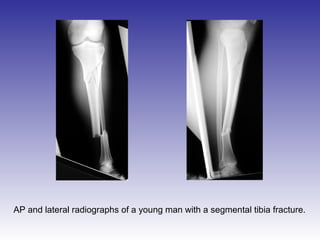
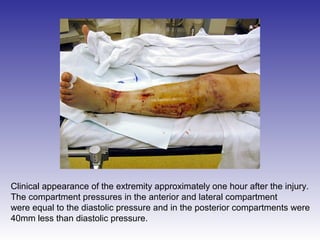
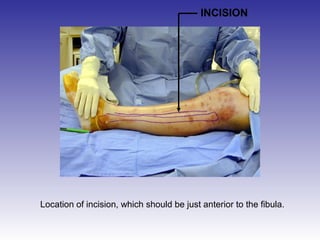
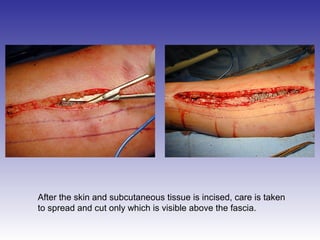
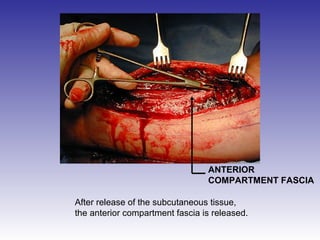
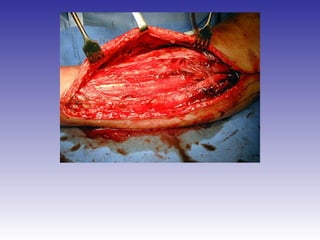
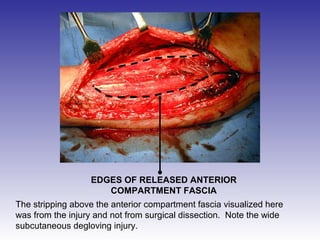
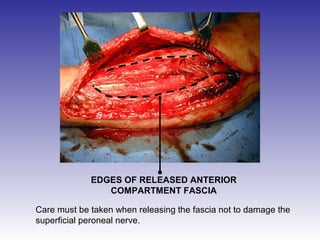
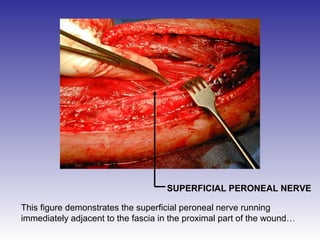
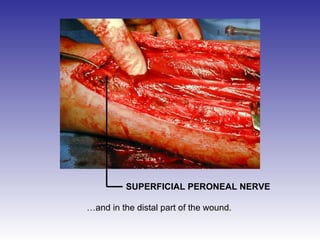
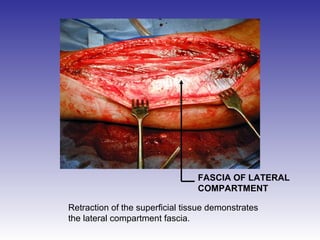
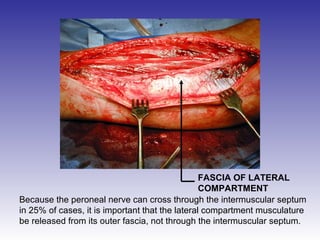
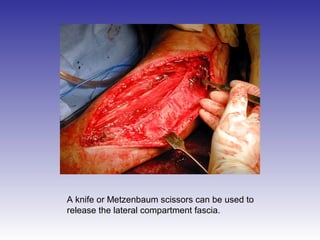
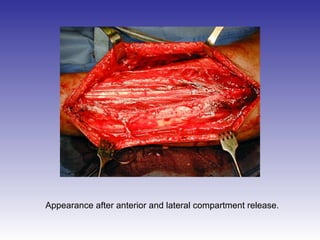
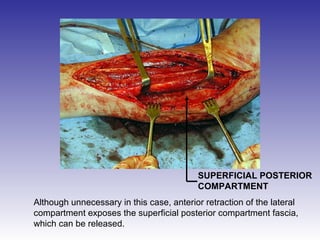
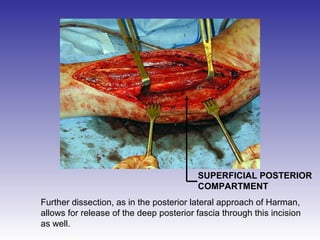
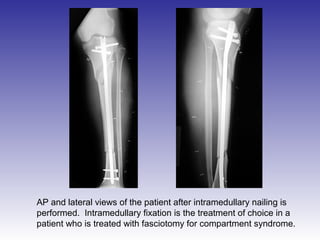
The document describes the procedure for performing a fasciotomy to treat compartment syndrome in a patient with a tibia fracture. It details making an incision anterior to the fibula to access the anterior and lateral compartment fascia. The anterior compartment fascia is released first, taking care to avoid damaging the superficial peroneal nerve. The lateral compartment fascia is then released, being aware the peroneal nerve can cross through in some cases. Releasing the fascia of the anterior and lateral compartments provides treatment for the compartment syndrome.