This document provides an overview of communication topics including:
1. Definitions of communication and its types such as downward, upward, and lateral.
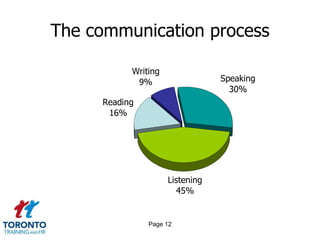
2. The communication process and its elements including senders, receivers, messages, and feedback.
3. Barriers to effective communication such as issues with the sender, receiver, or external factors.
4. Key aspects of communication skills like listening, body language, and adapting communication style for different audiences and purposes.