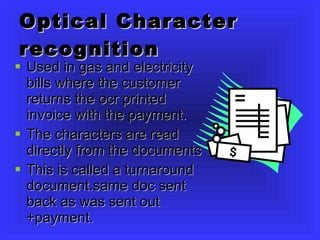
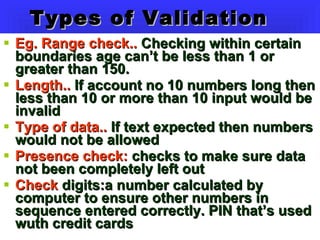
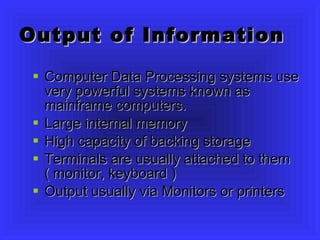
Commercial Data Processing involves using computers to handle clerical work normally done by staff. There are several steps: data collection and preparation, input, storage and manipulation, and output. Common methods of input include barcodes, magnetic strips, optical character recognition, and magnetic ink character recognition used on checks. Data is stored and processed either interactively in real-time or through batch processing overnight. Output is typically displayed on monitors or printed.