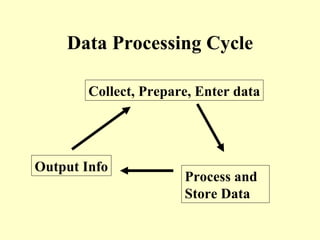
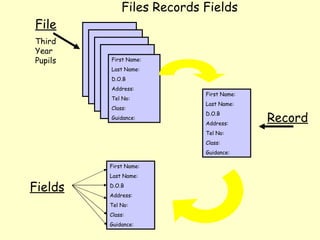
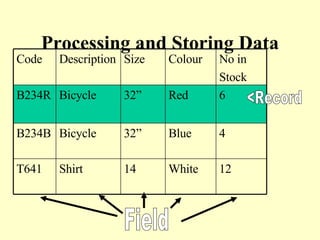
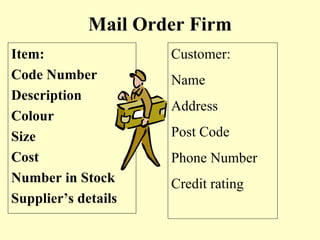
This document summarizes the use of commercial data processing (CDP) systems by businesses. It discusses how CDP systems are used for tasks like stock control, payroll processing, tracking orders, and producing invoices. The document also covers why CDP systems are better than manual processing due to abilities like handling large amounts of data quickly and accurately. It defines the difference between data and information and outlines the basic data processing cycle. Finally, it gives examples of how data is collected, prepared, and entered into CDP systems using technologies like magnetic stripes, barcodes, and mark sense cards.