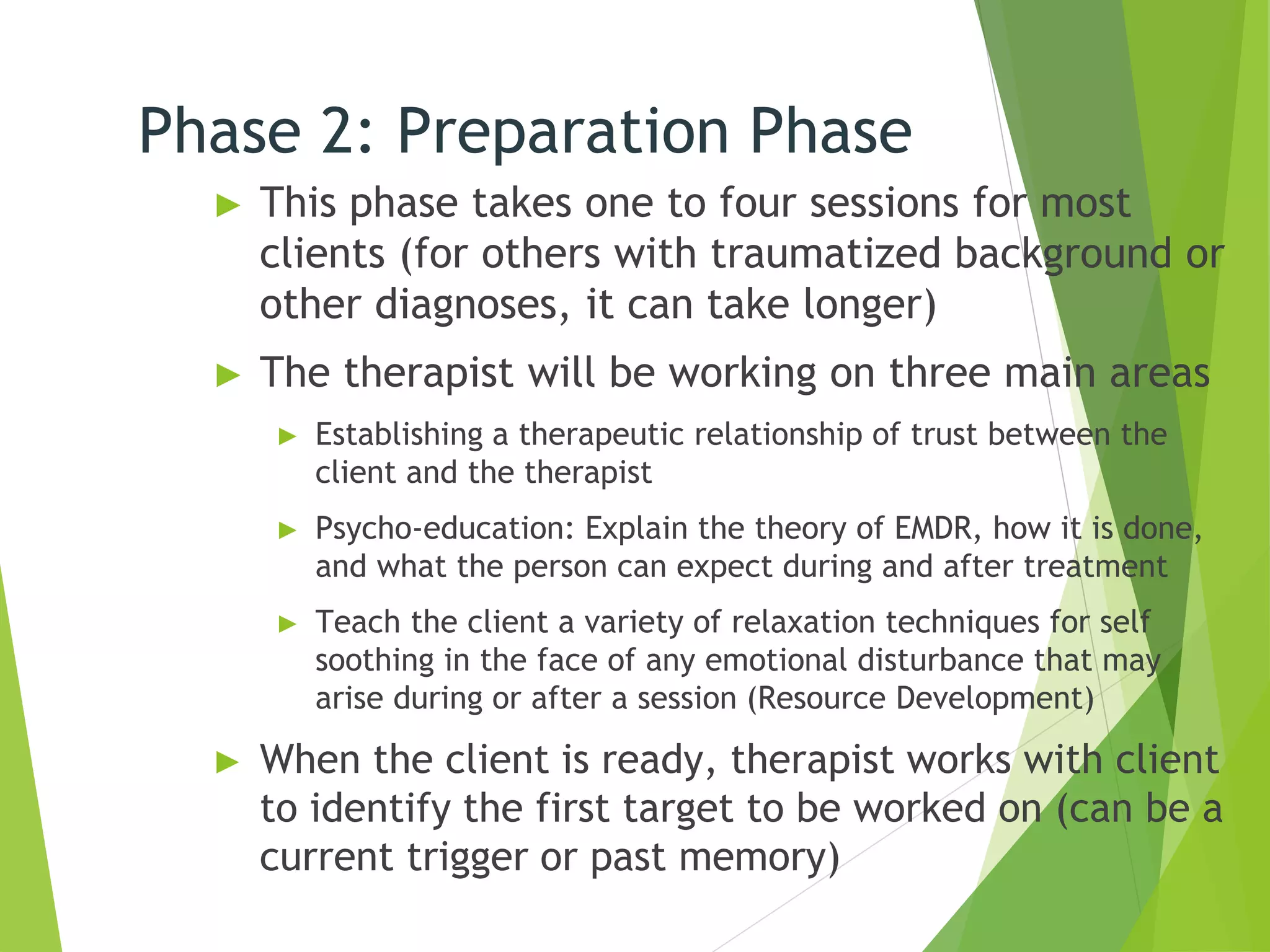
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) is a psychotherapy technique used to treat trauma. It was developed in the 1980s by Francine Shapiro and incorporates elements from different treatment approaches. During EMDR, a person recalls distressing memories while simultaneously focusing on an external stimulus like eye movements or hand tapping. This is believed to help the brain reprocess traumatic memories in a healthy way. EMDR usually proceeds through 8 phases, beginning with gathering history and assessing traumatic memories, then using bilateral stimulation during desensitization and installation of positive beliefs to reduce distress related to the memories. EMDR has been empirically validated for treating conditions like PTSD and has helped millions of people relieve psychological stress from trauma.