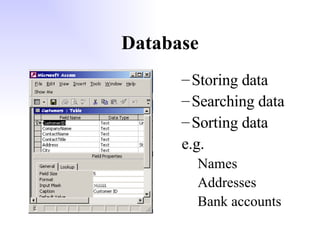
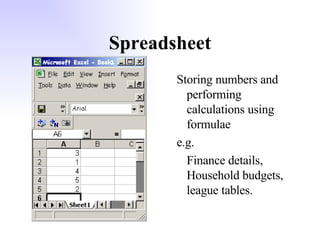
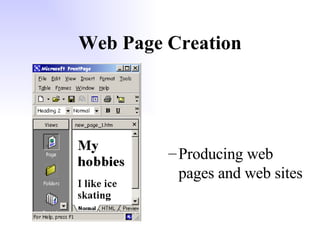
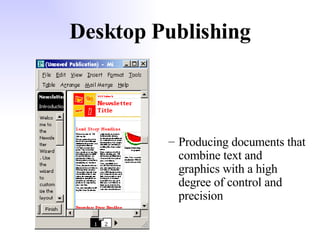
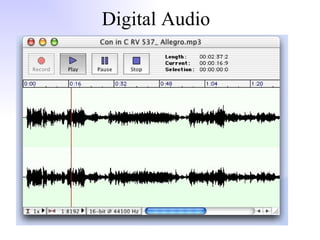
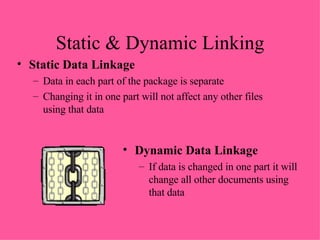
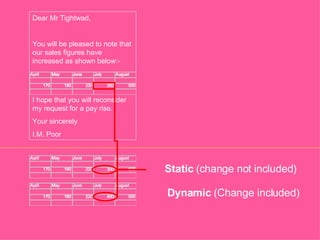
General purpose packages (GPPs) allow users to perform a wide range of tasks including word processing, graphics, spreadsheets, databases, presentations and multimedia. Common GPPs include word processors for producing documents, spreadsheets for storing and calculating numbers, and databases for storing and organizing data. GPPs save time, help ensure data accuracy, and allow flexible communication across different file formats and packages.