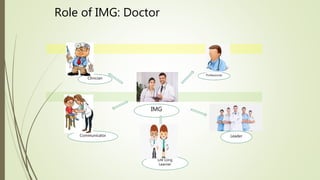
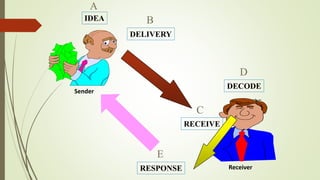
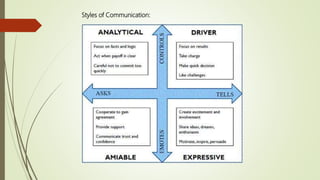
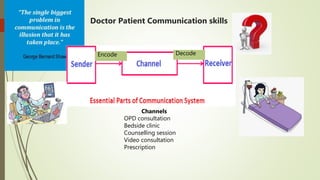
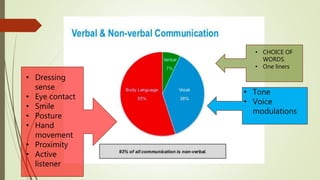
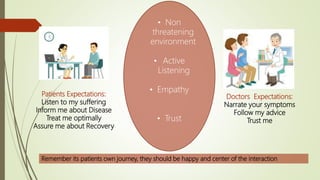
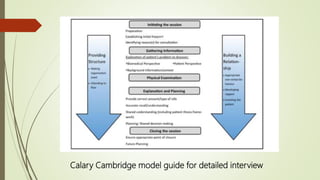
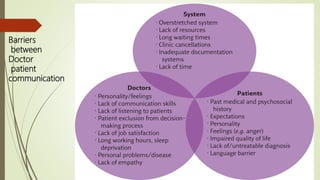
This document discusses the importance of communication skills for doctors. It outlines several key aspects of effective doctor-patient communication including building trust and rapport, active listening, empathy, sharing information, and reaching agreement. Barriers to communication such as differences in language, culture, and perceptions are also examined. The document emphasizes that communication is a lifelong skill for doctors and effective communication can help strengthen the relationship between doctors and patients.