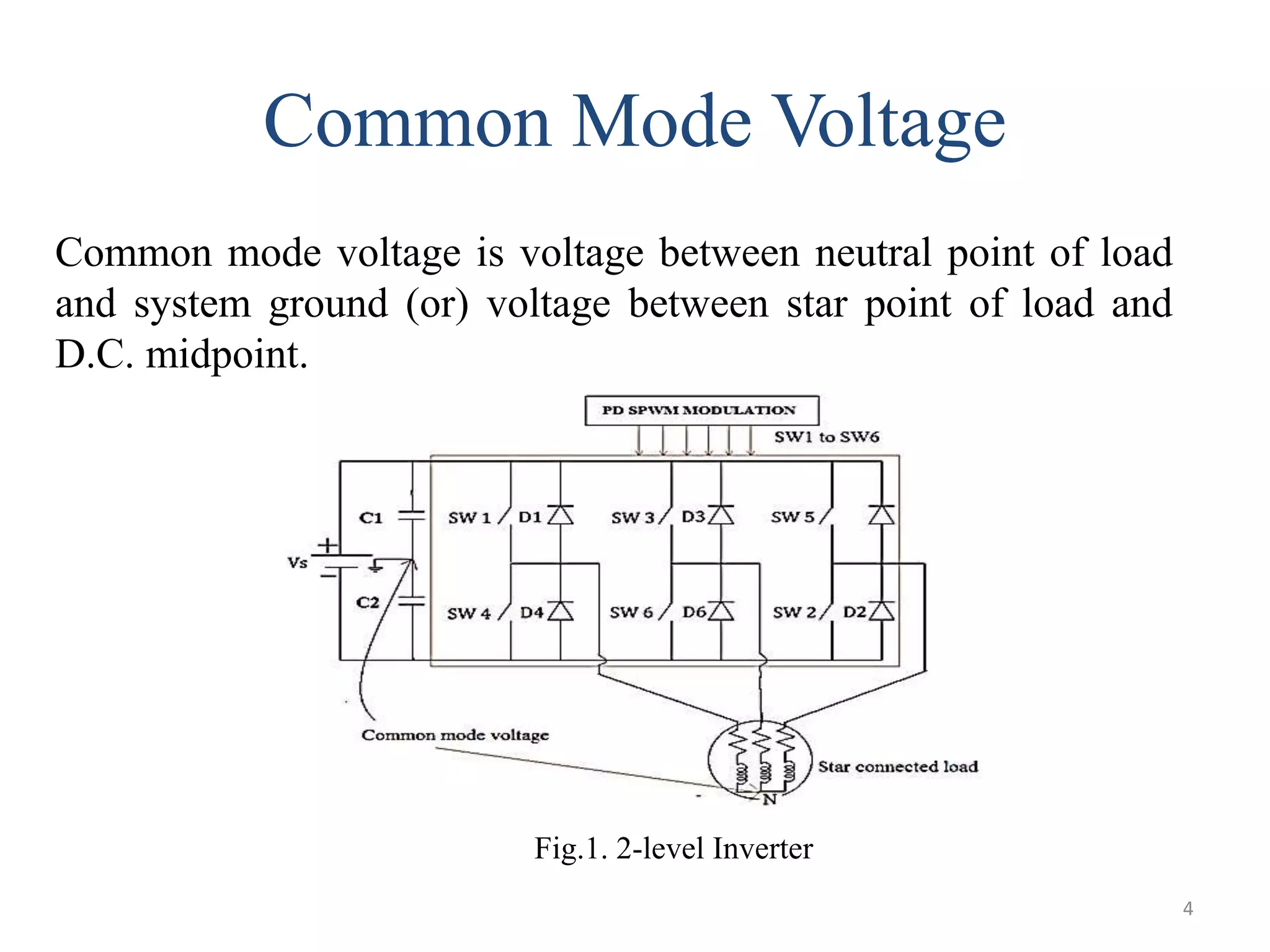
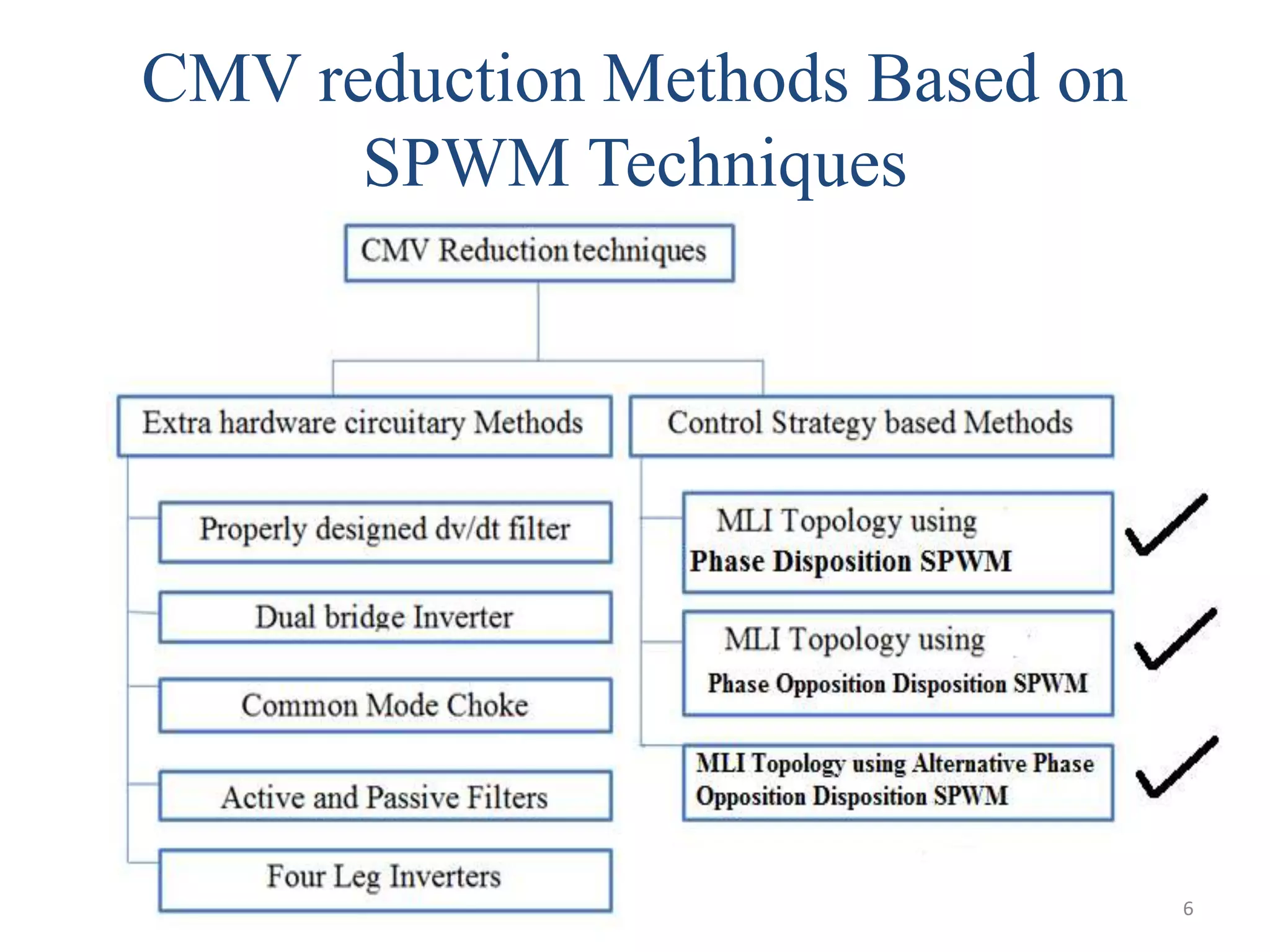
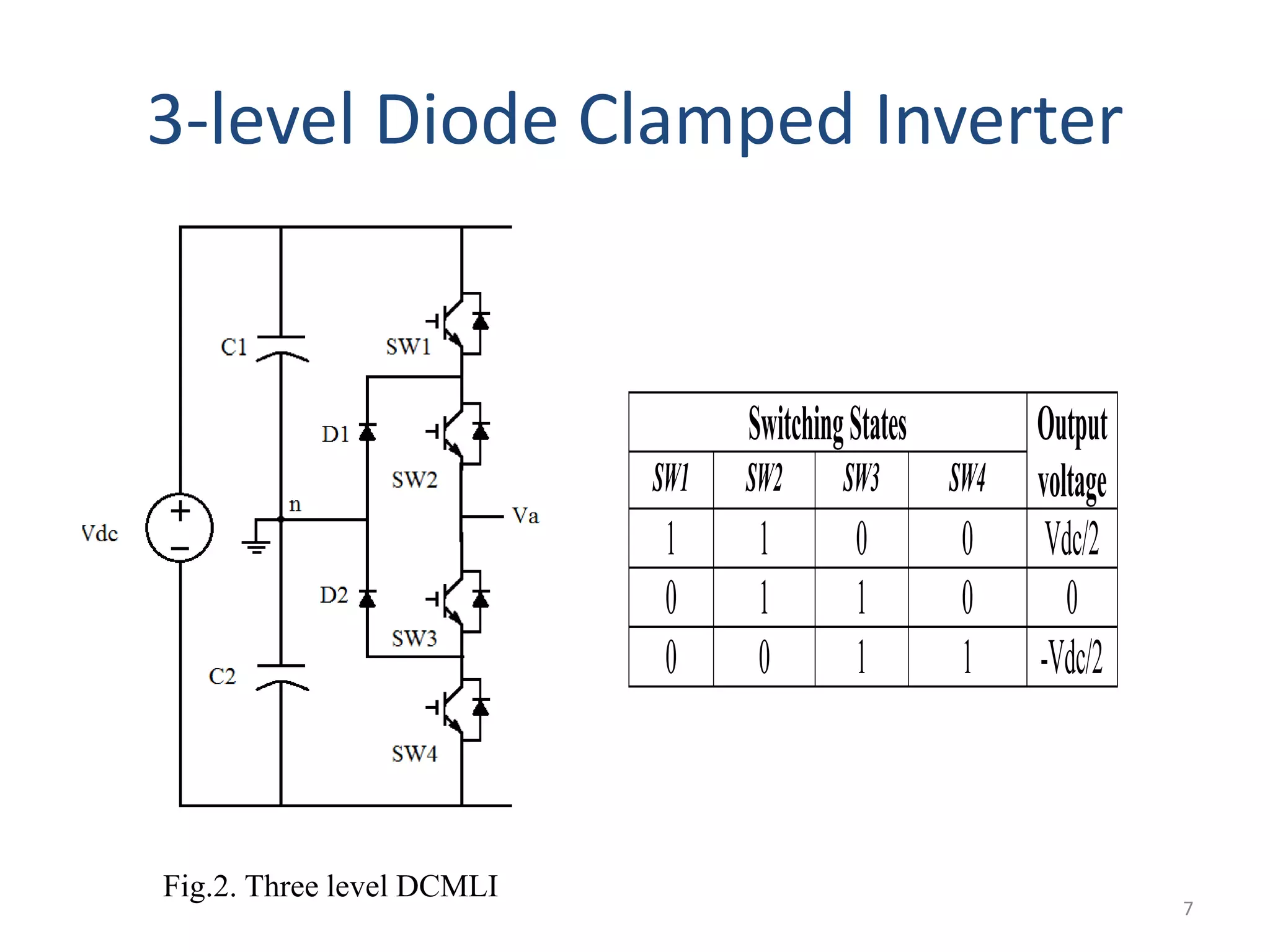
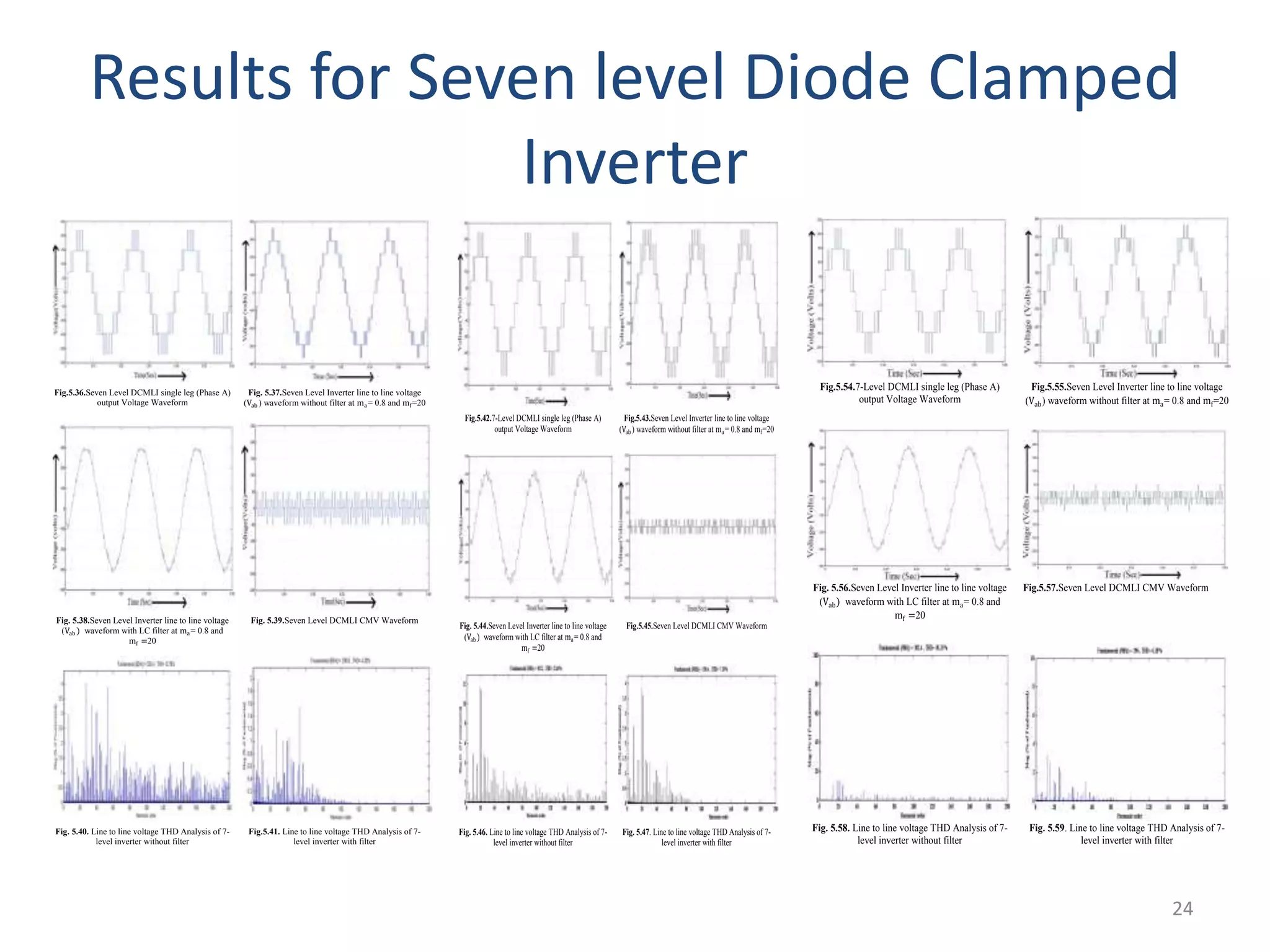
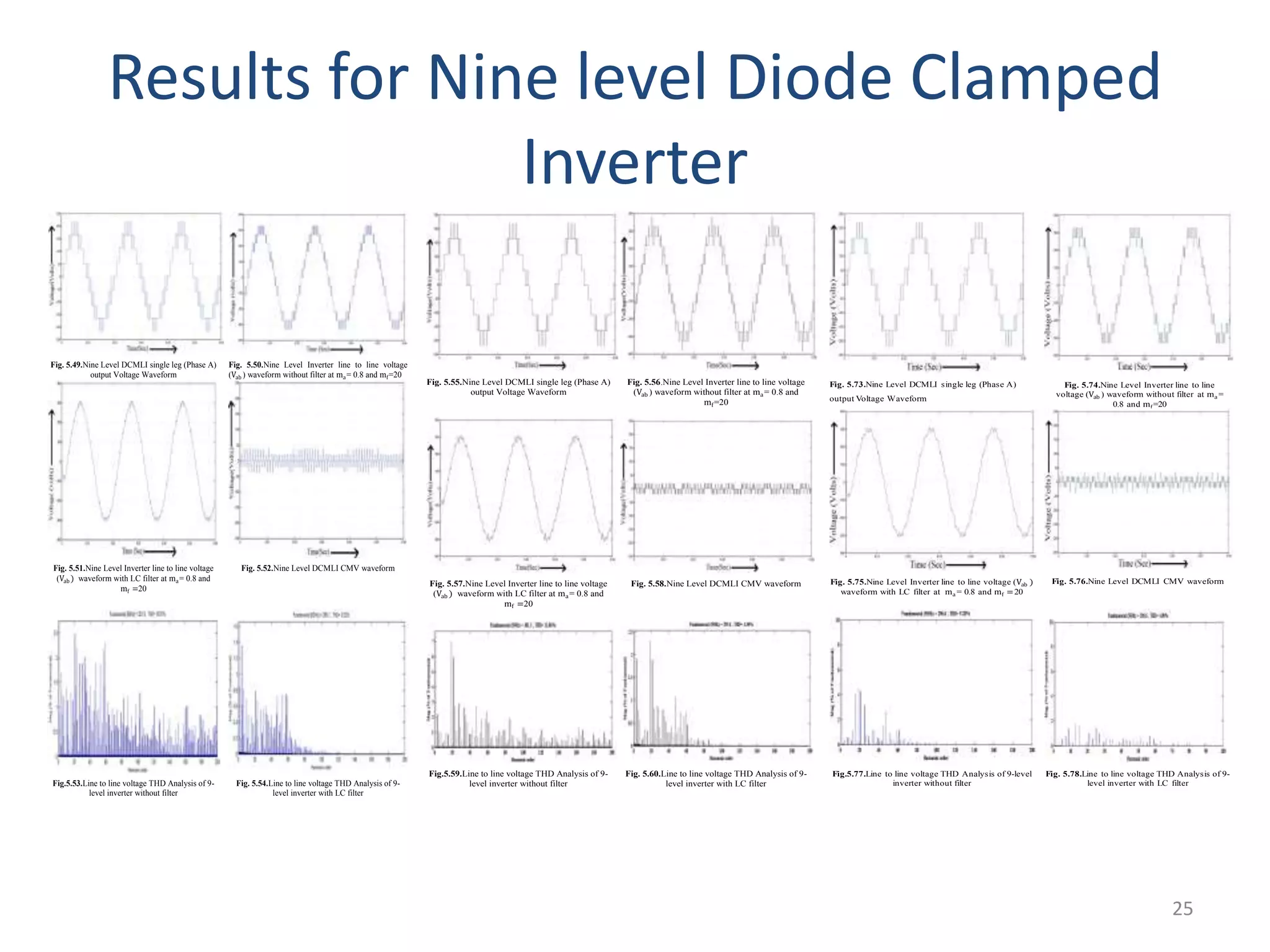
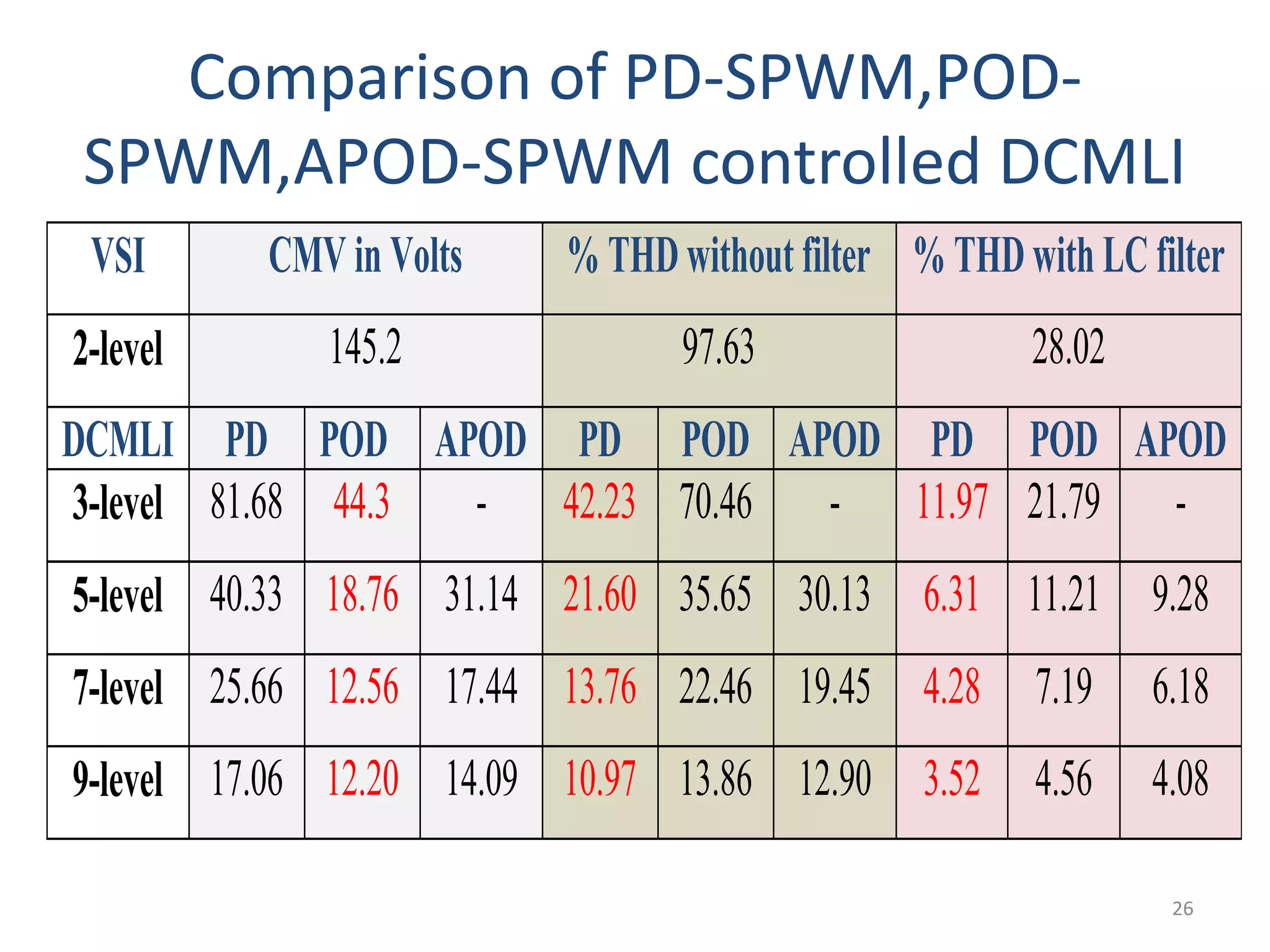
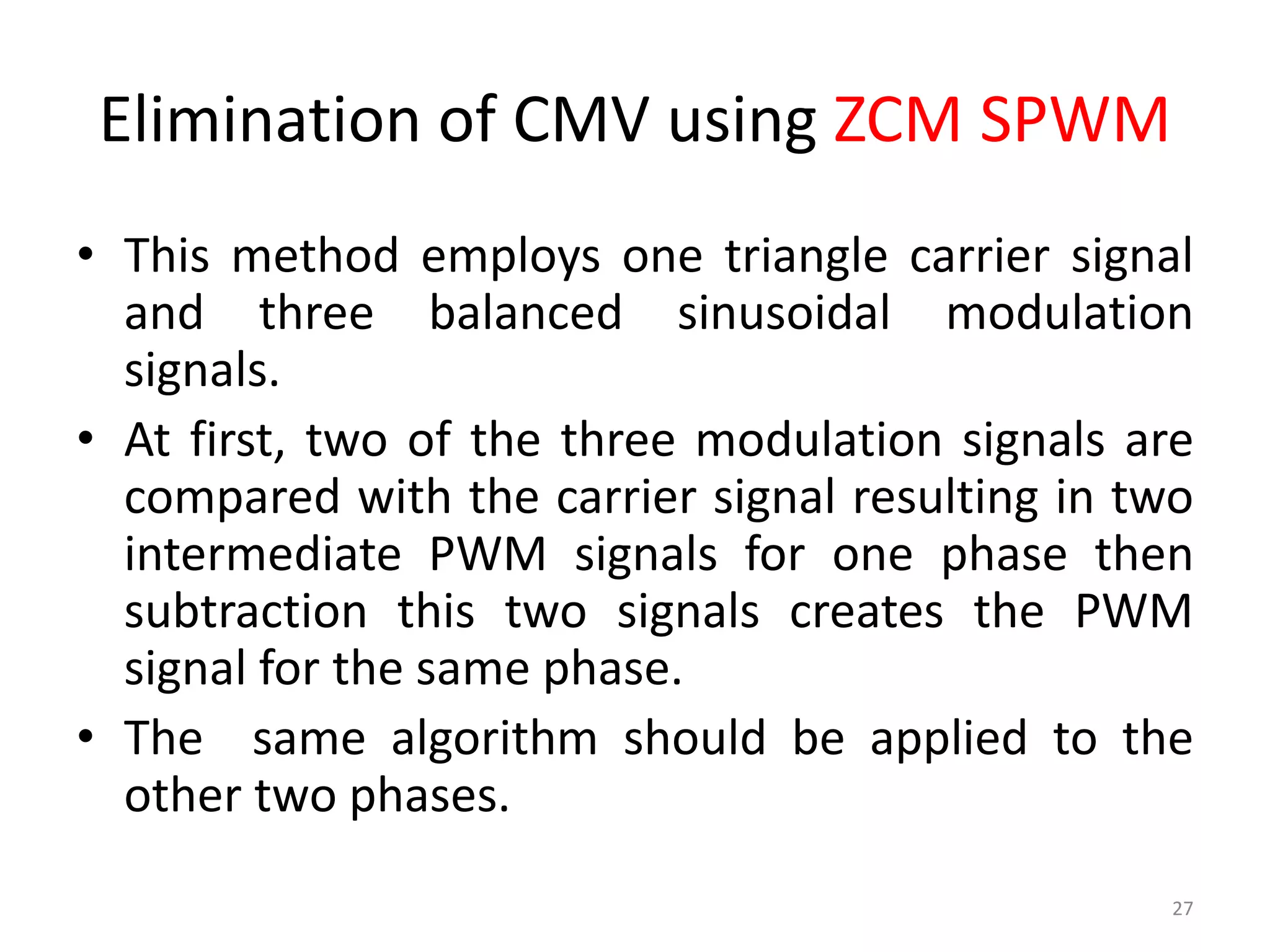
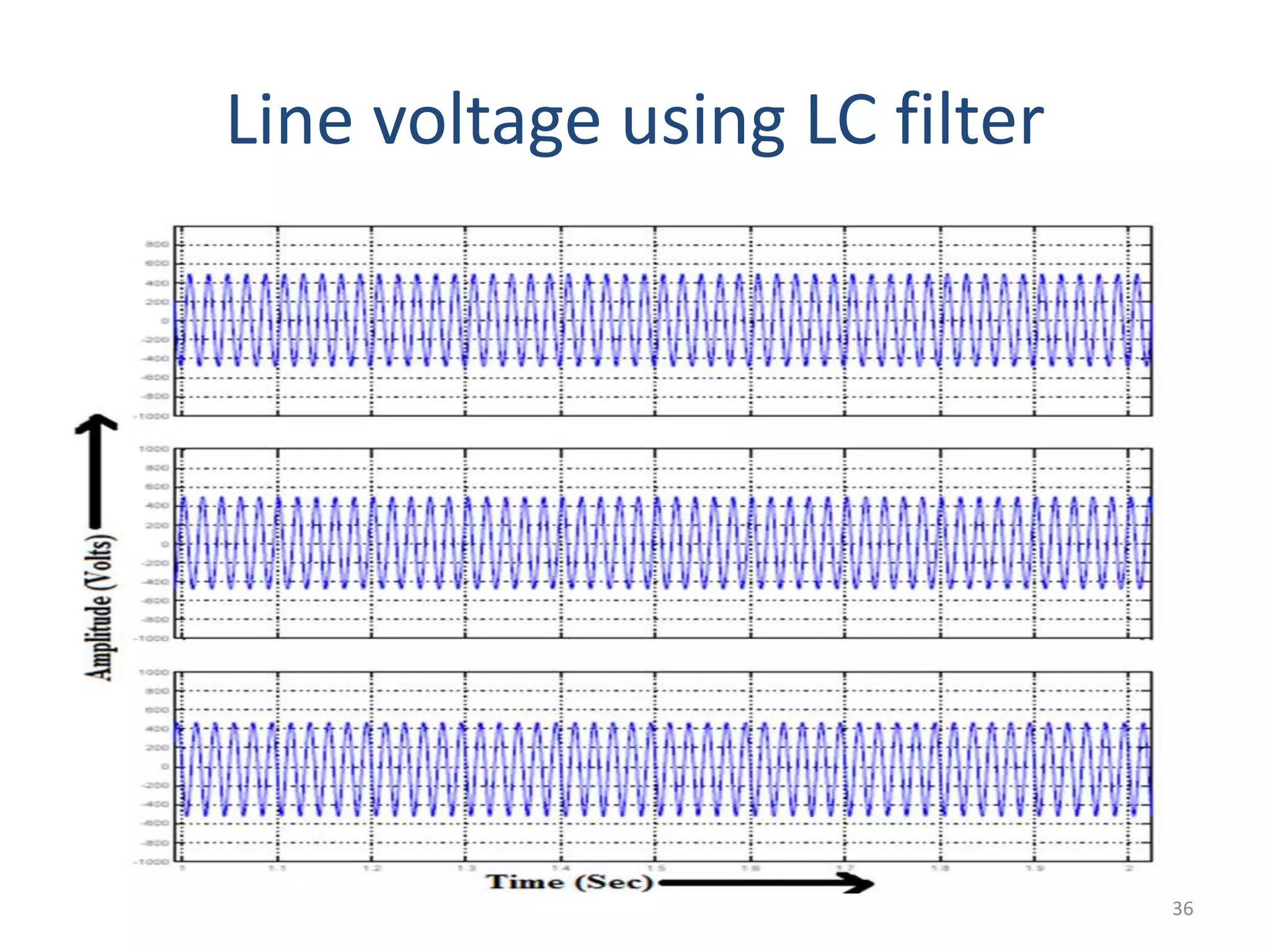
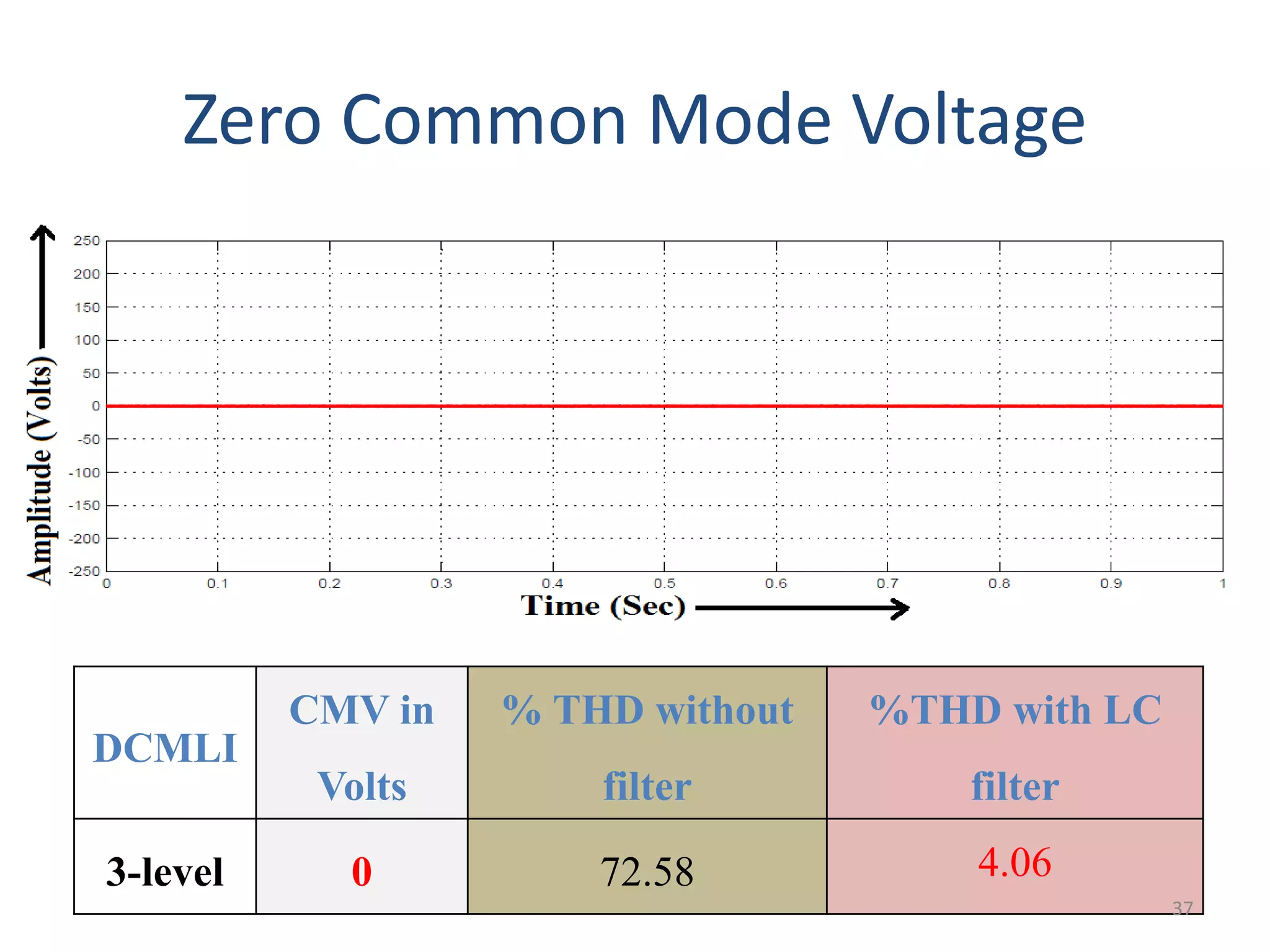
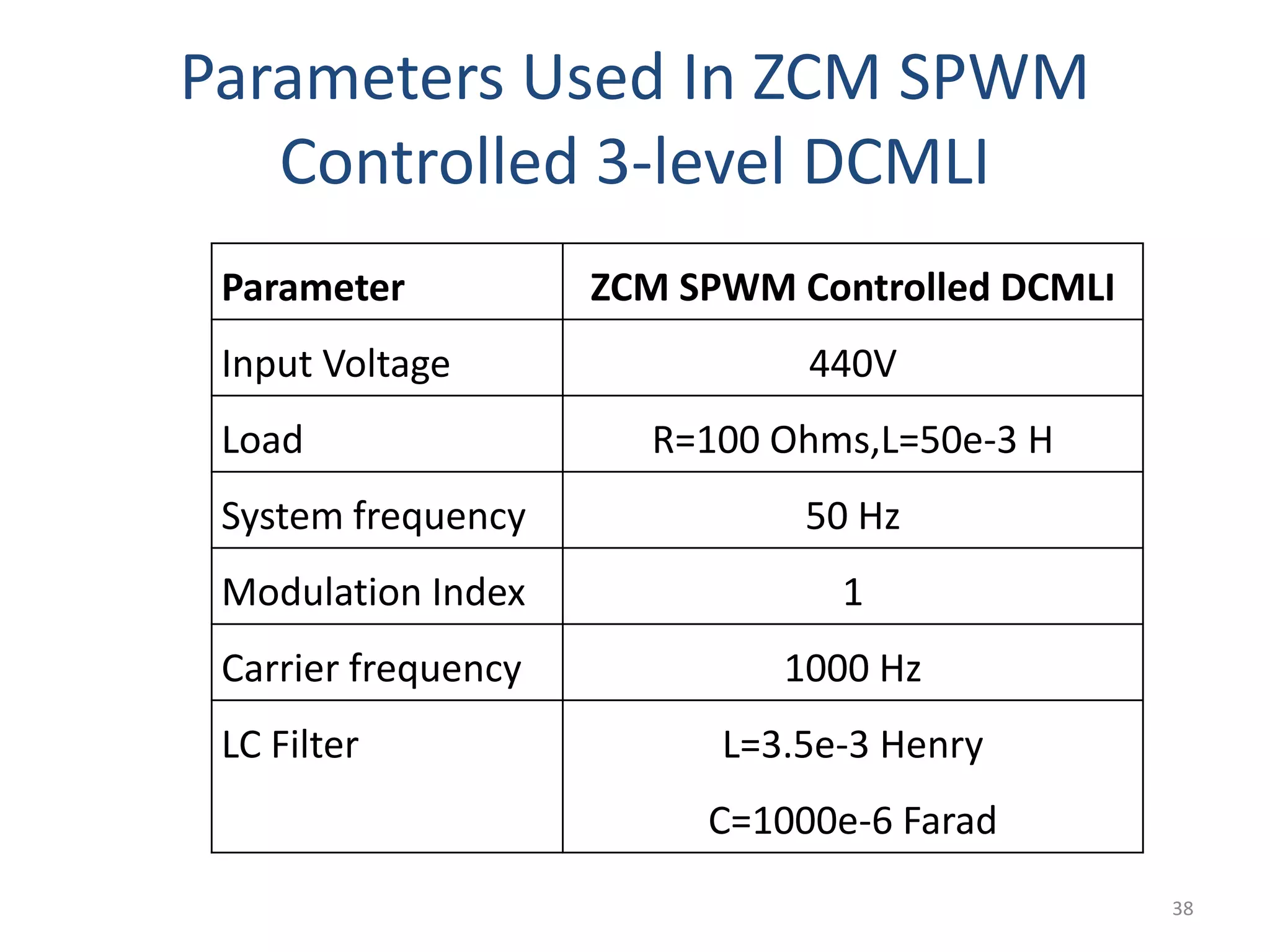
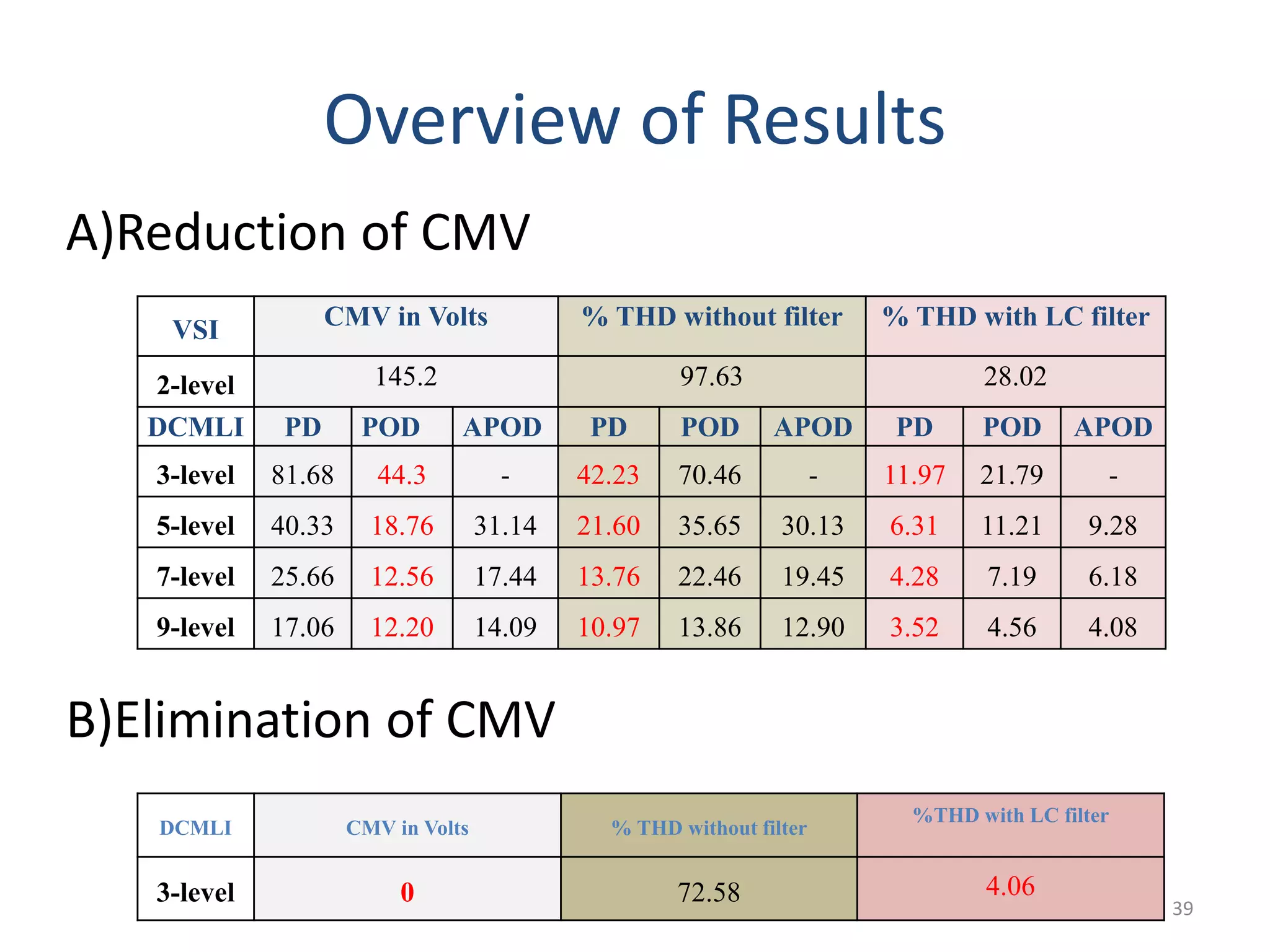
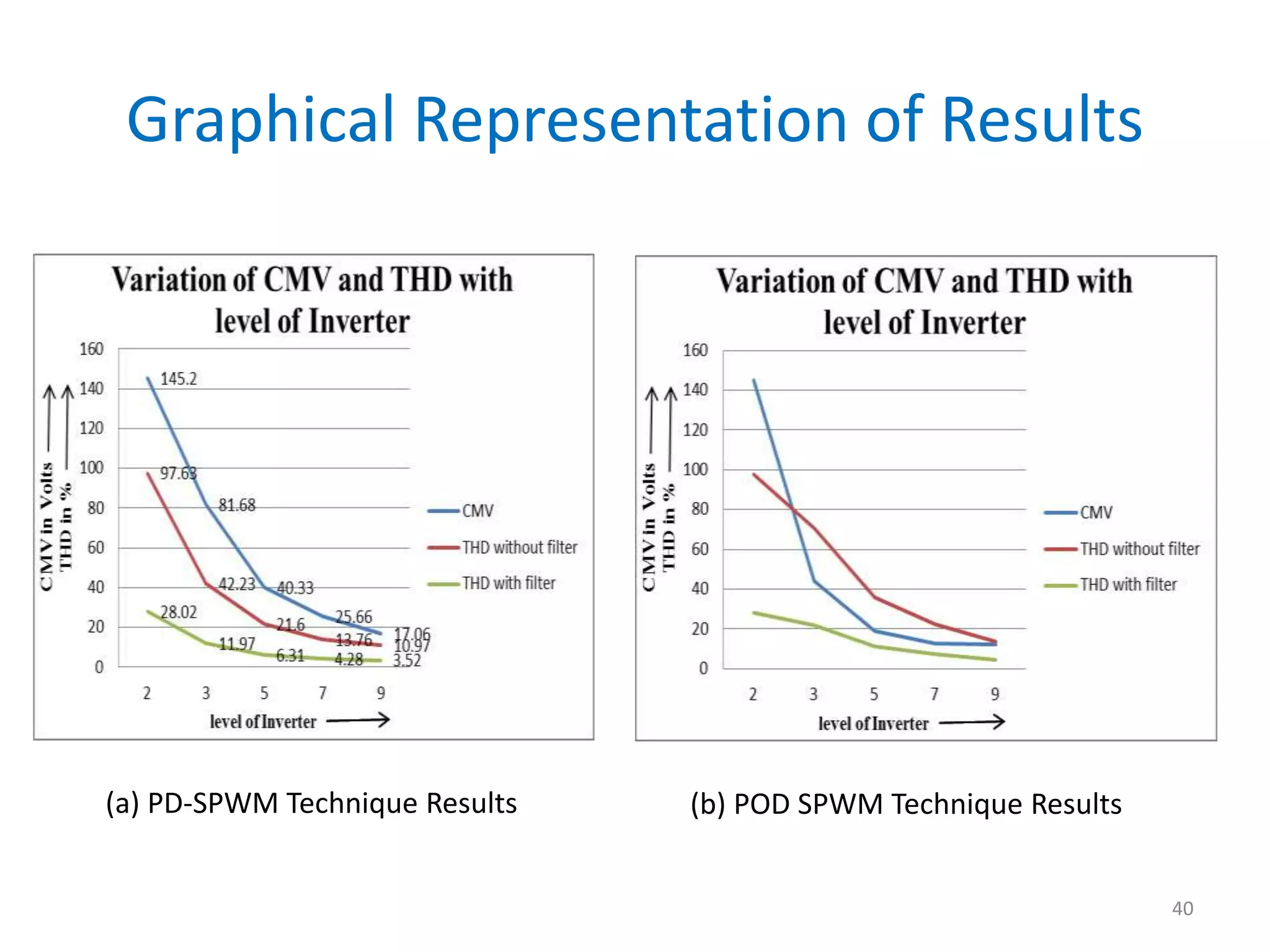
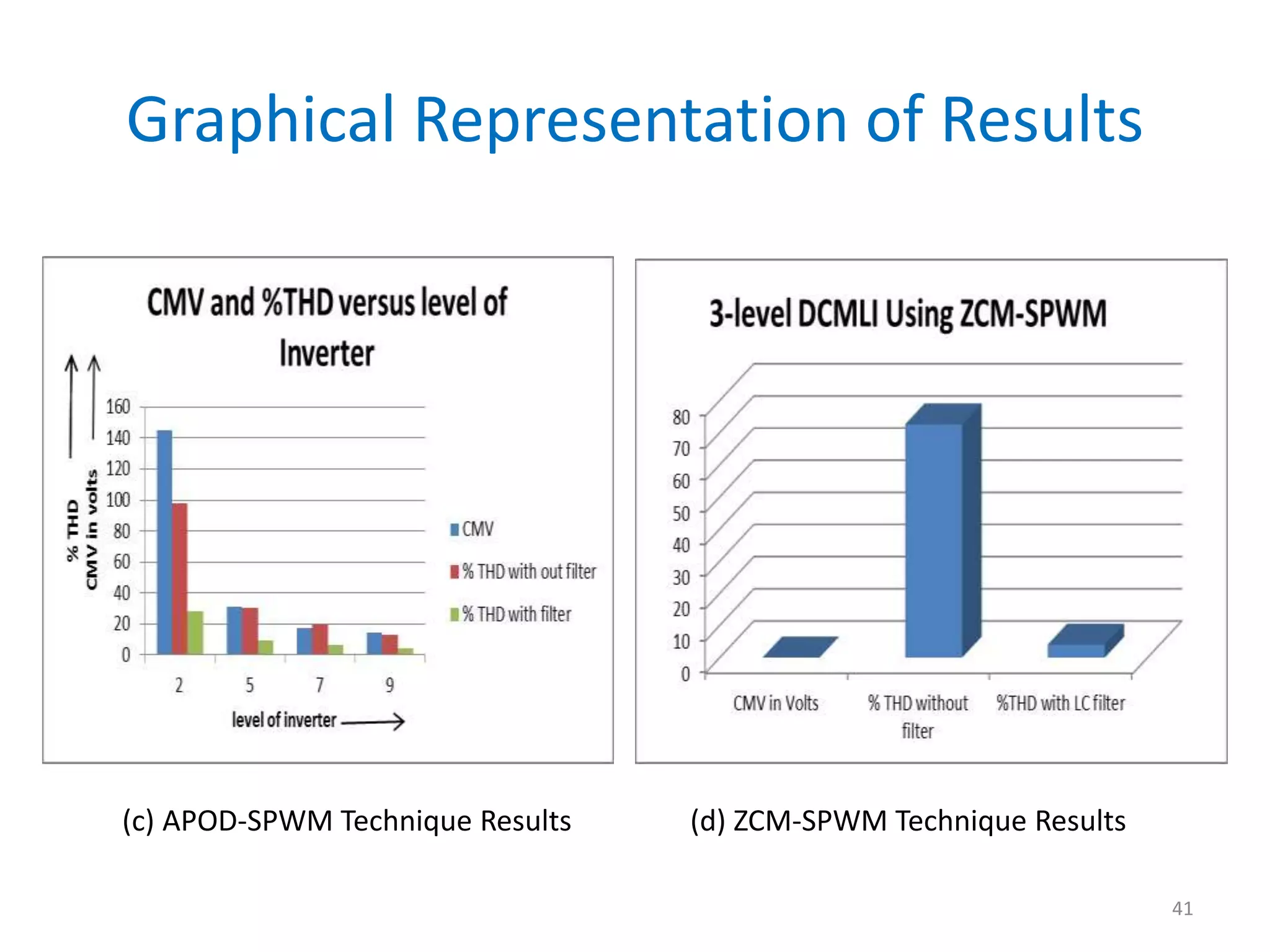
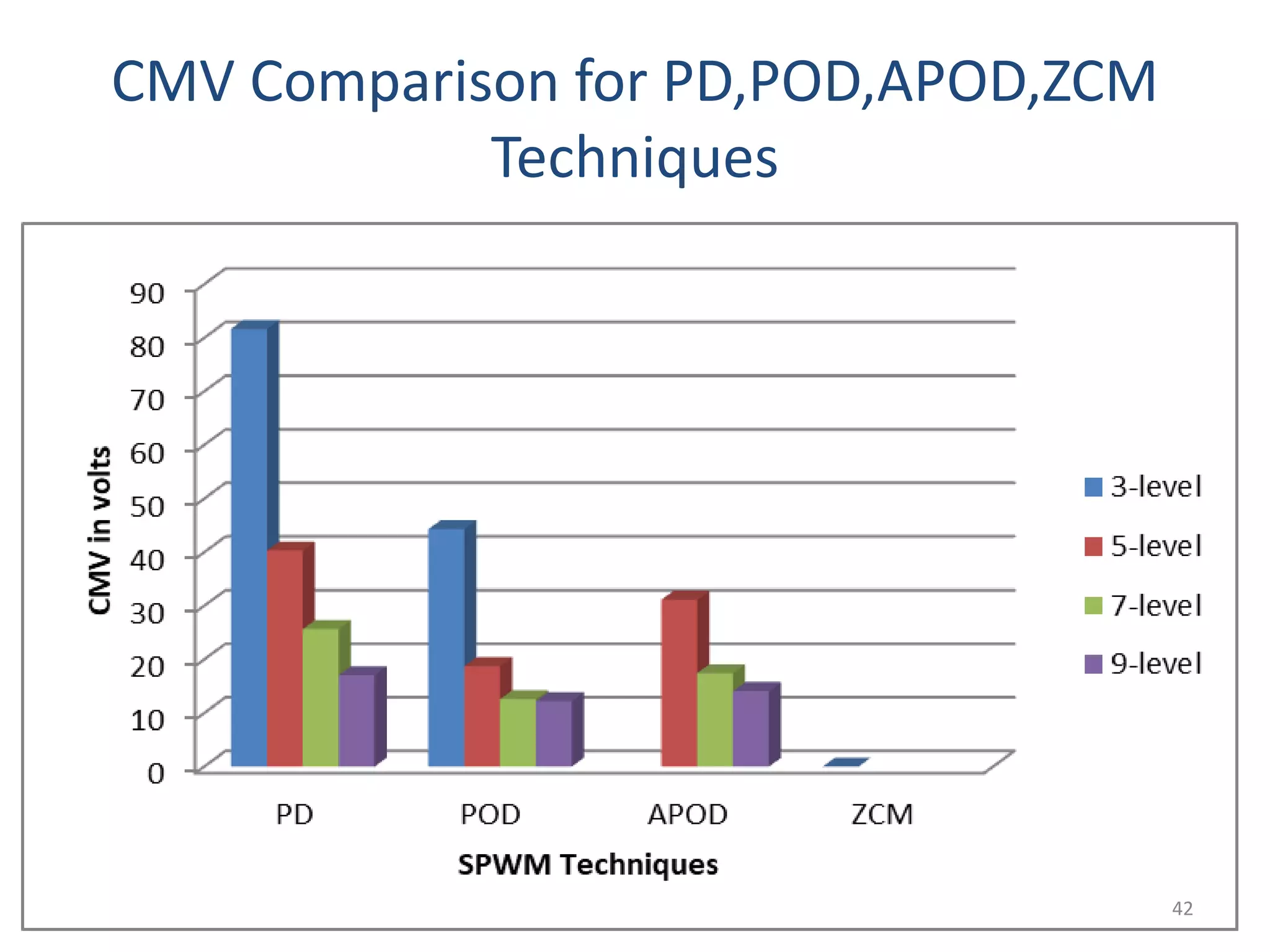
This document discusses techniques to reduce common mode voltage in diode clamped multilevel inverters using sinusoidal pulse width modulation. It presents simulation results comparing phase disposition, phase opposition disposition, and alternative phase opposition disposition SPWM methods in 3-level, 5-level, 7-level and 9-level inverters. The zero common mode SPWM technique is also analyzed, showing it can eliminate common mode voltage. Simulation results show that higher level inverters and carrier disposition techniques like alternative phase opposition disposition more effectively reduce common mode voltage and total harmonic distortion.


![Effects of CMV
a) Regardless of number of legs & levels, high amplitude &
high frequency CMV exists always in pulse width
modulated inverters because of its switching operation
which causes common mode current (CMC) through
parasitic capacitor components between inverter, loads &
ground respectively. This CMC cause’s mal operation of
inverter control system as it is a source of electromagnetic
interference noise [1].
b) Shaft voltages on the rotor are caused by pulse width
modulated inverters because of CMV.Premature failure of
IM bearings is caused when this shaft voltage exceeds the
voltage limit of lubricant in the bearings.CMV is necessary
to reduce by choosing specific reduction technique [2].
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1604-16-743-002-copy-180904044025/75/Common-Mode-Voltage-reduction-in-Diode-Clamped-MLI-using-SPWM-Techniques-5-2048.jpg)
![References
[1] MinZhang,“Investigation ofSwitchingSchemesfor3-phaseFour LegVoltageSourceInverters”,Athesissubmittedforthedegreeof DoctorofPhilosophy
June,2013,SchoolofElectricalandElectronicEngineering,NewcastleUniversity
[2] Anuradha V.Jadhav and Mrs.P.V.Kapoor, “Reduction of Common Mode Voltage using Multilevel Inverter”, Energy Efficient Technologies for
Sustainability[ICEETS],pp.586-590,06October2016,DOI:10.1109/ICEETS.2016.7583822,I.E.E.E.
[3] M.H. Rashid,“Power Electronics Circuits, Devices & Applications” Pearson Education Incorporated, 2005.
[4] Jay M.Erdman,R.J.Kerkman,D.W.Schlegel & G.L.Skibinski , “Effect of PWM Inverters on A.C. Motor Bearing currents and Shaft
voltages,” I.E.E.E. transactions on Industry applications, Vol.32, No. 2 , pp.250- 259,March/April,1996.
[5] Doyle Busse,Jay Eradman,R.J.Kerkman,Dave Schlegel & Gary Skibinski , “System Electrical Parameters and their effects on Bearing
currents,” I.E.E.E. transactions on Industry applications ,Vol.33, No.2, pp. 577-583, March/April,1997.
[6] R.S. Kanchan, P.N. Tekwani, M.R. Baiju, K. Gopakumar and A. Pittet, “3 level Inverter configuration with Common Mode Voltage
elimination for Induction Motor Drive,” I.E.E. Proceedings- Electric Power Applications, Vol. 152, No. 2, pp.261-270, March 2005.
[7] Alexander L. Julian, Giovanna Oriti, and Thomas A. Lipo, “Elimination of Common Mode Voltage in 3-Phase Sinusoidal Power
Converters,” I.E.E.E. transactions on Power Electronics Vol.14,No.5 , pp.982-989 ,September 1999.
[8] M.M.Renge and H.M.Suryawanshi , “ Multilevel Inverter to Reduce Common Mode Voltage in A.C. Motor Drives Using SPWM
Technique.” pp.21-27,Journal of Power Electronics, Vol. 11, No. 1, January 2011.
44](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1604-16-743-002-copy-180904044025/75/Common-Mode-Voltage-reduction-in-Diode-Clamped-MLI-using-SPWM-Techniques-44-2048.jpg)
![Published Papers
(National Conferences-01,IEEE Conferences-02,International Journals-01)
[1] Mohd Esa and J.E.Muralidhar,” Common Mode Voltage Reduction in Diode
Clamped MLI using Phase Disposition SPWM Technique”,ICEES Conference,Feb
2018,IEEE.
[2] Mohd Esa and J.E.Muralidhar,” Common Mode Voltage Reduction in Diode
Clamped MLI using Phase Opposition Disposition SPWM Technique”,EECCMC
Conference,Jan2018,IEEE.
[3] Mohd Esa and J.E.Muralidhar,”Investigation of Common Mode Voltage in 5-level
Diode Clamped MLI using SPWM Techniques”,NTSET Conference,Feb
2018,IJCRT.
[4] Mohd Esa and J.E.Muralidhar,” Common Mode Voltage Reduction in Diode
Clamped MLI using Alternative Phase Opposition Disposition SPWM Technique”,
April 2018,IJCRT.
45](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1604-16-743-002-copy-180904044025/75/Common-Mode-Voltage-reduction-in-Diode-Clamped-MLI-using-SPWM-Techniques-45-2048.jpg)
