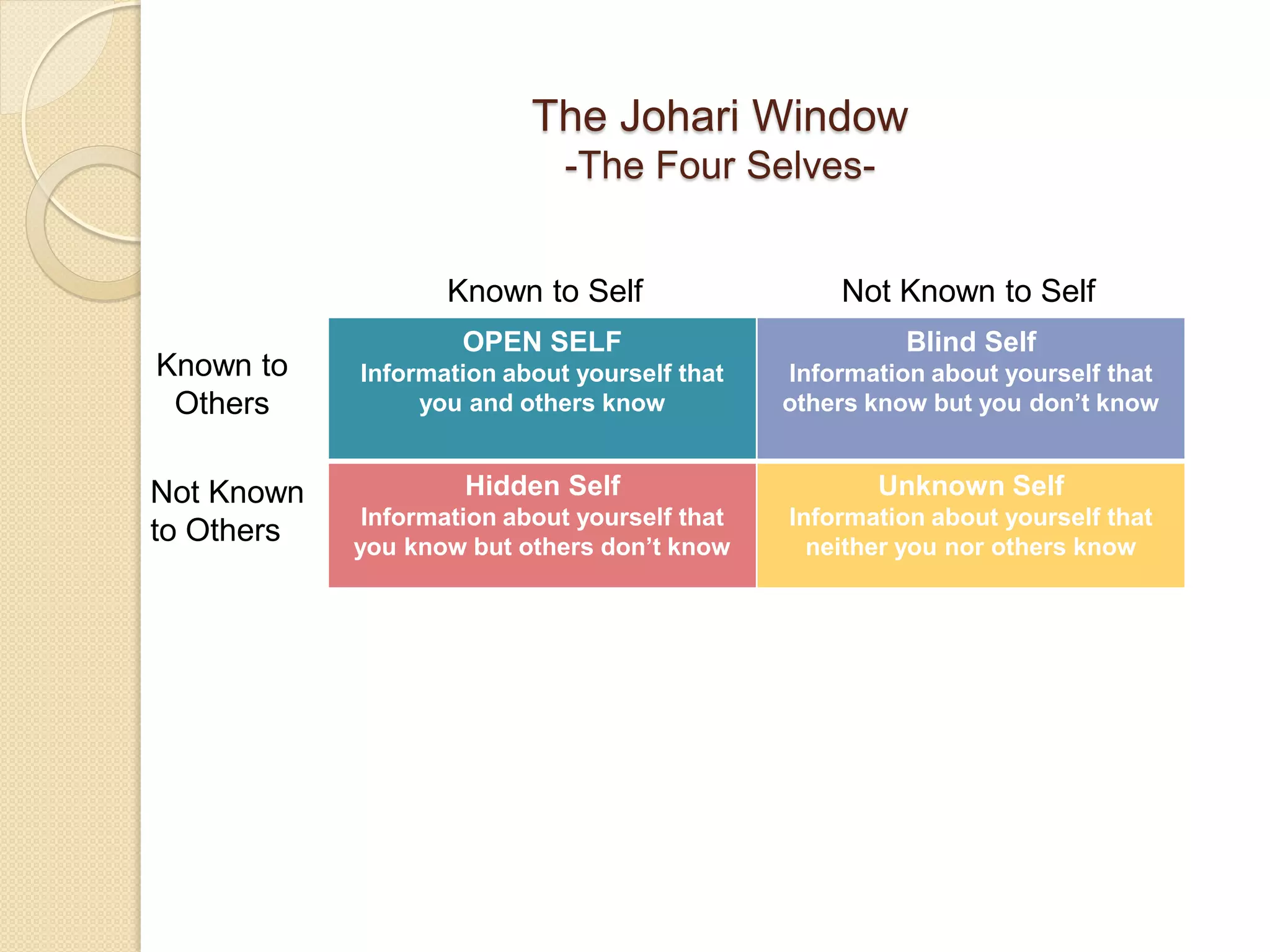
This chapter discusses the self in interpersonal communication, including sources of self-concept such as others' images and social comparisons. It describes ways to increase self-awareness and self-esteem through activities like asking yourself questions and seeking feedback from others. The chapter also examines perception and impression formation, outlining the stages of perception and the processes involved in forming impressions of other people.