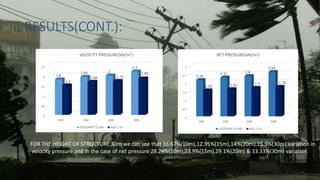
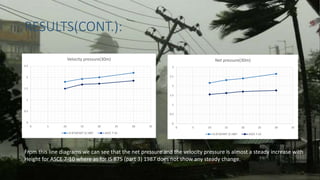
The document reviews IS 875 (Part 3) 1987 and compares it with ASCE 7-10, focusing on wind pressure design for buildings. It highlights significant differences in wind pressure calculations, revealing that IS 875 results are typically higher due to factors like gust effects not being included in the former. The conclusion emphasizes advancements in wind study methods over the past three decades, suggesting that ASCE code offers more accurate data compared to IS 875 (Part 3) 1987.